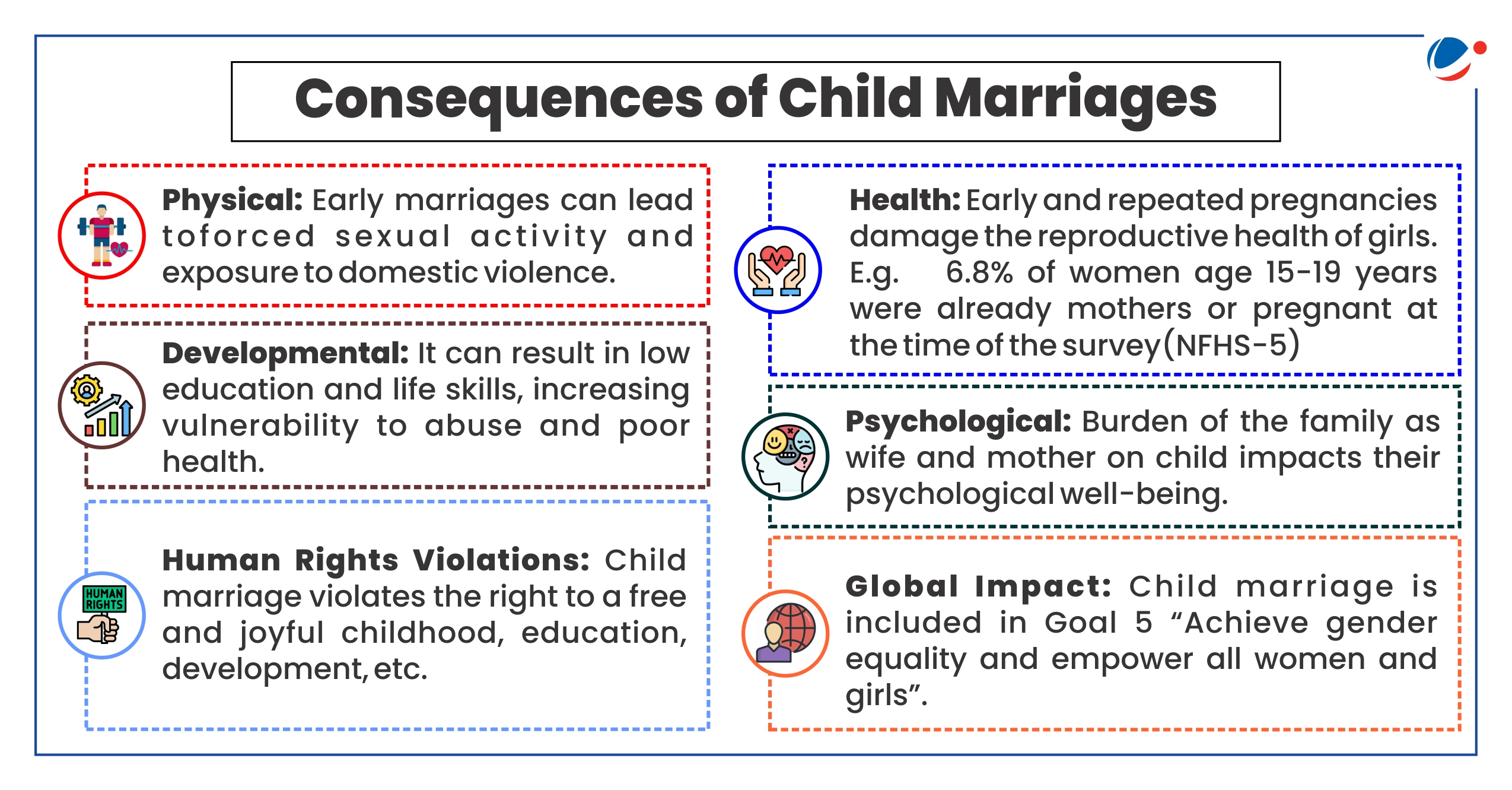
Why in the News?
Supreme Court in a petition filed by 'Society for Enlightenment and Voluntary Action' issued comprehensive guidelines for prohibition of child marriage.
