Why in the news?
Quadrilateral Security Dialogue Quad marked the 20th anniversary of Quad cooperation.
About Quad
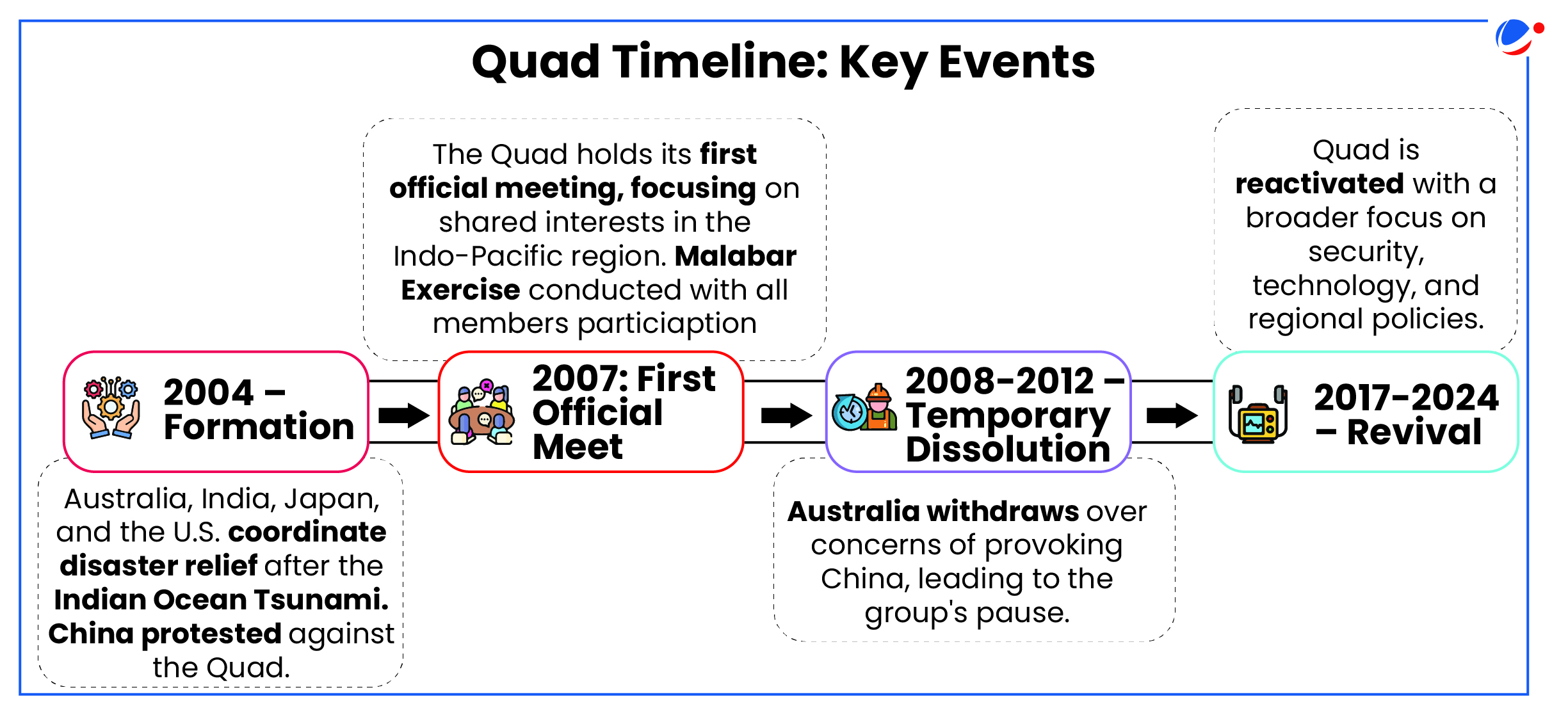
- Formalisation led by the then Japanese PM Shinzo Abe in 2007.
- Members: Australia, India, Japan, and the U.S
- Nature: An informal strategic partnership and an alliance of maritime democracies.
- Purpose: Supports an open, stable, and inclusive Indo-Pacific. Four Democracies acts as a force for global good, delivering positive and lasting impact.
- Vision: Launched Vision Statement in 2023 which is centred around theme 'Enduring Partners for the Indo-Pacific'.
- Working: Work of the Quad is taken forward through following six Leader level Working Groups in six areas: Climate, Critical and Emerging Technologies, Cyber, Health Security Partnership, Infrastructure and Space
- Key Summits: Annual Quad Leaders' Summits and Foreign Ministers' Meetings.
