All India Rural Financial Inclusion Survey 2021-22
NABARD released Second All India Rural Financial Inclusion Survey (NAFIS) 2021-22.
- NAFIS was launched in 2016-17 as a national level survey that offers comprehensive overview of rural population in terms of their status of livelihoods and level of financial inclusion (including loans, insurance, pension etc.).
- Second NAFIS provides key insight into economic and financial indicators of rural development since 2016-17.
Key highlights of survey
- Average monthly income of households increased by 57.6%.
- Share of food in consumption basket of households declined from 51% to 47%.
- Kisan Credit Card as a prominent instrument of financial inclusion in rural farm sector has been found to be very effective.
- Average size of landholding declined to 0.74 hectare from 1.08 hectare.
- Proportion of respondents indicating good financial literacy increased from 33.9% to 51.3%.
- Proportion of agricultural households that took loans from institutional sources increased from 60.5% to 75.5%.
Reasons for rise in rural income
- Government Support: Example, under Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme, 5.6 crore households availed employment (January 2023), thus increasing their incomes and provides livelihood security.
- Rise in Rural Female Labour Force Participation Rate: From 19.7% in 2018-19 to 27.7% in 2020-21 (Economic Survey 2022-23).
About NABARD (National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development)
NAFINDEX: Measure of Financial Inclusion
|
- Tags :
- NABARD
- Financial Inclusion
- All India Rural Financial Inclusion Survey
- NAFINDEX
Government notifies Offshore Areas Operating Right Rules, 2024
Rules notified under Offshore Areas Mineral (Development and Regulation) Act, 2002 aim at regulating exploration and production of minerals in specified offshore regions.
- This is significant in the backdrop of the planned first-ever offshore mineral auction of 10 blocks. These blocks will include sand, lime mud, and polymetallic nodules.
Key Highlights of Rules
- Applicability: All minerals in offshore areas, except Mineral oils and hydrocarbons and specified Atomic minerals
- Lease Surrender: Provides for surrender of lease after 10 years in case of uneconomic production operations.
- Provide for Priority access to government and government-owned companies, in case of operating rights for reserved offshore zones.
Offshore mining and its significance:
- Also called deep sea mining, Offshore mining is process of retrieving mineral deposits from deep seabed i.e. ocean below 200m.
- It will cater to increasing demand for metals in context of depleting terrestrial deposits and reduce dependence on mineral imports.
Issues/Challenges in offshore Mining:
- Potential environmental damage: Can endanger biodiversity by habitat destruction, underwater noise, and pollution.
- Impact on fishing communities: May harm fish populations, impacting livelihood of fishing communities.
- Technology: Lack of adequate R&D and technological development for deep-sea mining.

- Tags :
- Polymetallic nodules
- Offshore Mining
- Deep Ocean Mission
- Offshore Areas Operating Right Rules
- Deep Sea Mining
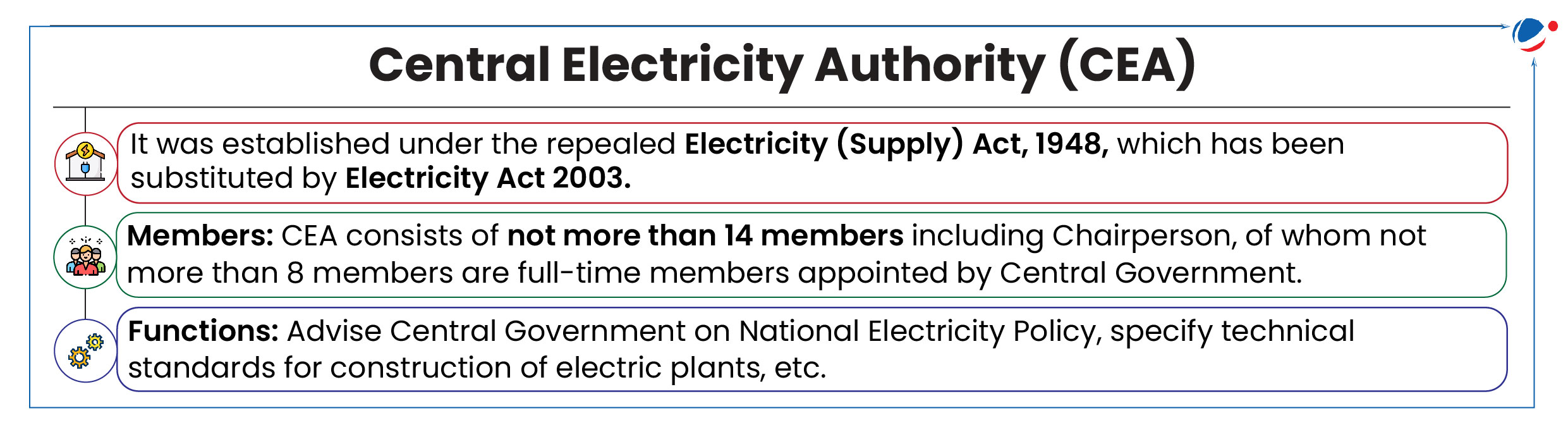
National Electricity Plan (Transmission)
Union Ministry of Power launched National Electricity Plan (Transmission).
