Why in the News?
Recently, the Indian rupee's exchange rate against the US dollar has breached the 85 mark. The Rupee faced its sharpest depreciation in last two years.
What is Rupee Depreciation?
- It refers to the decline in the value of the Indian Rupee (INR) relative to a foreign currency, typically the US Dollar (USD) or other major global currencies.
- Exchange Rate: It is the price of one currency in terms of other.
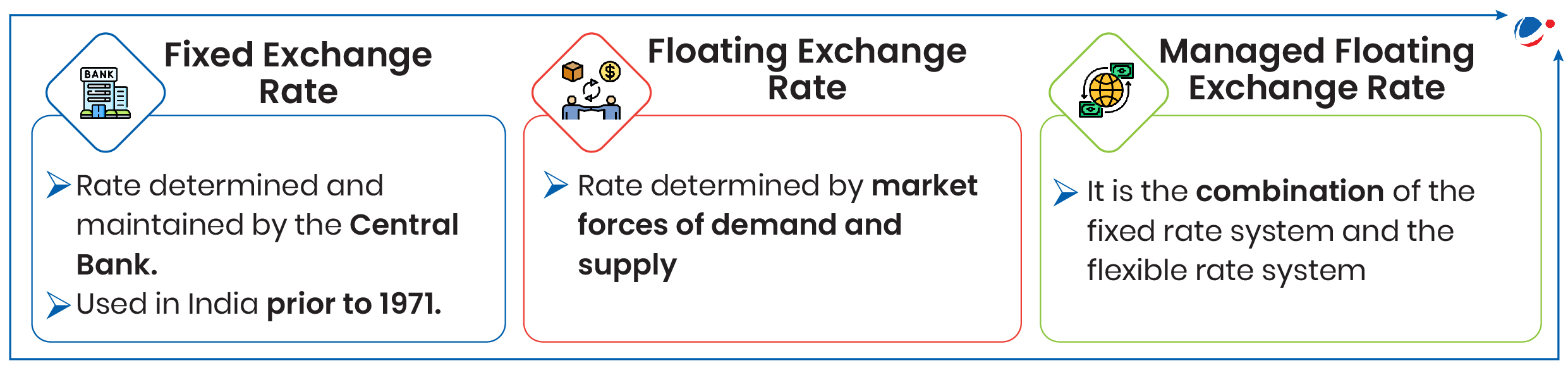
Note: Currently, India follows "Managed Floating Exchange Rate " in the sense that there is a currency market and the exchange rate is not visibly administratively determined. However, RBI actively trades on the market, with the stated goal of "containing volatility", and influencing the exchange rate.
Key Factors Responsible for Rupee's Depreciation
- Confidence in Central Bank: Modern generations of currency crises seem to be triggered by markets that conduct value at risk assessments of the central bank's balance sheet. This affects the investor confidence.
- Illiquidity: It arises out of short term foreign currency debt becoming larger than liquid foreign currency assets.
- Inflation: Higher inflation in India compared to trading partners erodes purchasing power of Indian Rupee and adversely affects the exchange rate.
- Monetary policy: RBI's interest rate decisions and foreign exchange interventions impact the rupee's strength.
- RBI's market operations to buy USD to maintain sufficient Forex reserve also affects exchange rate of the INR.
- Capital Outflows: Foreign investors pulling out funds from Indian markets reduce Forex reserves, leading to depreciation.
- The recent depreciation can be significantly attributed to the outflow of Foreign Portfolio Investments.
- Trade Deficit: When imports exceed exports, demand for foreign currency rises, weakening the rupee.
- India's traditional demand for high-value imports such as crude oil and gold boosts demand for the dollar and weakens the rupee.
- Global economic factors: High crude oil prices, US Federal Reserve interest rate hikes, or global recessions can also weaken the rupee.
Impact of Rupee's Depreciation
Positive Impact | Negative Impact |
|
|
Way Forward
- Short-term measures
- RBI's market operations to sell dollars, Currency swap agreements with other countries, Monetary Policy Adjustments to attract foreign investment, import rationalization to restrict non-essential imports, etc.
- Long-term measures
- Diversifying trade payments: Boosting forex reserves and diversifying trade payments (e.g., using INR for international trade) to strengthen the rupee. (Economic Survey 2022-23)
- Export promotion: It can result in reduction of the current account deficit to improve rupee stability. (Rangarajan Committee on Balance of Payments, 1993)
- Strengthening of the Free Trade Agreements, improving ease of doing business to attract global companies, etc., can help enhance India's exports.
- Others: Fiscal Prudence, inflation control, reducing energy import dependence, etc.




