The signing of the BIT between both nations will promote economic cooperation and create a more robust and resilient investment environment.
- It will increase the comfort level and boost the confidence of investors.
About BIT
- BIT is a reciprocal agreement for according protection to investments by nationals and companies of one State in another State.
- India approved new Model BIT Text in 2015, which replaced Indian Model BIT, 1993.
- Since then, Model text 2015 is used for (re)negotiations of BITs and investment chapters of FTAs/ Economic Partnership Agreements.
- Key Features of Model BIT
- National Treatment: Similar treatment as domestic investors.
- Protection from expropriation: Limiting country’s ability to dominate foreign investments in its territory.
- Settlement of Disputes: Exhaust local remedies before commencing international arbitration.
- Other: Enterprise based definition of investment, etc.
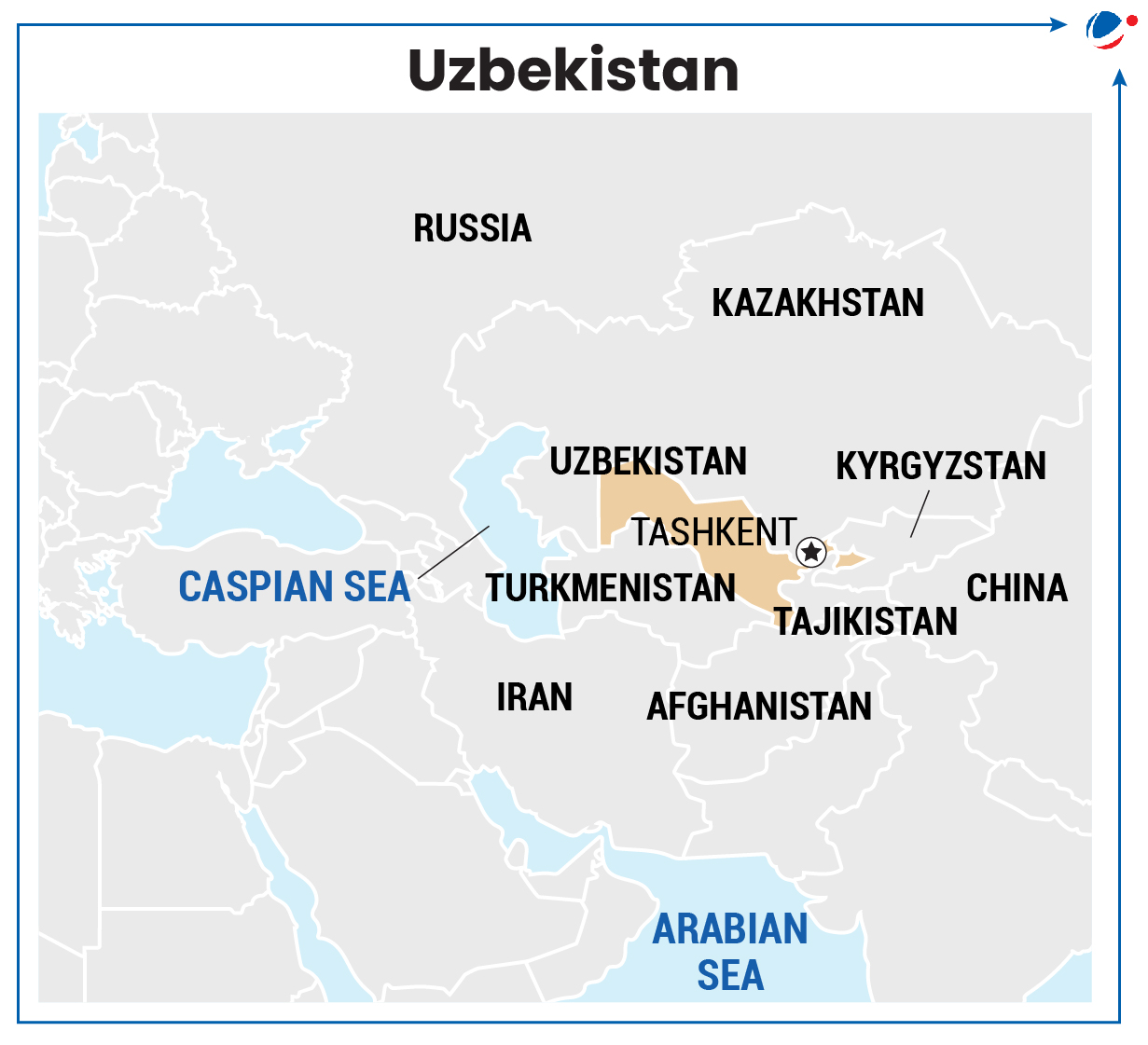 India - Uzbekistan RelationsUzbekistan is India’s key Partner in the Central Asian Region. Different dimensions of engagement includes
|
Article Sources
1 sourceBIT, signed in Abu Dhabi in February (2024), entered into force with effect from 31st August, 2024.
