US House Approves 3.5% Outward Remittance Tax
US House Approves 'One, Big, Beautiful Bill' with 3.5% outward remittance tax provision
- Called the ‘Excise tax on remittance transfers’, the newly proposed provision will be effective from January 1, 2026.
Remittances
- Definition: The movement of funds from the country of work back to a home country is known as remittances.
- In 2023, remittances back to home countries totalled about $656 billion.
- India got 14.3% of global remittances in 2024 (its highest ever).
Key highlights of the Bill
- Remittance tax (excise tax) will apply only to non-US citizens and US citizens are exempted.
- Affected groups include Visa holders (H-1B, F-1), Green card holders, etc.
- The bill reduced the Outward remittance tax from 5% (which was previously proposed) to 3.5%.
Impact of Excise tax on remittance transfers’
- Global Economic ripple: Countries like El Salvador, Mexico, India, which rely on US remittances, may face economic setbacks.
- The proposal may also discourage foreign workers from maintaining assets or employment in the US.
- Dent India’s Inward Remittance Flow: The United States is the largest source of remittances to India, accounting for $32.9 billion of the total remittance inflows in 2023-24.
- A remittance tax could push some funds from Indians in the U.S. to grey or black markets, bypassing regulation.
Related NewsStudent remittances under the Liberalised Remittances Scheme (LRS) in FY2025 dropped to a five-year low ($2.92 billion), indicating reduced student outflows (RBI) About Liberalised Remittances Scheme
|
- Tags :
- Remittance tax
Alternative Investment Funds (AIFS)
RBI has revised the rules for investment in Alternative Investment Funds.
About AIFs
- Any fund incorporated in India which is a privately pooled investment vehicle which collects funds from sophisticated investors, whether Indian or foreign, for investing it in accordance with a defined investment policy for the benefit of its investors.
- AIFs are regulated by the SEBI, as per the SEBI (Alternative Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012.
Categories of AIFs
- Category I AIF: Invest in start-ups, early-stage ventures or sectors considered socially or economically beneficial.
E.g. Venture Capital Funds, Angel funds, SME Funds, Infrastructure Funds
- Category II AIF: They do not use leverage or debts other than to cover their day-to-day operational expenses.
E.g. Private Equity Funds, Debt Funds, Real Estate Funds.
- Category III AIF: It may use leverage including through investment in listed or unlisted derivatives.
E.g. Hedge Funds, Private investment in public equity (PIPE).
- Tags :
- AIFs
Predatory Pricing
Recently, Competition Commission of India has notified the Cost Regulations, 2025 providing new definitions to curb predatory pricing.
About Predatory Pricing
- Definition: The sale of goods or provision of services at a price below the cost with a view to reduce competition or eliminate competitors.
- Section 4(2) of the Competition Act, 2002 identifies predatory pricing by a dominant enterprise as an abusive practice.
- Impact of predatory pricing:
- On customers: Beneficial in the short term with lower prices but they suffer in the long term due to lesser options and higher prices.
- On Companies: Harms all companies in the short term but once competitors are driven out, the monopolised companies raise prices and recover lost profits.
- Tags :
- predatory pricing
Payments Regulatory Board
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) notified the Payments Regulatory Board Regulations, 2025, under Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007.
- These regulations replace the earlier Board for Regulation and Supervision of Payment and Settlement Systems Regulations, 2008.
About Payments Regulatory Board
- Composition
- Chairperson: RBI Governor
- Ex-officio Members: Deputy Governor in charge of payment systems, 1 RBI-nominated officer.
- 3 members nominated by Central Government.
- Board may also invite experts from fields like payments, IT, cybersecurity, law etc.
- Tenure of Members: Government-nominated members will have a fixed tenure of 4 years and no re-nomination is allowed.
- Meetings: At least twice a year.
- Quorum: Minimum of 3 members, including Chairperson or Deputy Governor.
- Decisions: by majority vote. In case of a tie, Chairperson has a casting vote.
- Tags :
- Payments Regulatory Board
RBI (Digital Lending) Directions, 2025
Key objectives of directions include enhancing borrower protection, ensuring data transparency, and promoting responsible Digital lending practices.
Key Highlights of the RBI Directions
- Defines digital lending as a remote and automated lending process by use of digital technologies for customer acquisition, credit assessment, loan approval, disbursement, recovery etc.
- Applies to: Commercial Banks, Primary (Urban)/State/Central Co-operative Banks, NBFCs (including Housing Finance Companies) and All-India Financial Institutions.
- Mandatory reporting of Digital Lending Apps (DLAs): via the RBI’s Centralized Information Management System (CIMS) portal to create a transparent public directory of legitimate DLAs.
- Enhanced due diligence: BY the financial entities on Lending Service Providers’ (LSPs) technical capabilities, data privacy, borrower conduct, and regulatory compliance.
- LSP is an agent of a financial entity who carries out digital lending functions on their behalf.
- Disclosures to borrowers: Financial entities and LSPs must disclose key details such as terms and conditions, privacy policies etc. allowing borrowers to make informed choices.