- National Electricity Plan (NEP) (Transmission) has been developed by the Central Electricity Authority (CEA), entrusted under Electricity Act 2003.
- Transmission system establishes the link between source of generation and distribution system, which is connected to load / ultimate consumer.
Key highlights of NEP (Transmission)
- Aim of transmitting of 500 GW of Renewable Energy Installed Capacity by 2030 and over 600 GW by 2032.
- It is aimed at meeting a peak demand of 458 GW by 2032 and will expand transmission network from 4.85 lakh ckm (circular kilometer) in 2024 to 6.48 lakh ckm in 2032.
- Inter-regional transmission capacity is planned to increase to 168 GW by 2032, from present level of 119 GW.
- Incorporates innovative elements in transmission sector such as integration of 10 GW offshore wind farms, 47 GW battery energy storage systems, and 30 GW pumped storage plants.
- Aims to address power needs of Green Hydrogen and Green Ammonia Manufacturing hubs of coastal locations.
- Covers Cross border interconnections with Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and probable interconnections with Saudi Arabia, UAE etc.
Challenges in India’s Transmission System: Transmission losses, issues in integration with renewable sources, obsolete technology, skewed focus of regulators towards generation, cyber security etc.
- Tags :
- National Electricity Plan (Transmission)
- Central Electricity Authority (CEA)
- Electricity Act, 2003
Articles Sources
National Agriculture Code (NAC)
Bureau of Indian Standards is creating a NAC similar to National Building Code and National Electrical Code.
About NAC
- Code will have two parts. First will contain general principles for all crops, and second will deal with crop-specific standards for paddy, wheat, oilseeds, and pulses.
- NAC will cover all agriculture processes and post-harvest operations, like crop selection, land preparation, sowing/transplanting etc.
- Objectives
- Create national agricultural code that considers agro-climatic zones, crop types, etc.
- Create comprehensive guide for farming community to ensure effective decision making in agricultural practices.
- Address horizontal aspects of agriculture like SMART farming, sustainability, etc.
- Tags :
- Bureau of Indian Standards
- National Agriculture Code (NAC)
- Agricultural Reforms
Central Silk Board
Recently, the platinum jubilee of the Central Silk Board was celebrated.
About Central Silk Board
- Statutory body established in 1948 by an Act of Parliament.
- Ministry: Ministry of Textiles
- Mandate:
- Advise the government on all matters concerning sericulture and silk industry.
- Standardization of various production processes, etc.
- HQ: Bengaluru
About Silk Production in India
- India is 2nd largest silk producer in the world with 42% of global production (2023)
- Karnataka contributed around 32% of the total silk production, followed by Andhra Pradesh.
- Silk Produced: Mulberry, Eri, Tasar and Muga.
- Tags :
- Central Silk Board
- Silk
Articles Sources
Humsafar Policy
Union Minister of Road Transport & Highways launched the Humsafar Policy.