- Bilateral Investment Promotion and Protection Agreement between India- UAE (signed in 2013) expired in September, 2024
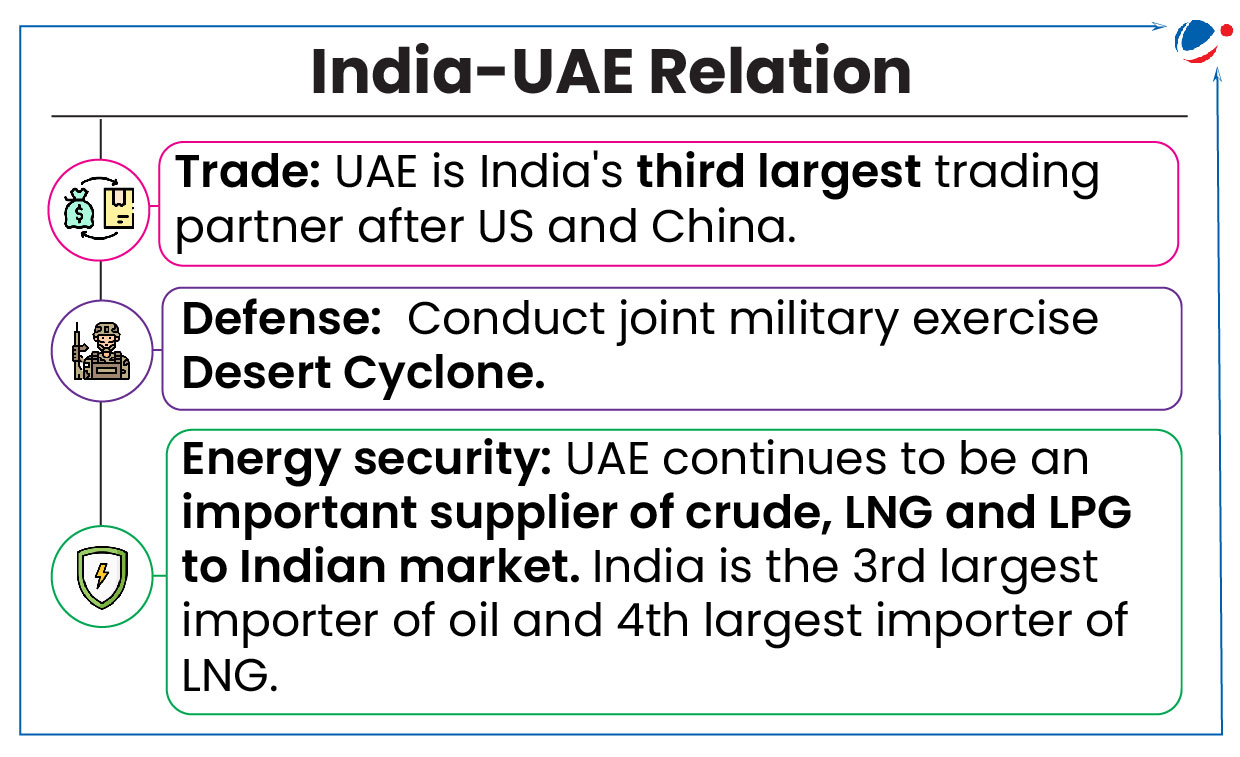
Key features of India-UAE BIT
- Investor-State Dispute Settlement through arbitration with mandatory exhaustion of Local remedies for 3 years.
- Closed asset-based definition of Investment with coverage of Portfolio Investment.
- Treatment of Investment with obligation for no denial of justice, no fundamental breach of due process.
- Provides protection to investments from Expropriation, provides for Transparency, Transfers and Compensation for losses.
Significance of India – UAE BIT 2024
- UAE is seventh largest FDI source for India with share of 3% ($19 billion) in total FDI received by country from April 2000-June 2024.
- Boost confidence of investors by assuring minimum standard of treatment and non-discrimination while providing an independent forum for dispute settlement by arbitration.
Indian External Affairs Minister participated in the first-ever Joint Ministerial Meeting of the C-10 and L.69 groupings.
- L69 is a grouping that includes countries from Africa, Latin America, Caribbean, Pacific Island states and Asia.
- India is also member.
C-10 Group
- Genesis: Committee of Ten African Ministers of Finance and Central Bank Governors (C-10) was created in 2008.
- Members: Algeria, Botswana, Cameroon, Egypt, Kenya, Nigeria, South Africa, Tanzania, the Central Bank of West African States (CBWAS), and the Central Bank of Central African States (CBCAS).
- Mandate: Advocating enhanced African participation in governance of international financial institutions (IFIs), etc.