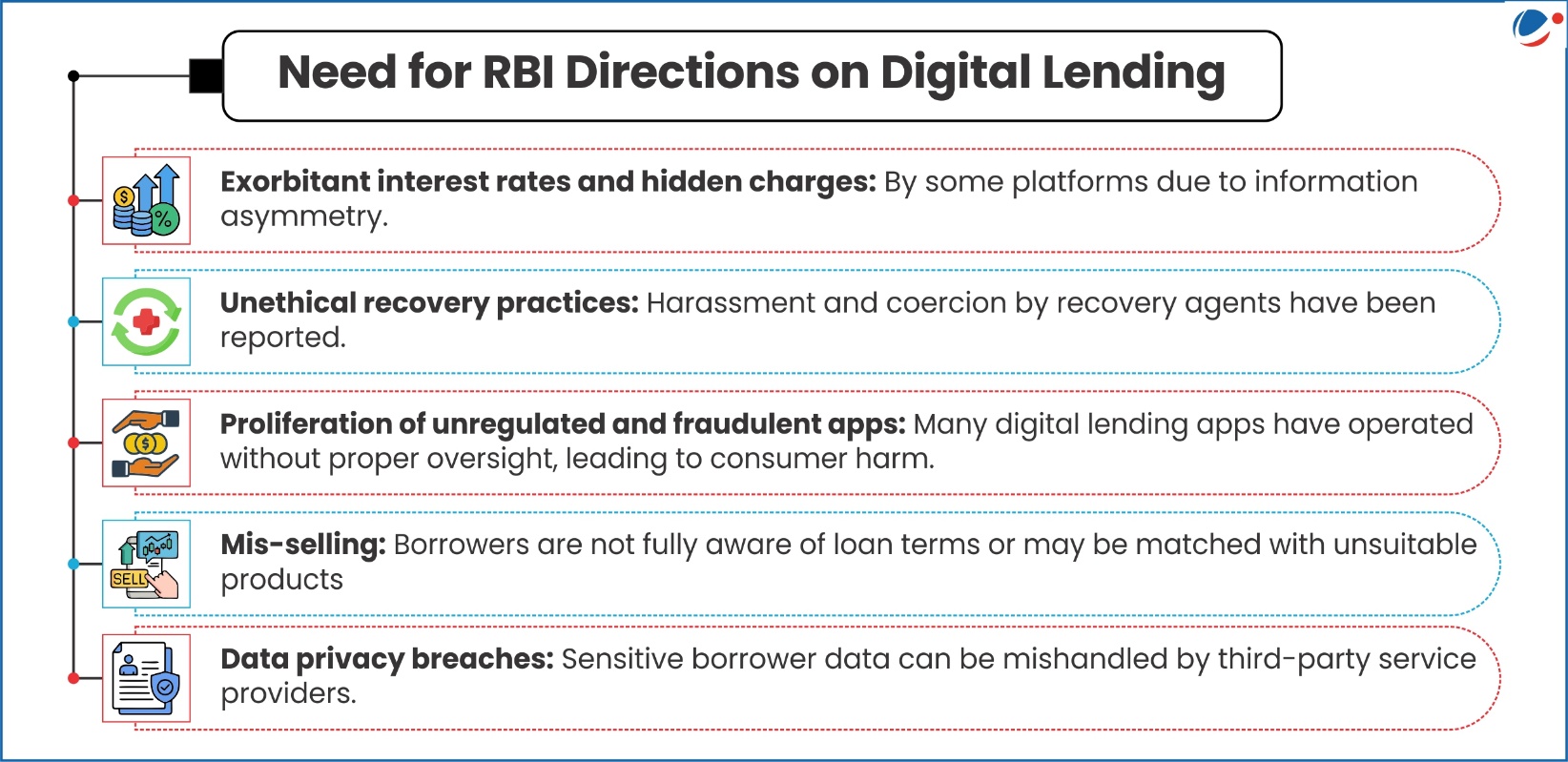
- Grievance redressal Officer: To be appointed by LSPs to deal with digital lending-related complaints and issues.
- Tags :
- Digital Lending
Opinion Trading Platforms
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has cautioned investors against dealing with opinion trading platform.
About Opinion trading platforms
- Concept: These platforms allow participants to earn money by investing in their predictions on any sports, political, weather, or crypto events,
- Participants can bet on any event based on their predictions.
- If the predictions are correct, a participant makes money, and in case the prediction goes wrong they lose.
- Legal Status: not regulated by SEBI because the items being traded are not classified as securities under Indian law.
- Economy: These platforms have registered transaction volumes of over Rs 50,000 crore a year with a user base of more than 5 crore people.
- Tags :
- opinion trading
World Bank Land Conference
India assumed the role of a Country Champion at the World Bank Land Conference 2025.
- During the conference, global attention was drawn towards India’s flagship land management initiatives like SVAMITVA Scheme and Gram Manchitra platform, as models of inclusive, technology-driven rural governance.
- With 68,000 sq. km surveyed and Rs.1.16 trillion worth of land monetized, SVAMITVA stood out as a scalable model for inclusive economic transformation at the global level.
- SVAMITVA aims at establishment of clear ownership of property in rural areas by mapping of land parcels using drone technology.
- Gram Manchitra’s role in promoting climate resilience, infrastructure planning, and convergence of schemes drew appreciation for its applicability in global south context.
- Gram Manchitra is a geospatial planning platform that empowers Gram Panchayats to prepare data-driven, localized development plans.
Efficient Land Management Systems and Economic Growth
- Jobs and Growth: Streamlined access to property facilitate entrepreneurship, expansion, wealth reinvestment and alternate livelihoods.
- Private Capital: Registered property rights provide landowners with collateral access, boosting private credit and investment opportunities.
- Infrastructure Funding: Generate stable government revenue for essential public services and infrastructure.
- Land and property taxes generate just 0.6% of GDP in low-income countries, compared to 2.2% in industrialized nations.
- Urban Management: Help cities plan for growth, protecting public spaces, identify development opportunities, and manage disaster risks.
- Food Security: Improving women’s access to land can increase agricultural outputs by 4%.
- Tags :
- Land Conference
- World Bank Land Conference