About Humsafar Policy
- Aim: To provide a comprehensive framework to ensure that the commuters have access to standardized, well-maintained, and hygienic facilities along National Highways and Expressways
- Key Benefits:
- Registered service providers will be able to avail a waiver of renewal fees for access permissions, if they maintain an average rating of 3 or higher.
- Reliable passenger convenience establishments at regular intervals
- Tags :
- Ministry of Road Transport and Highways
- National Highways (NH)
- Humsafar Policy
Articles Sources
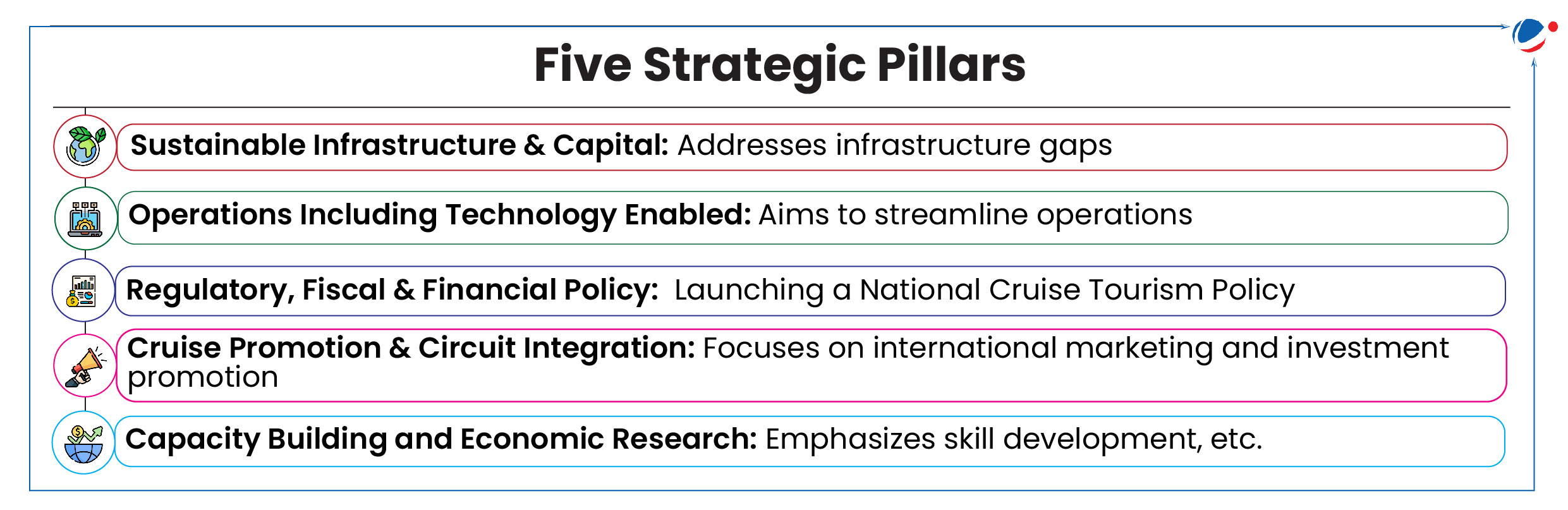
Cruise Bharat Mission (CBM) Launched
Mission has been launched by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways.
About Cruise Bharat Mission
- Aim: To excel in India’s vision to become a global hub for cruise tourism and promote the country as the leading global cruise destination. It also aims to
- double cruise passenger traffic within five years; i.e. by 2029.
- In 2024 passengers traffic is 4.6 lakh.
- double volume of cruise calls from 254 in 2024 to 500 by 2030.
- double cruise passenger traffic within five years; i.e. by 2029.
- Phase-wise implementation:
- Phase 1 (2024 to 2025): Focus will be on forming cruise alliances with neighbouring countries, etc.
- Phase 2 (2025 to 2027): Developing new cruise terminals, destinations etc.
- Phase 3 (2027 to 2029): Integrating all cruise circuits across the Indian Subcontinent.