Both countries have reached a historic political agreement to hand over Chagos Islands to Mauritius (Still subject to finalization of a treaty).
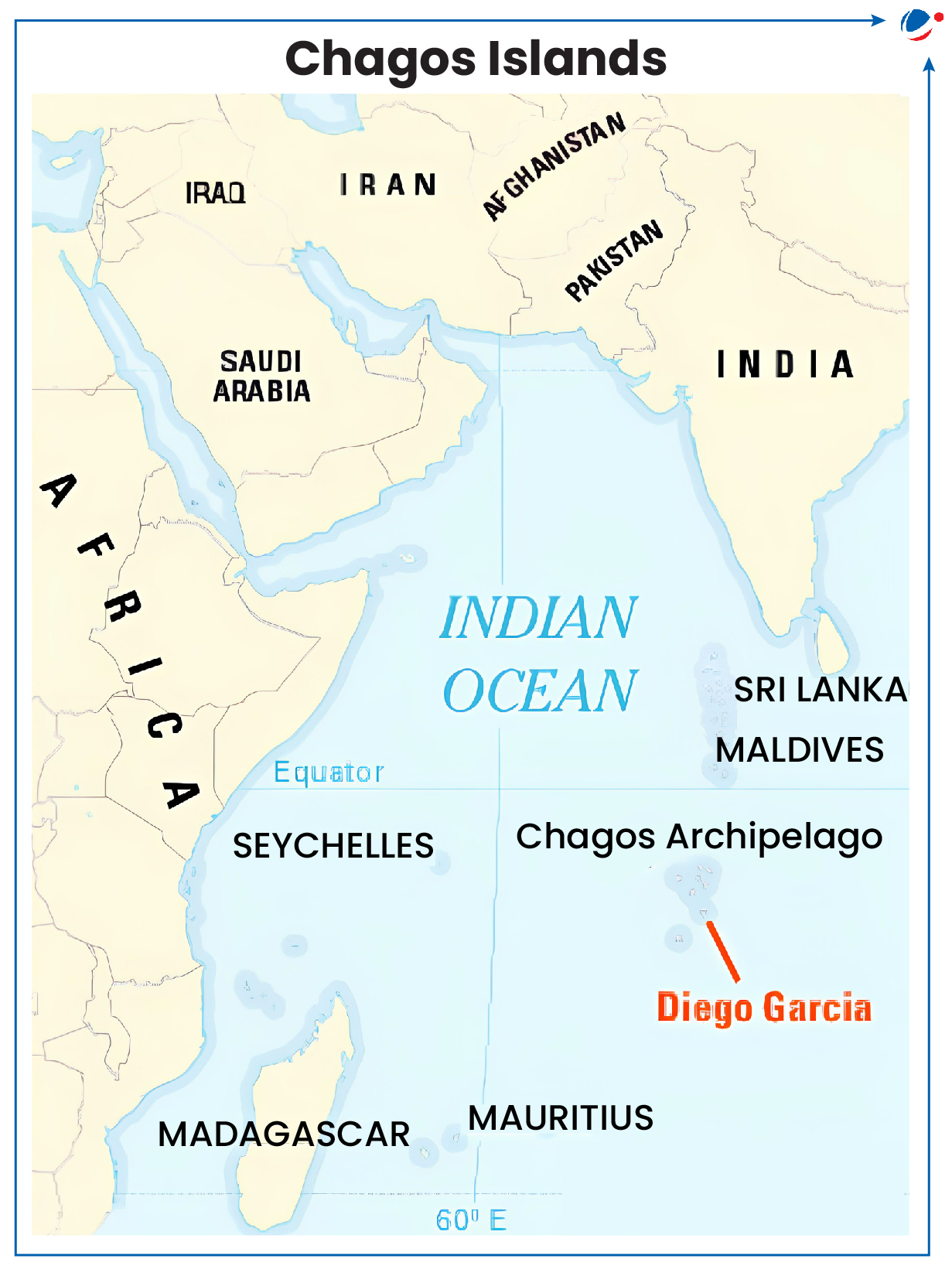
- While US-UK joint base will remain on Diego Garcia atoll.
About Chagos Archipelago
- It is an island group, located 500 km south of Maldives in Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Uninhabited until 18th century, later French colonized it. French ceded island to British in 1814.
- British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT): Formed by UK in 1965, with Chagos as a central part.
- Some BIOT islands were ceded to Seychelles in 1976.
- Archipelago was detached from Mauritius by UK in 1965, three years before Mauritius gained independence.
Significance of Treaty
- Addressing colonial legacy: Ends a long-standing dispute over last British colony in Africa.
- Regional Security Dynamics: As Mauritius may seek to balance its relations with major powers.
- Security Importance: Diego Garcia base allows US to monitor Malacca Strait, crucial for global trade, and maintain its presence in IOR.