Status of Child Marriage in India (NFHS-5)
|
Reasons for prevalence of child marriages in India
- Poverty and Resource Scarcity: Families marry off daughters early to reduce financial burdens, particularly dowries, and view girls as economic liabilities.
- Deep-rooted Cultural and Traditional Beliefs: In conservative set-ups, child marriage is seen as a way to preserve family honour, ensure virginity, and protect girls from premarital sexual relationships.
- Traditional, religious, entrenched customs and social acceptance of child marriage is a predominant reason for the prevalence of child marriage.
- Patriarchy and Gender Inequality: Girls are seen as a burden on their family and marrying one's daughter at a young age is viewed as a way to ease economic hardship by transferring this 'burden' to her husband's family.
- Low value placed on Girls education: Girls are not seen as being worthy of investment in education. Poor educational opportunities limits power of child to resist marriage as alternative aspirations gets diminished.
- Fear of Safety and Security: Many parents feel that it is in best interest of girl child to marry early to ensure her safety where girls are at high risk of harassment and physical or sexual assault.
- Legal and Enforcement Gaps: Weak law enforcement, lack of awareness, and inadequate monitoring especially in rural and remote areas leads to continuation of menace of child marriage. E.g. Conviction and Reporting of child marriage cases are extremely low
Measures taken by Government
- Enactment of 'Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA), 2006': It prohibits marriage of girls under 18 and boys under 21. Section 16 of Act authorises State Government to appoint Child Marriage Prohibition Officers (CMPO).
- The Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015: It has provisions for care and protection of children who are at imminent risk of marriage before attaining the age of marriage.
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao Scheme (2015): Implemented by Ministry of Women and Child Development, it aims to break gender stereotypes & challenges son-centric rituals. It incorporates components of celebration of Birth of Girl Child, linking Sukanya Samriddhi accounts with birth of girl child and preventing child marriages.
- The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR): It undertakes various activities with stakeholders such as representatives of Child Welfare Committees (CWC), Police, Women and Child Development Department and Civil Society organizations on the issue of child marriages
- National Action Plan to Prevent Child Marriage: It is a comprehensive framework which aims at providing support to girls who are at risk of early marriage. It includes better data collection, awareness programs, and stronger coordination between state and local governments.
- Emergency Outreach Services: Government of India has introduced CHILDLINE with short code 1098, a 24X7 telephone emergency outreach service for children in crisis, including for prevention of child marriages
- Partnership of State Governments with UNICEF and other NGOs: E.g. UNICEF(in Bihar) is building capacity of local faith-based leaders and kathavachaks on child marriage and creating a fleet of Yuvacharyas to act as door messengers at the village level
Way Forward
Supreme Court has issued comprehensive guidelines to prevent child marriages in India covering various components:
- Legal Enforcement: Appointment and accountability of CMPO by state governments and Union Territories (UTs) at the district level. These officers should not be burdened with additional duties that could impede their focus on preventing child marriage.
- District-Level Responsibility for Prevention of Child Marriages to Collectors and Superintendents of Police
- Establishment of a Special Police Unit and Special Child Marriage Prohibition Unit
- Judicial Measures: Empowering Magistrates to take Suo Moto Action to prevent solemnization of child marriage
- Exploration of Special Fast-Track Courts for Child Marriage Cases
- Mandatory action against neglectful public servants
- Community Involvement: Adoption of the Child Marriage Free Village Initiative and "Child Marriage Free" certifications for villages and gram panchayats on the lines of "Open Defecation Free Village" under the Swachh Bharat Mission
- Awareness Campaigns and Capacity Building: Comprehensive Sexuality and Rights Education by integrating it into school curricula
- Use of Technology: Establishment of a Centralized Reporting Portal for Child Marriages by Ministry of Home Affairs, Ministry of Women and Child Development, and NALSA
- Leveraging Technology for Support Services by states and UTs to disseminate information against child marriage across all media, focusing on high-risk regions.
- Data analytics to identify high-risk areas and patterns for swift interventions.
- Funding and Resources: Dedicated Annual Budget Allocation for each State specifically aimed at preventing child marriage
- Training for community health workers, educators, law enforcement and judicial officers
- Institutionalization of Juvenile Justice Fund established under Section 105 of the Juvenile Justice Act.