- Three key cruise segments:
- Ocean & Harbour Cruise segment: Encompasses ocean cruises, including deep-sea and coastal cruises, along with harbour-based yachting and sailing cruises.
- River & Inland Cruise segment: Focuses on river and inland cruises on canals, backwaters, creeks, and lakes.
- Island Cruise segment: Highlights inter-island cruises, lighthouse tours, etc.
- Tags :
- Cruise Bharat Mission
- Cruise tourism
- Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways
Z-Morh Project
Recently militants attacked Z-Morh Project site in Jammu and Kashmir.
About Z-Morh Project:
- It is a 6.4-km tunnel on the Srinagar-Sonamarg highway at an altitude of 8,500 feet aimed at all weather connectivity to Sonamarg, a famous tourist destination.
- It has acquired its name from presence of a Z-shaped road stretch at the construction location.
- Strategic importance:
- It is part of the Zojila tunnel project that aims to provide all weather connectivity from Srinagar to Ladakh throughout the year.
- It connects Srinagar, Dras, Kargil and Leh regions , apart from this all-weather connectivity reduces army’s reliance on air transport.
- Tags :
- Jammu and Kashmir
- Zojila Tunnel Project
- Z-Morh Project
Responsible Capitalism
Need for responsible capitalism for large economies highlighted by Union Finance Minister
- At the Tech Leaders Roundtable in Mexico, Minister while emphasizing on need for responsible capitalism said that for large economies, the challenge is not just to grow but also to reduce inequality and create opportunities for everyone.
What is meant by Responsible Capitalism?

- It can be understood as an economic approach that integrates ethical values into business practices.
- It emphasizes balancing profit with social responsibility, ensuring businesses contribute to societal well-being, fairness, and environmental sustainability, rather than focusing solely on shareholder returns.
What’s the need for Responsible Capitalism?
- Addressing global challenges: It can help companies and governments respond to challenges like sustainability, inequality, and exclusion.
- Long-term business sustainability: Purely profit-driven models may not be viable in long-term; responsible capitalism can also help in better adaptation to tech-disruptions like AI, etc.
