Recently, RBI notified the calendar for issuance of T-Bills, one of the types of Government Securities (G-Sec).
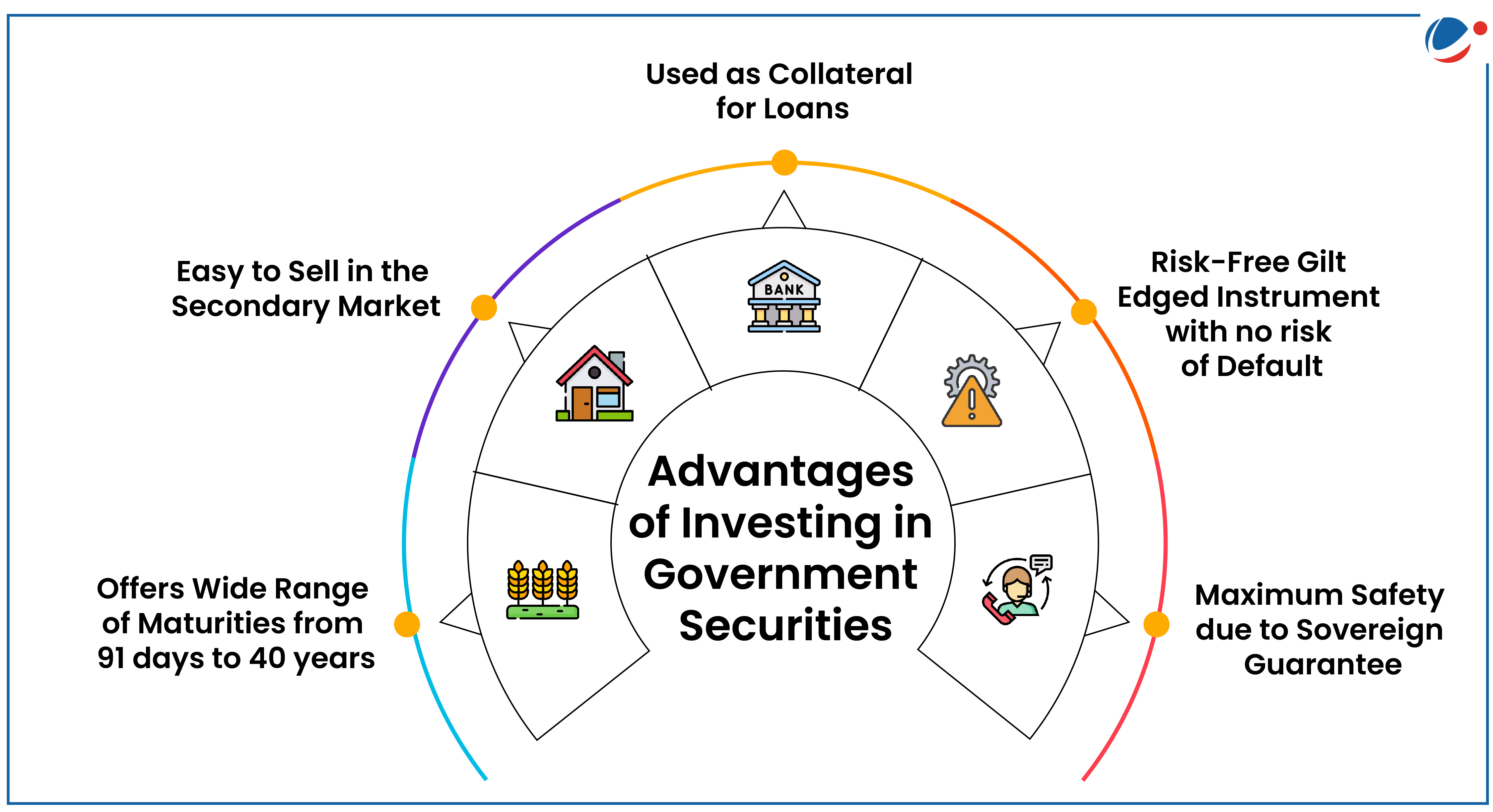
Government Securities Market in India
- About: It is a tradeable instrument issued by the Central or State Governments acknowledging the Government’s debt obligation.
- Issued by: RBI through an auction on its electronic, E-Kuber platform.
- RBI’s Public Debt Office (PDO) acts as its registry / depository.
- Major Participants: Commercial banks, Primary Dealers, Insurance companies, co-operative banks, regional rural banks, mutual funds, retail investors (non-competitive bidding section), etc.
Types of G-Sec
- Short term with original maturities less than a year. E.g., T-Bills
- Treasury Bills (T-bills)
- Money market and short term debt instruments issued by the Government of India (GOI)
- Zero coupon securities and pay no interest.
- Issued at a discount and redeemed at the face value at maturity.
- Issued in 3 tenors, namely, 91 day, 182 day and 364 day.
- Cash Management Bills (CMBs)
- Short-term (maturities less than 91 days) instrument introduced by the GOI in 2010 to meet the temporary mismatches in its cash flows.
- Treasury Bills (T-bills)
- Long Term, with original maturity of one or more year. E.g., Government Bonds or Dated Securities.
- Dated G-Sec: They carry a fixed or floating interest rate paid on the face value, on half-yearly basis, with maturities ranging from 5 to 40 years.
- SDLs: Dated securities issued by State Governments with half-yearly interest payments.
- NOTE: In India, the Central Government issues both T-Bills and bonds or dated securities while the State Governments issue only bonds or dated securities, called the State Development Loans (SDLs).