- Global Footprint: Represents-
- 24% of the world's population,
- 35% of global GDP
- 18% of global trade
Changing Dynamics of QUAD: From Military to Economic Alliance
Even though Quad is not a formal military bloc, it has transitioned from a military-focused group to a broader alliance emphasizing economic cooperation and regional stability, adapting to global geopolitical shifts.
Sector of cooperation | Description |
Military Focus (initial phase) |
|
Economic Expansion (recent phase) | Post Covid-19, most of the Quad initiatives are more focused on economic and sustainable development. Some of them are as follows:
|
Challenges faced by QUAD
- Lack of Institutional Framework: Quad lacks a formal structure like NATO and operates through informal meetings. This weakens its ability to act decisively in crises.
- Unequal Burden-Sharing: Quad members have varying financial resources, strategic priorities, and military capabilities. This creates an imbalance, placing more responsibility on certain members.
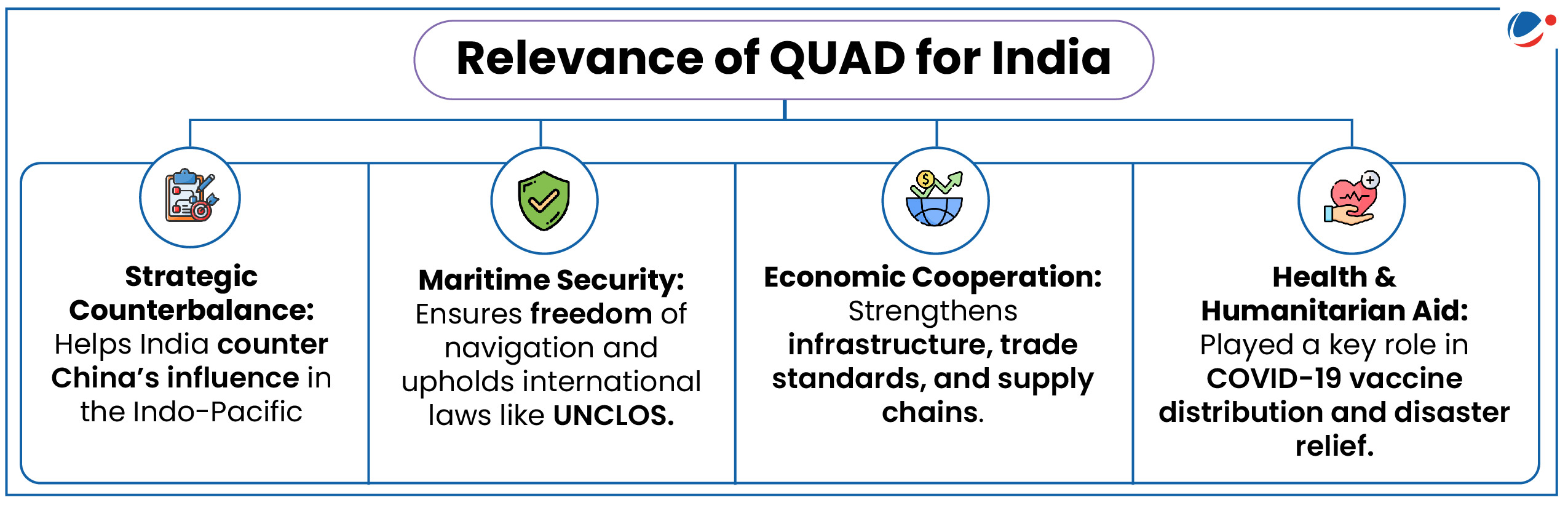
- Conflicting Partnerships: India's ties with Russia and the SCO may contradict Quad's strategic objectives. Australia's economic dependence on China could make it vulnerable to coercion.
- Quad's focus on security, maritime defense, and intelligence sharing even fuelled speculation about it becoming an "Asian NATO."
- Diverging China Strategies: Japan and Australia rely on China for trade but oppose its military assertiveness. India has a direct strategic rivalry but continues economic engagement with China.
- India's Specific Concerns
- Geopolitical Strains: Strengthening Quad ties could alienate key partners like Iran (enemy of US) and Myanmar (ally of China).
- Different Indo-Pacific Visions: India focuses on the Indian Ocean, while others emphasize the Pacific.
Way Forward for Strengthening Quad
- Defining a Clear Indo-Pacific strategy: Quad must articulate a well-defined Indo-Pacific strategy to align economic and security goals. This will reassure smaller nations about its role in regional stability.
- Expanding Membership: India should advocate for the inclusion of countries like Indonesia and Singapore. A broader Quad could enhance regional credibility and influence.
- Strengthening India's Maritime Strategy: India needs a robust Indo-Pacific maritime doctrine. This should address security challenges, integrate military and diplomatic efforts, and engage strategic allies.