- Ethical Governance and Stakeholder Capitalism: Promotes fairness in decision-making, ensuring stakeholders are treated justly and business operations comply with legal and moral standards.
Measures taken to promote Responsible Capitalism in India
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Mandated under section 135 of Companies Act, 2013.
- Environmental regulations: Plastic Waste Management Rules, stricter emission norms for vehicles under BS-VI, etc.
- Labor reforms: Code on Wages, Occupational Safety; Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020, etc.
- Financial sector initiative: RBI’s Priority Sector Lending norms, SEBI’s Green Bond guidelines, etc.
- Tags :
- Responsible Capitalism
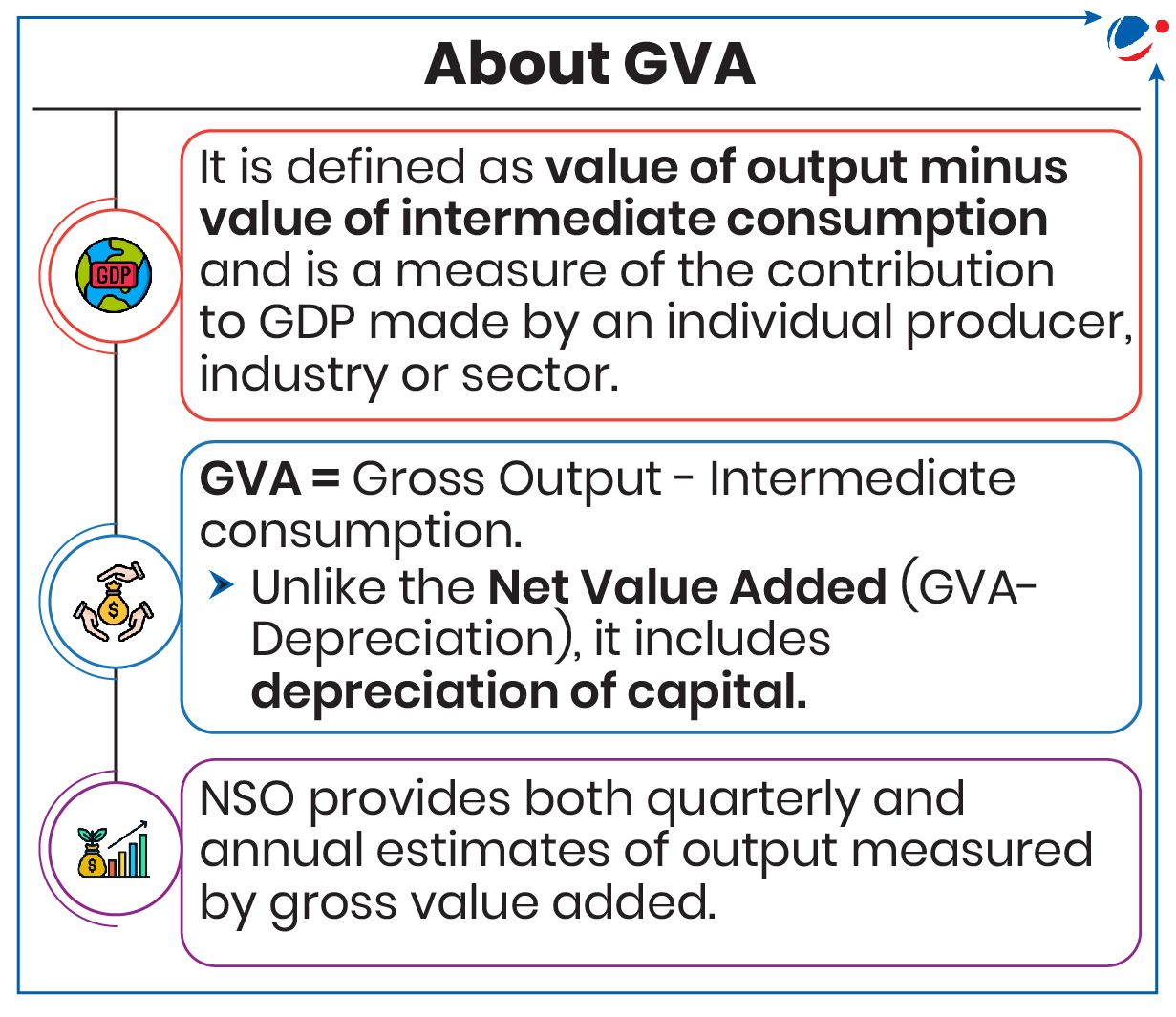
Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) for FY 2022-23
ASI released by Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) for FY 2022-23
- ASI provides insight into dynamics of change in composition, growth and structure of manufacturing industries in terms of key economic indicators.
Key Highlights
- Manufacturing Gross Value Added (GVA): Grew by 7.3% in current prices in 2022-23 over 2021-22.
- Maharashtra topped followed by Gujarat in terms of Manufacturing GVA.
- Growth in economic parameters: Surpassed pre-pandemic level in absolute value terms e.g. in invested capital, GVA, employment and wages etc.
- Growth drivers of Manufacturing-Sector: Manufacture of Basic metal, Coke & Refined Petroleum Products, Food Products, etc.
- Employment: 7.4% increase in manufacturing employment in 2022-23 over previous year.
- Highest Employing States: Tamil Nadu followed by Maharashtra.
About ASI:
- Conducted by Collection of Statistics Act, 2008 except in Jammu & Kashmir (Conducted under J&K Collection of Statistics Act, 2010).
- Industries covered:
- Factories registered under Sections 2m(i &ii) of Factories Act,1948
- Bidi and cigar manufacturing establishments under the Bidi & Cigar Workers (Conditions of Employment) Act,1966
- Electricity undertakings not registered with Central Electricity Authority (CEA)
- Units with 100 or more employees registered in the Business Register of Establishments (BRE) maintained by the States.
