- Global Environment Facility (GEF)-funded Financing Agrochemical Reduction and Management (FARM) Programme launched.
- Key highlights of FARM
- About: One of the first such concerted efforts on a global scale, is a $379 million initiative that will realign financial incentives to:
- Prevent the use of harmful inputs in food production.
- Encourage the adoption of low and non-chemical alternatives.
- Tenure: 5 Years
- It will support:
- Government regulation to phase out Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) -containing agrochemicals and agri-plastics and adopt better management standards.
- Strengthening banking, insurance and investment criteria to improve the availability of effective pest control, production alternatives and trade in sustainable produce.
- Members: India, Ecuador, Kenya, Lao PDR, the Philippines, Uruguay and Vietnam.
- Implementing Agencies: Led by UNEP and implemented by the ADB, UNDP, and UNIDO with execution carried out in-country by FAO.
- About: One of the first such concerted efforts on a global scale, is a $379 million initiative that will realign financial incentives to:
- Significance of FARM Initiative:
- Nearly 4 billion tons of pesticides and 12 billion kg of agricultural plastics are used every year which has a harmful impact on health and environment.
- Highly hazardous pesticides and mismanaged agricultural plastics release toxic POPs (chemicals which do not break down in the environment and contaminate air, water, and food).
- However, currently farmers have little incentive to adopt better practices as these chemicals are generally cheaper than sustainable alternatives.

- India's First City-Specific Zero Carbon Buildings Action Plan (ZCBAP) launched in Nagpur.
- Zero carbon buildings are buildings that improve their lifecycle environmental performance through measures that reduce embodied, operational and end-of-life GHG emissions without compromising visual and thermal comforts.
- Nagpur’s ZCBAP aims to achieve net-zero carbon emissions in all buildings by 2050, contributing to India's 'net zero by 2070' target.
- ZCBAP in Nagpur has been developed jointly with implementing partners of Zero Carbon Building Accelerator (ZCBA) project.
- ZCBA project was launched by World Resources Institute (WRI) in 2021 along with its global partners.
- Nagpur is one of six global cities (other in Kenya, Costa Rica, Turkey, and Colombia) where ZCBA project is being implemented.
- Need for ZCBAP:
- India’s building related Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions have more than doubled from 2000 to 2017.
- Over next 20-30 years, GHG emissions from India’s steel and cement industry are estimated to increase by nearly three and six times respectively.
- Brick kilns are another major source of carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, Nitrous Oxide (NOx), and other particulate emissions.
- Nagpur’s ZCBAP builds upon national policy frameworks and initiatives supporting building decarbonization, which include:
- India’s Nationally Determined Contributions
- India’s Long-Term Low-Carbon Development Strategy
- Energy Conservation Building Code, 2017
- Green Building Rating Systems such as Indian Green Building Council (IGBC), Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment (GRIHA) and
- Eco-Niwas Samhita 2018
- Ethanol 100 fuel was launched by the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas.
- About Ethanol 100:
- A cleaner and greener alternative to gasoline
- It is a blend of 92 to 94 percent ethanol, 4 to 5 percent motor spirit to provide colour to flame and 1.5 percent Co-solvent higher saturated alcohol.
- Significance:
- It produces lower emissions of greenhouse gases, a reduction by around 63% on well to wheel basis.
- Its high-octane rating makes it suitable for high-performance engines, ensuring enhanced efficiency and power output.
- Significant reductions in foreign exchange savings.
- The 2024 Tyler Prize for Environmental Achievement will be awarded to Johan Rockstrom for his work on the Planetary Boundaries framework.
- About Planetary Boundaries framework
- First published in 2009, the Planetary Boundaries integrate nine systems that determine the functioning and the state of the planet.
- Nine planetary boundaries include Climate Change, Biosphere Integrity, Land-System Change, Freshwater Change, Biogeochemical Flows, Novel Entities, Stratospheric Ozone Depletion, Atmospheric Aerosol Loading, and Ocean Acidification.
- They provide life-support to humans and humanity is well outside of safe operating space on first six planetary boundaries.
- RCPs have emerged as one of the latest approach to determine emission scenario.
- About RCPs
- RCPs describe four different 21st century pathways of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and atmospheric concentrations, air pollutant emissions, and land use.
- Developed using Integrated Assessment Models (IAMs) as input to a wide range of climate model simulations to project their consequences for climate system.
- These climate projections, in turn, are used for impacts and adaptation assessment.
- European Parliament adopted NRL to restore 20% of EU’s land and sea.
- NRL will restore degraded ecosystems in all member states, help achieve the EU’s climate and biodiversity objectives, and enhance food security.
- It is a key element of the EU Biodiversity Strategy, which calls for binding targets to restore degraded ecosystems.
- Objective: Enable long-term and sustained recovery of biodiverse and resilient nature.
- Implementation: EU countries are expected to submit National Restoration Plans to the Commission within 2 years of the Regulation coming into force.
