Why in the News?
Odisha government launched a collaborative initiative 'SAHAYOG' to facilitate access to government welfare schemes for the urban poor.
About SAHAYOG Initiative
- Aim: To improve the living standards of the economically backward through various government schemes.
- Objective: Identifying eligible beneficiaries in urban poor communities and connecting them to appropriate schemes through mass awareness, doorstep delivery of services etc.
- In the initial phase, a door-to-door survey will be conducted in 44 urban areas of 8 districts to identify and register the deprived beneficiaries of 13 schemes.
Current Status of Urbanization and Urban Poverty in India
According to the latest World Bank Poverty & Equity Brief,
|
Difference between Urban and Rural poverty
- Access to Basic Amenities: Urban poverty is distinguished by inadequate housing and lack of basic services like sanitation, while rural poor face issues related to security of tenure on land.
- Living conditions: Urban poor face issues of congestion, lack of proper hygiene leading to a higher risk of disease and crime, whereas rural poor face issues related to lack of pucca houses, caste discrimination, etc.
- Psychological impact of poverty: Poverty is more visible in urban areas compared to rural due to greater feeling of relative deprivation and social exclusion. E.g. slums like Dharavi coexisting with skyscrapers in Mumbai.
- Urban poor also face issues like segregation, loneliness and related anxiety. Rural poor face a more culturally institutionalized impact of poverty with stronger linkages to caste or gender.
- Economic structure: Rural economy is primarily dependent on agriculture whereas, urban economy is more diverse and complex. Thus, urban economy provides wider economic opportunities but also makes urban poverty more complex and multi-faceted.
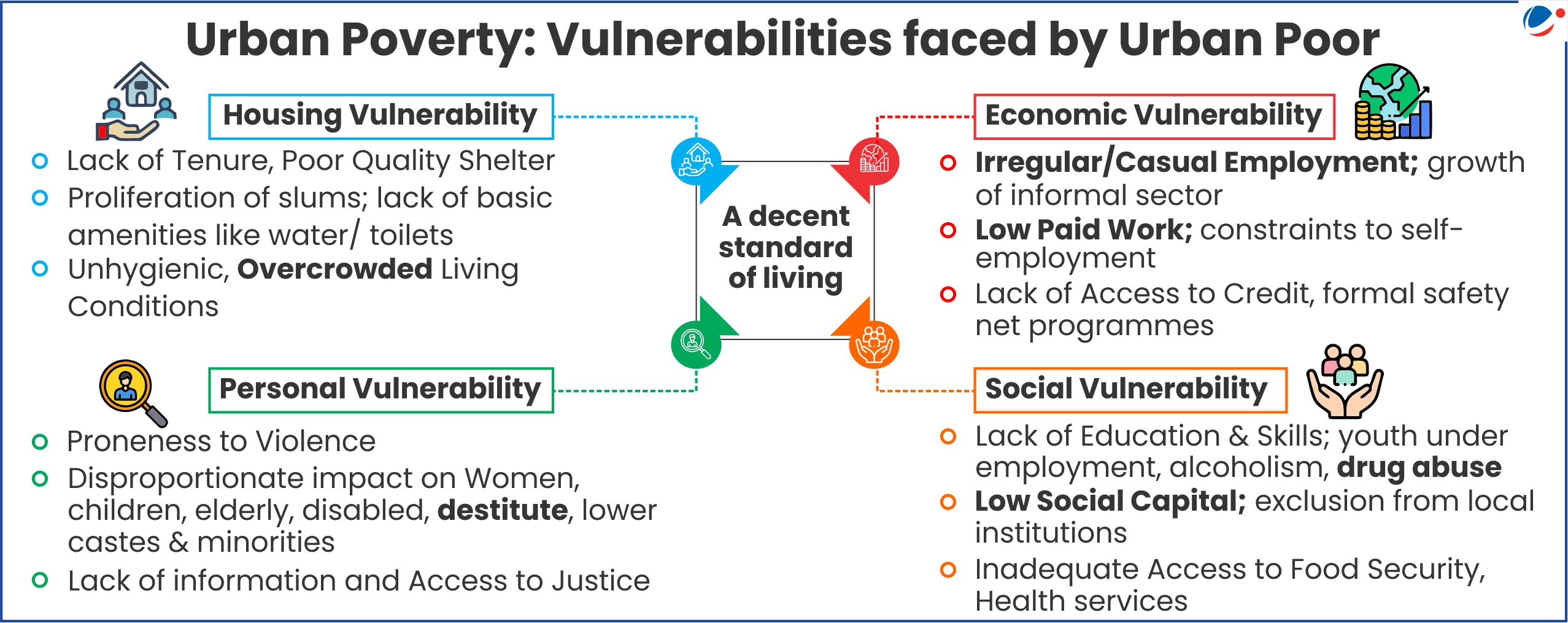
Reasons for persistence of Urban Poverty
- Lack of Planned Urban Development: Haphazard urbanization, rural-urban migration and growing urban population, and lack of accounting for urban poor in policy formulation. E.g. lack of affordable housing projects
- Regional disparity in urbanization: Insufficient development of Tier II and Tier III cities has led to excessive population pressure on megacities like Delhi, Mumbai, etc.
- Inaccessibility to social security: Many poor migrants in urban areas lack proof of residency or identity, which excludes them from government welfare programs and traps them in a cycle of poverty.
- Vicious cycle of poverty: Poverty limits access to opportunities for socio-economic mobility like education, employment etc. which perpetuates inter-generational poverty.
Government Initiatives for eliminating Urban Poverty
- One Nation One Ration Card: Aadhaar-based national ration card portability scheme to ensure food security for all, including internal migrants.
- Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0 (SBM-U 2.0): A sanitation scheme for the construction of Individual Household Latrines (IHHL) for urban households.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U): To provide housing to EWS/LIG and MIG categories including slum dwellers.
- Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana - National Urban Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NULM): To enable urban poor to access gainful self-employment and skilled wage employment opportunities.
- PM Street Vendor's AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi): A special micro-credit facility launched by ministry for providing affordable loans to street vendors.
- Others: Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation 2.0 (AMRUT 2.0), Smart Cities Mission, etc.
Way Forward
- Inclusive urbanization: Decentralize decision-making with people's participation for inclusive urban development planning. Promote mixed-use development and inclusive zoning policies to prevent the formation of ghettos and ensure access to employment opportunities
- E.g., role of self-help groups in slum rehabilitation and redevelopment; Kudumbashree (a women's community network) involved by Kerala in the implementation of the National Urban Livelihoods Mission (NULM).
- Development of Tier-II and Tier-III cities: Promote balanced regional development by incentivizing economic activities in smaller towns and cities to reduce pressure from megacities.
- Improve rural infrastructure and employment opportunities to reduce distressed migration to urban centres.
- Sustainable urbanization: Role of Urban Local Bodies in prioritizing sustainability in planning and program implementation. E.g., Indore's cleanliness drive under SBM.
- Empowerment of urban poor: Encourage skill development, growth of labour-intensive industries and MSMEs through improved access to credit, business development services, and market linkages.
- Targeted delivery of social security programmes: Promoting portability, correcting inclusion-exclusion errors and improving monitoring of scheme implementation.
Conclusion
By 2050, Indian cities are expected to contribute more than 75% of our GDP and about 60% of our Green House Gas emissions. Thus, it is vital to effectively tackle the issue of urban poverty for sustainable development of our urban areas. This will contribute to the goal of 'Viksit Bharat' and make India a $5 trillion economy.