- Tags :
- ASI for FY 2022-23
Input Tax Credit
Recently, Supreme Court laid down twin tests - ‘functionality’ and ‘essentially’ - for Input Tax Credit eligibility in construction.
- Court stated that if a building is essential for supplying services like renting or leasing (as per Schedule 2, clauses 2 and 5 of CGST Act), it may be considered a plant.
- Functionality test determines whether a building qualifies as a plant or not.
About Input Tax Credit
- It is a mechanism to avoid cascading of taxes, i.e, ‘tax on tax’.
- A registered taxable person under GST Act who is paying tax due in the course or furtherance of business can claim and avail ITC credited in electronic ledge.
- Tags :
- Input Tax Credit
Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP) Scheme
Government approved changes to the RoDTEP scheme.
Key Changes
- For Domestic Tariff Area (DTA) units: Extended by 1 year till 30th September, 2025.
- For Authorisation holders (except Deemed exports), export-oriented units and special economic zone units: Applicable till the end of this year.
- Applicability of New rates: From October 10th, 2024 based on the recommendations of RoDTEP Committee.
About RoDTEP Scheme
- Introduced in 2021 by Ministry of Commerce and Industry
- Aim: Refunding taxes, duties, and levies at the central, state and local levels on the exported products.
- It replaced the Merchandise Exports from India scheme which was challenged at World Trade Organization.
- Tags :
- RoDTEP scheme
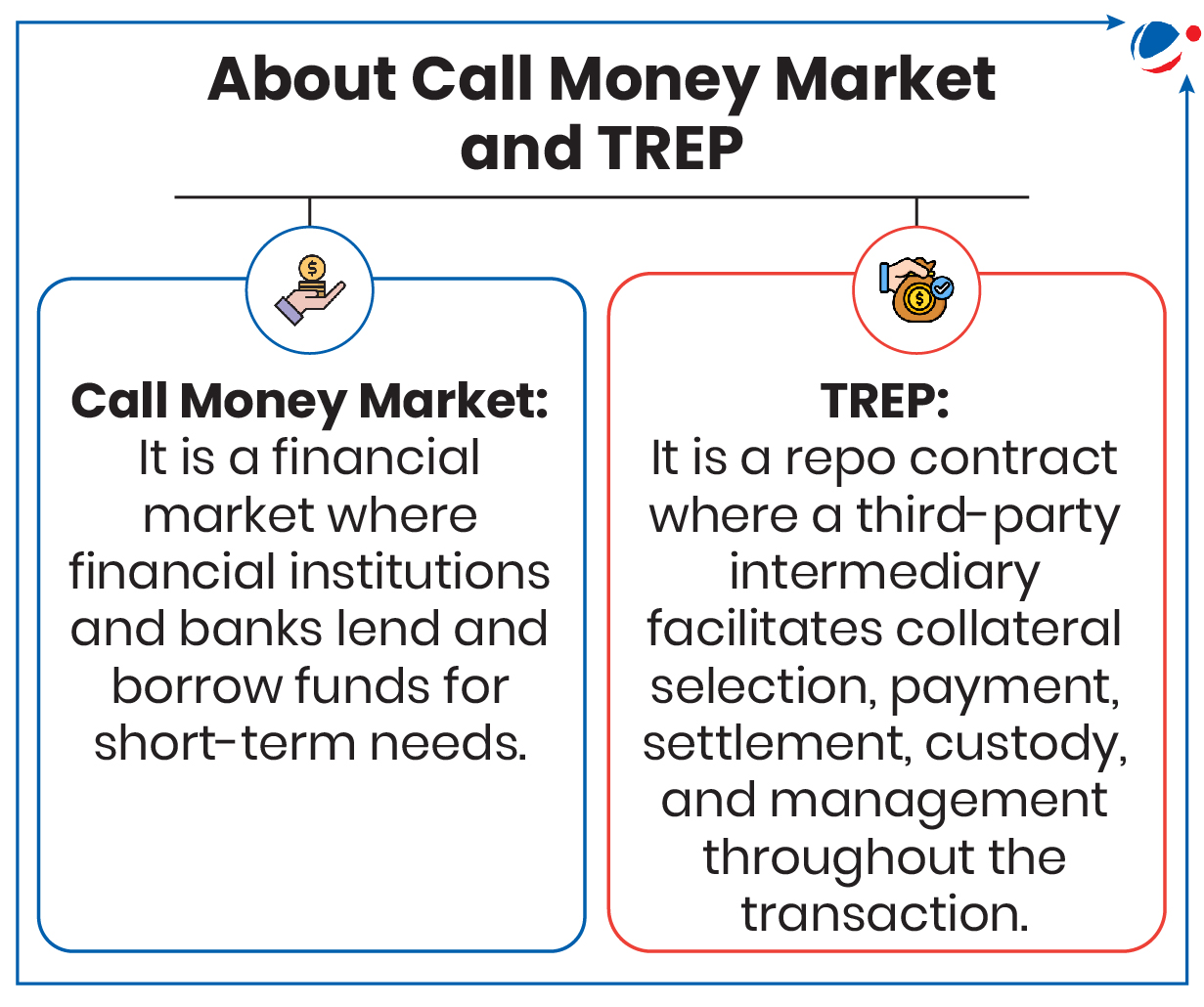
RBI released Report of the Committee on MIBOR Benchmark
Recently, RBI released a report recommending key changes in methodology for computation of Mumbai Interbank Outright Rate (MIBOR) and proposed transition to a new secured money market benchmark for widely used product derivatives.
What is MIBOR?
- First introduced by National Stock Exchange (NSE) in 1998, it is the interest rate benchmark at which banks borrow unsecured funds from one another in the Indian interbank market.
- It is computed and published by Financial Benchmarks India Pvt. Ltd. (FBIL) on a daily basis.
- Currently, it is computed based on trades executed on Negotiated Dealing System or NDS-Call system in the first hour.
