Sovereign Credit Rating
S&P upgraded India’s long-term Sovereign Credit Rating to ‘BBB’ from ‘BBB-’ and its short-term rating to ‘A-2’ from ‘A-3’, with a Stable Outlook.
- This marks the India’s first sovereign upgrade by S&P after 2007 when India was elevated to investment grade at BBB-.
- The upgrade reflects India’s commitment to fiscal consolidation, improved quality of public spending, and strong corporate, financial and external balance sheets.
About Sovereign Credit Ratings (SCR)
- It refers to an independent evaluation of a country’s creditworthiness, and seeks to quantify issuers’ ability to meet debt obligations.
- Major SCR agencies: S&P, Fitch and Moody’s.
- Rating Grades: SCR broadly rate countries as either investment grade or speculative grade, with the latter projected to have a higher likelihood of default on borrowings.
- The Investment grade rating ranges from BBB- to AAA for S&P and Fitch and Baa3 to Aaa for Moody’s.
- Significance: When favourable, these can facilitate countries access to global capital markets and foreign investment, andreduce borrowing cost.
- Issues: There are concerns over bias in rating processes, conflicts of interest, and rating ceiling.
- Rating ceiling relates to the notion that a corporate issuer is not rated higher than the country that it resides within, constraining growth of a country’s domestic marketplace.
- Tags :
- Sovereign Credit Rating
Articles Sources
GIFT City-like Financial Centers
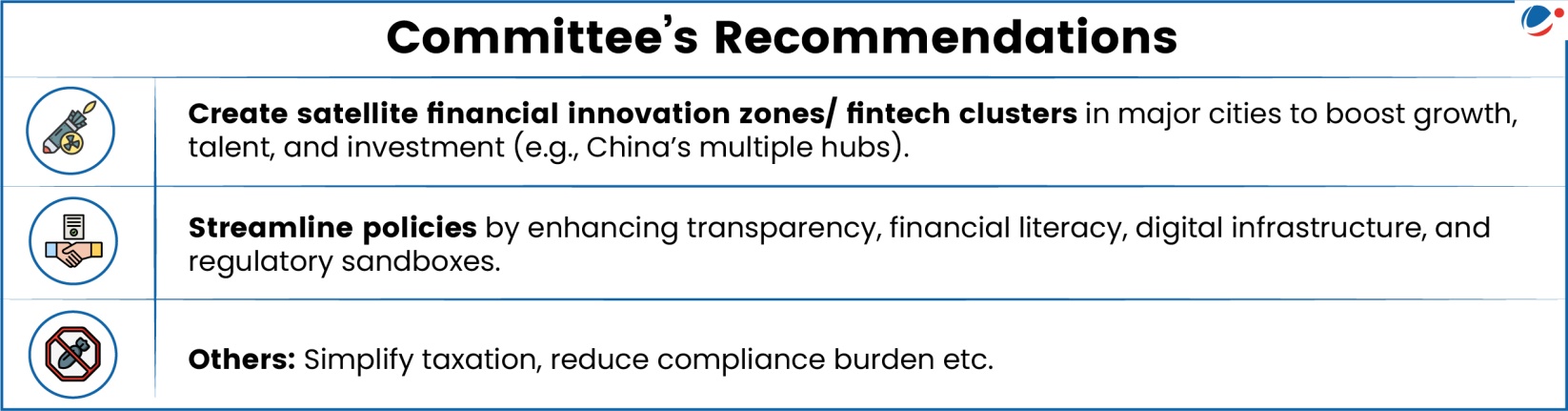
Parliamentary Standing Committee on Finance has recommended for development of more GIFT City-like Financial Centers in major metro cities.
- India’s first and only International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) was established within Gujarat International Financial Tec City (GIFT City).
About GIFT City IFSC (Gandhinagar, Gujarat)
- It was established as a Special Economic Zone (SEZ) in 2015. Designated as a non-resident zone under Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA).
- IFSC is a jurisdiction that provides onshore and offshore financial services to non-residents and residents (institutions), in a foreign currency.
- Functions:
- Favorable tax structure: Offers cross-border financial products and services within a competitive tax environment.
- Trusted regulatory environment: Provides onshore talent with an offshore technological and regulatory framework.
- Ease of doing business: Facilitates movement of international financial services based on global standards, promotes inbound and outbound investment to India.
- Regulatory body: International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) regulates financial products, financial services and financial institutions in IFSCs in India.
- Established in 2020 under the IFSCA Act, 2019.
- Current Status: GIFT-IFSC ranked 46th in the Global Financial Centres Index (a 5-rank improvement); ranked 45th in the FinTech rankings (a 4-rank improvement).
- Tags :
- GIFT City
RBI’s FREE-AI Vision for Financial Sector
RBI committee unveiled Framework for Responsible and Ethical Enablement of Artificial Intelligence (FREE-AI) to balance innovation with risk management in financial services.
