The technique showcases no toxicological, nutritional, or microbiological issues and has been endorsed by reputed scientific bodies including the American Medical Association.
About Food Irradiation
- It is a physical process in which food and agricultural commodities, in pre-packed form or in bulk, are exposed to a controlled amount of radiant energy to achieve desirable effects.
- E.g., Radiolysis (splitting of water due to interaction with radiation) of water molecules (major constituent of food and cells of insects and pathogens) helps in food preservation.
- Significance: Inhibition of sprouting, delay in ripening, killing of insect pests, parasites, pathogenic and spoilage microorganisms, while preserving the food quality.
- lonizing radiations act through two basic processes
- Primary Processes: Causing Formation of ions or excited molecules by direct deposition of energy.
- Secondary Processes: Involving interaction of products of primary events. They are affected by variables like water content, oxygen, and pH of food.
- Products of primary and secondary processes are called radiolytic products, which cause almost negligible chemical changes in the food.
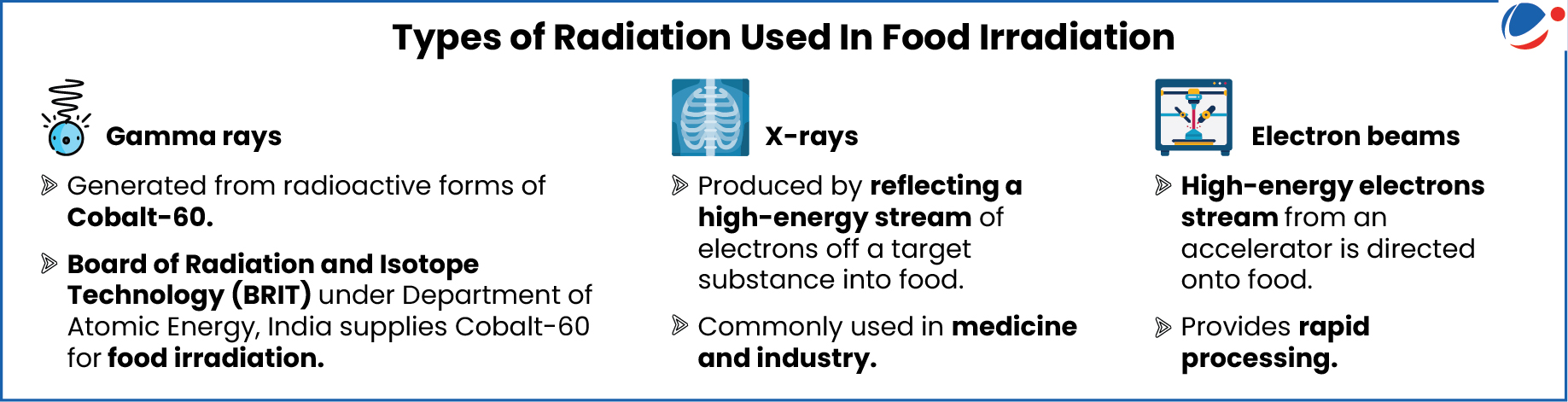
Food Irradiation in India
- Ministry of Food Processing Industries supports setting up of multiproduct food irradiation units under - Integrated Cold Chain & Value Addition Infrastructure (Cold Chain scheme) of Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana (PMKSY).
- As of August 2025, 16 project proposals have been approved for setting up of multi-product food irradiation units, of which 9 are operational.