- Issues with current MIBOR: Based on a narrow volume (1% of daily money market volume) of call transactions, thin call money market volumes making MIBOR susceptible to volatility, etc.
Key recommendations of the report
- Change in computation methodology of MIBOR: Include transactions based on first 3-hours instead of first hour, to make MIBOR more representatives of transactions in call money market and potentially increase its reliability.
- Benchmark based on secured money market: FBIL to develop and publish a benchmark based on secured money market computed from trades in the first three hours of basket repo and the TREP (tri-party repo) segments.
- Tags :
- MIBOR
RBI Study on Monetary Policy Transmission
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released study on Monetary Policy Transmission (MPT) and Labour Markets in India.
- Study analyzes impact of informality in labor markets on inflation stabilization and monetary policy offering new insights on MPT.
About Monetary Policy (MP)

- MP is a set of actions available to a nation's central bank (RBI in India) to achieve sustainable economic growth & Maintaining price stability by adjusting money supply.
- Statutory Basis: RBI, Act,1934 (amended in 2016).
- MP Framework: Central Government, in consultation with RBI, determines inflation target in terms of Consumer Price Index (CPI) every 5 years.
- Flexible Inflation Targeting: Currently, it is 4% (with a tolerance of +/- 2%) till March, 2026.
- Tools: Direct and indirect instruments like Repo Rate, Reverse Repo Rate etc.
- Types: Expansionary (Lowering interest rate to stimulate economic activity); and Contractionary (Increasing interest rate to slow down activity and prevent inflation)
Key findings of Study:
- MP Transmission: Improves with more formality in the labor market.
- Impact on Unemployment: Contractionary Monetary Policy (CMP) leads to Rise in unemployment in both formal and informal markets.
- Impact on Macroeconomic variables: Contractionary Monetary Policy (CMP) leads to a decline in aggregate consumption, inflation, investment, output, capital stock, etc.