About FREE-AI Vision
- Aim: Ensuring safe, fair and accountable AI adoption in India’s financial sector
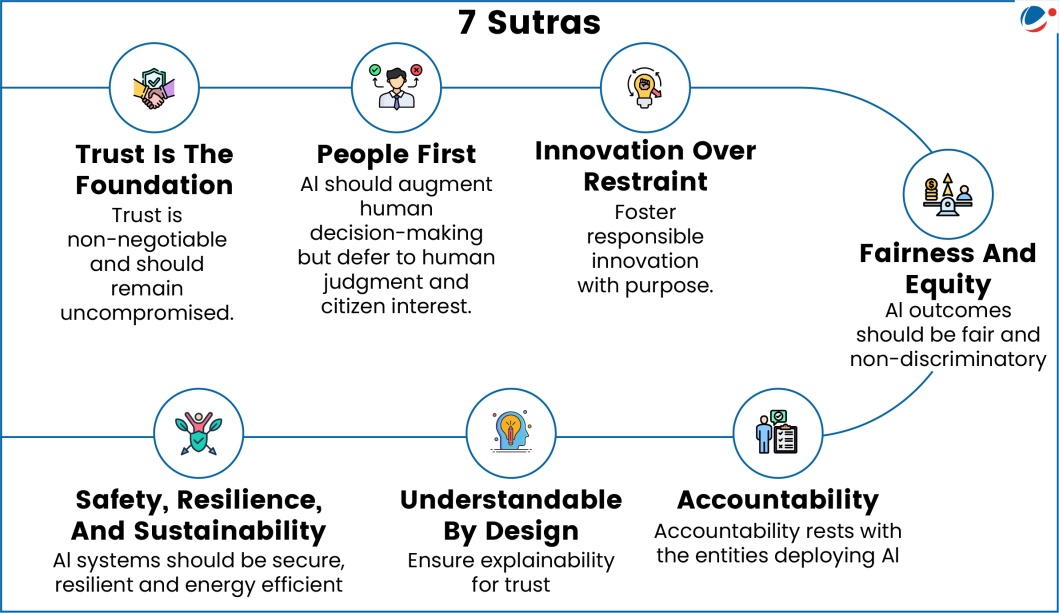
- 7 Sutras: Foundational principles for AI adoption (refer to the infographics)
- Dual Approach:
- Fostering Innovation
- Shared infrastructure for democratized data and compute access, which may be integrated with the AI Kosh established under the IndiaAI Mission.
- AI Innovation Sandbox for testing indigenous financial AI models
- Create AI policy for regulatory guidance
- Institutional capacity building (boards and workforce)
- Relaxed compliance for low-risk AI solutions to facilitate inclusion and other priorities
- Mitigating Risk:
- Board-approved AI policies by Regulated Entities
- Inclusion of AI-related aspects in product approval processes, consumer protection frameworks and audits
- Strengthened cybersecurity and incident reporting
- Robust AI lifecycle governance
- Consumer awareness when they interact with AI
Why FREE-AI Vision Matters?
- AI’s Growing Impact: The financial sector’s AI investment is projected to reach:
- ₹8 lakh crore ($97 billion) by 2027 across banking, insurance, capital markets, and payments
- ₹1.02 lakh crore ($12 billion) by 2033 for GenAI alone, growing at 28-34% annually
- Emerging Complex Risks: AI introduces data privacy, algorithmic bias, market manipulation, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and governance failures that traditional risk frameworks struggle to address.
- These risks could undermine market integrity, erode consumer trust, and create systemic vulnerabilities without proper management.
- Tags :
- FREE-AI
RBI tightens Co-lending norms
Recently, RBI issued revised directions for Co-lending Arrangements (CLA) between banks and Non-bank Financial Companies (NBFCs) under various provisions of the Banking Regulation Act (1949), Reserve Bank of India Act (1934), and National Housing Bank Act (1987).
What is co-lending?
- Under CLAs, Regulated entities (Res) can enter into a lending arrangement with other Res for extension of credit to the borrowers, subject to compliance with the extant prudential regulations.
Key highlights of the revised Directions
- Minimum share: Each RE to retain a minimum 10% share of the loans.
- Priority Sector Lending (PSL) status: Each lender can claim PSL status for its share under co-lending, if the loan qualifies as priority sector.
- Uniform asset classification system: If one lender tags a loan as Non- performing Asset (NPA), other co-lenders must do the same.
- Blended interest rate: Interest rate charged to borrowers will be calculated based on the weighted average of each RE’s internal rate, proportionate to their funding contribution.

- Tags :
- Co-lending
Safety in the Civil Aviation Sector
Parliamentary Standing Committee released Report on Review of Safety in the Civil Aviation Sector. The report examines civil aviation safety environment and effectiveness of Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) amidst increasing growth of civil aviation in India.
Key Highlights of Report
Key Areas for Systemic Improvement | Issues | Recommendations |
Enhancing Regulatory Autonomy and Capacity |
|
|
Mitigating Air Traffic Controller (ATCO) Fatigue and Staffing Deficits |
|
|
Strengthening Surveillance and Enforcement Mechanisms |
|
|
Addressing Recurring Operational Risks |
|
|
Developing Domestic Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) Capabilities |
|
|
Establishing Just Culture and Whistleblower Protection |
|
|
- Tags :
- Safety in the Civil Aviation Sector
Steel Scrap Recycling Policy (SSRP)
Standing Committee on Coal, Mines and Steel recently released Report on Steel Scrap Recycling Policy (SSRP).
SSRP was notified by Ministry of Steel (MoS) in 2019, with following objectives:
- Promotes Circular Economy (6Rs – Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Recover, Redesign & Remanufacture).
- Formal & scientific collection, dismantling & processing activities for end-of-life products that are sources of recyclable ferrous, nonferrous & metallic scraps
- Creation of Mechanism for treating waste streams and residues produced from dismantling and shredding facilities, etc.
Key Highlights of the Report
Issue Highlighted | Relevant Recommendations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Tags :
- SSRP
- Steel Scrap Recycling Policy