- Compliance with International Law: Handing over island is aligned with judgment of International Court of Justice In 2019 & UNGA resolution in 2019.
- India supported Mauritius' claim by voting in its favor at UNGA in 2019
- It was in line with India’s “principled stand on decolonization and support for sovereignty and territorial integrity of nations”.
- India supported Mauritius' claim by voting in its favor at UNGA in 2019
Taiwan’s navy recently claimed that China's military is employing an 'anaconda strategy' to constrict the island.
About Anaconda strategy
- It refers to a military strategy proposed by Union General Winfield Scott during early stages of the American Civil War.
- Its key objective was to suffocate the Confederacy economically and militarily, similar to how an anaconda snake coils around and asphyxiates its prey.
- China's 'anaconda strategy’ against Taiwan involves a mix of military manoeuvres, psychological tactics, and cyber warfare.
- Its goal is to force Taiwan into submission without engaging in a full-scale invasion.
Article Sources
1 sourceIsrael has made control of the Philadelphi corridor a condition in ceasefire negotiations between Israel and Hamas.
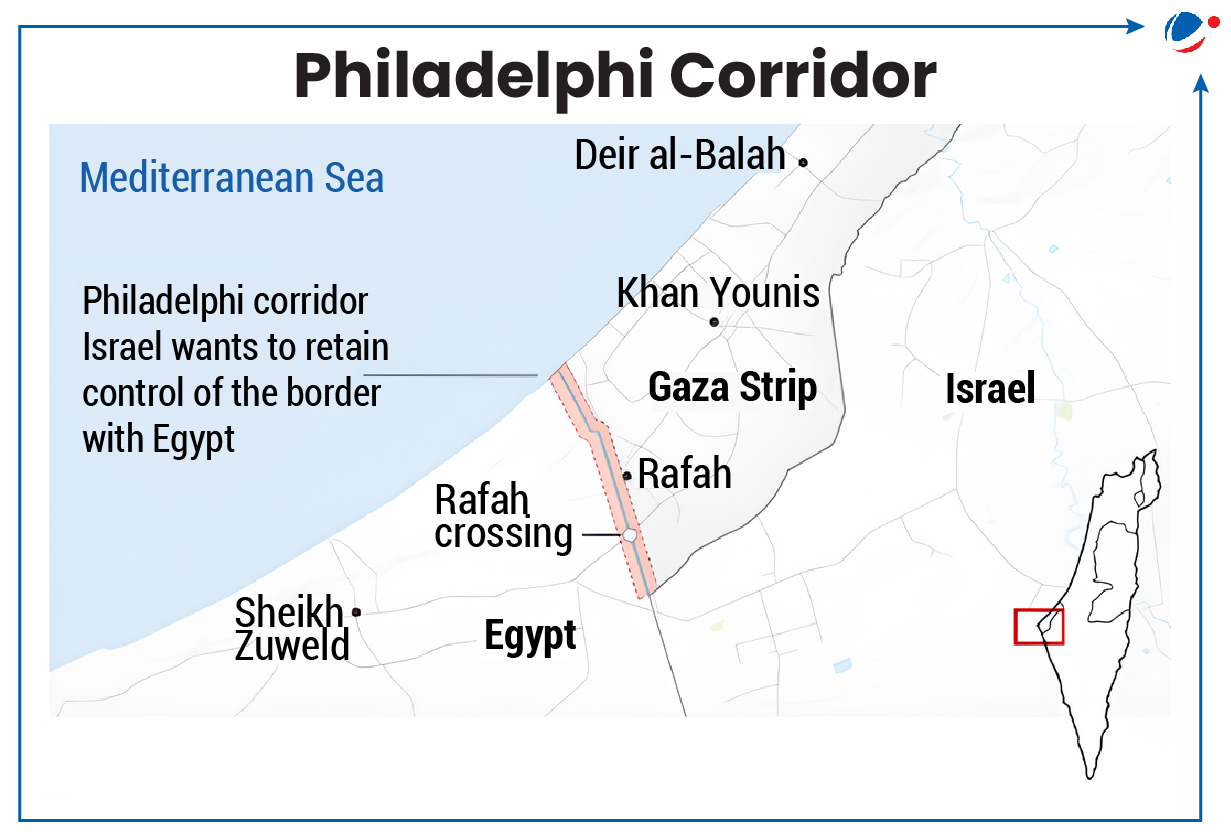
About Philadelphi corridor
- It is a ribbon of land about nine miles (14kms) in length and 100 metres wide along Gaza’s border with Egypt, including the Rafah crossing.
- It was designated as a demilitarised border zone after the withdrawal of Israeli settlements and troops from Gaza in 2005.
- It runs from the Mediterranean to Kerem Shalom crossing with Israel.
- After the Israeli withdrawal, it was the responsibility of Egypt and the Palestinian Authority.