- Tags :
- Monetary Policy Transmission
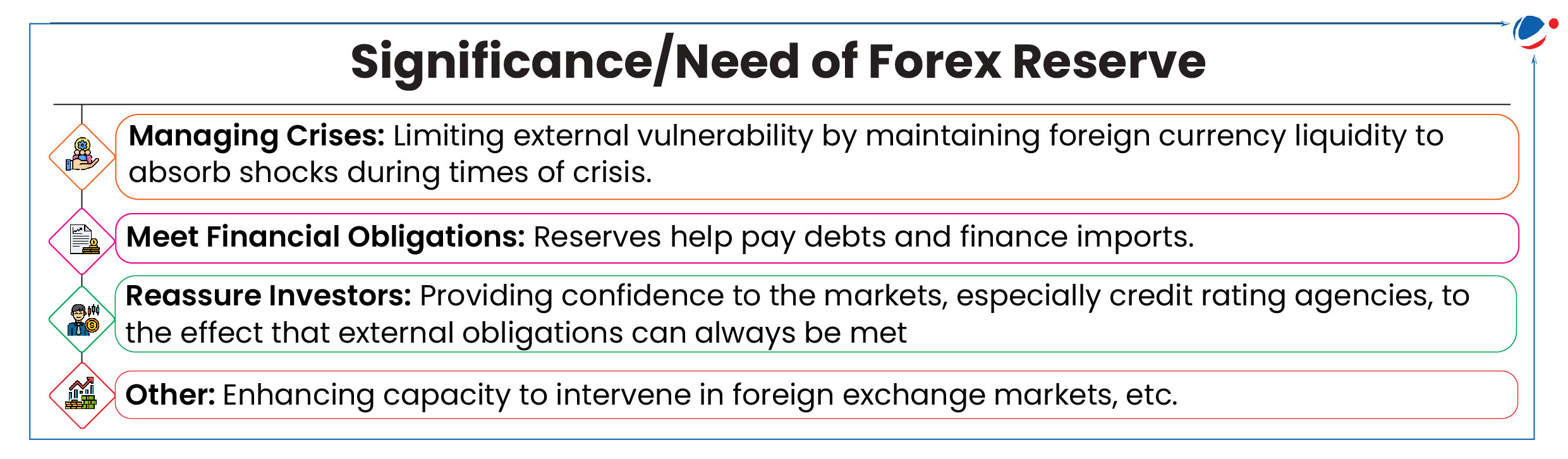
India Forex Reserve Cross 700 Billion Dollar
India is now the fourth country in the world to have over $700 billion in foreign reserves, following China, Japan, and Switzerland.
- India's reserves can cover 11.9 months of imports, well above the general norm of six-months.
About Forex (Foreign Exchange) Reserve-
- It comprises of different assets that are held by a central bank.
- In India, the RBI Act of 1934 contains the enabling provisions for the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to act as the custodian of forex reserve, and manage reserves within the defined objectives.
- Components of Reserve (in descending order as per their value)-
- Foreign Currency Assets (FCA): It is valued in currencies other than the country's own
- Gold reserves
- Special Drawing Rights: A reserve asset provided by International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- It is value is based on a mix of five major currencies- the US dollar, euro, Chinese renminbi, Japanese yen, and British pound sterling.
- Reserve Tranche Position (RTP): It is equal to the member’s quota less the IMF’s holdings of the member’s currency in account.
- Key deriving factor behind rise in reserve: Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI), Remittances, etc.
- Tags :
- India Forex Reserve
UPI 123 and UPI Lite
To encourage wider adoption of Unified Payments Interface (UPI), RBI enhances transaction limits for UPI123Pay, UPI Lite.
UPI123Pay
- Started in March 2022 to enable feature-phone users to use UPI.
- It is available in 12 languages.
- Technology alternatives include IVR number, app functionality, missed-call and proximity sound-based payments.
- RBI enhanced the per-transaction limit from ₹5000 to ₹10,000.
UPI Lite
- It allows users to make low-value transactions without entering a UPI PIN.
- RBI enhanced per-transaction limit to ₹1,000 from ₹500 and overall wallet limit to ₹5,000 from ₹2000.
- Tags :
- UPI Lite
- UPI 123