- Researchers finds that Bioenergy Trigeneration (BioTRIG) becomes technically feasible for pyrolysis.
- Pyrolysis is a process of thermal decomposition of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. (“Pyro-“ means “fire” and “lysis-“ means “loosening” in Greek, roughly translating to loosening with fire.)
- Pyrolysis can convert carbonaceous materials like waste biomass (crop residues, food waste and animal manure) into biochar and bio-oil and generate syngas.
- These pyrolysis products (bioenergy trigeneration) can help overcome three major challenges of rural communities in India -
- Biochar can improve soil quality.
- Bio-oil can be used for electricity generation.
- Syngas can be used as a clean efficient cooking fuel.
- Earth Hour” is set to be observed on March 23 from 8.30pm to 9.30pm (IST).
- Earth Hour
- Earth Hour was famously started as a lights-out event in Sydney, Australia in 2007.
- It is a global event observed annually on the last Saturday of March.
- It is organized by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF).
- It is symbolic to raise awareness about climate change and promote energy conservation.
- Beyond the hour, Earth Hour inspires people to take further action for a sustainable future.
- Belgium has become the first country in Europe to recognize ‘ecocide’ as a national as well as an international crime.
- Ecocide:
- It means unlawful or wanton acts committed with knowledge that there is a substantial likelihood of severe and either widespread or long-term damage to the environment being caused by those acts. Ex: Deforestation, Ocean damage etc.
- Term was invented by American Biologist Arthur Galston in 1970.
- India is yet to make it an offense.
- Communities, particularly those in western Rajasthan, are concerned about the state’s proposal to classify orans (sacred groves) as deemed forests.
- As per the directives of Supreme Court, Oran, Dev-vans and Rundhs as forest lands will be given the status of deemed forest.
- A sacred grove comprises patches of natural vegetation ranging from a few trees to several acres that are dedicated to local deities or tree spirits.
- About Deemed Forest
- The concept of deemed forests has not been clearly defined in any forest law.
- In the Godavarman Thirumalpad (1996) case, SC brought in the concept of ‘deemed forests,’.
- It means an area that wasn’t officially classified as forest by the government but looked like it.
- Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change notified Living Animal Species (Reporting and Registration) Rules, 2024.
- Rules were notified under Section 63 of Wild Life (Protection) Act (WPA), 1972 for the purpose of Section 49M of the WPA, 1972.
- Section 49 M provides for registration of possession, transfer, and birth and reporting of death of living scheduled animal species which are listed in Appendices of CITES or Schedule IV of WPA, 1972.
- Section 49M was added through Wild Life (Protection) Amendment Act, 2022.
- Key highlights of Rules
- Application for registration of possession: Mandatory electronic registration for any possession of any animal species within 6 months.
- Reporting and registration of birth: Report birth of an offspring of animal species and apply for registration within a period of 7 days.
- Reporting and registration of transfer within 15 days.
- Maintenance of stock for people involved in captive breeding through regular health check-up of animals, inform any escape of the animal species, etc.
- Wild Life (Protection) Amendment Act, 2022 and CITES
- 2022 Amendment sought to implement CITES.
- Schedule IV of the WPA includes specimen of Flora and Fauna listed under CITES.
- It also provides for management authority to grants export or import permits for trade of species.
- 2022 Amendment sought to implement CITES.
- According to latest survey, there are around 7,396 Golden langurs in India.
- About Golden langur
- Protection Status:
- IUCN: Endangered
- CITES: Appendix I
- Wildlife Protection Act: Schedule-I
- Characteristics:
- Belong to a large group of Old World monkeys called the colobines (leaf-eating primates having a ruminant-like multi-chambered stomach).
- Coat colour varies seasonally becoming cream colored in summer and dark golden in winter.
- They are diurnal and arboreal in nature and live in troops (3-15).
- Habitat: Endemic to subtropical and temperate broadleaf forests in Assam (Brahmaputra River Valley) and Bhutan.
- Protection Status:

- Named after President of India, by Zoological Survey of India M. droupadi is a new marine species of head-shield sea slug discovered from West Bengal and Odisha coast.
- It shares habitat with Melanochlamys bengalensis which discovered in 2022, but differs morphologically.
- M. droupadi is smaller and has mottled brown to black colouration with a ruby red spot on the posterior shield.
- The sea slugs are rapid hunters.
- They feed upon mobile prey such as other shelled and unshelled sea slugs, roundworms, marine worms and small fishes.
- Scientists unveiled the first in-depth study of Earth’s magnificent desert star dunes revealing the internal structure.
- The study focused on a star dune in Erg Chebbi (eastern Morocco) called Lala Lallia, meaning “highest sacred point”.
- About Star Dunes
- Formed in areas with complex wind regimes, which means winds blowing from different directions.
- They make up just under 10% of the dunes in Earth’s deserts and are the tallest ones.
- Earth's largest star dunes are found in the Badain Jaran desert (China).
- They also have been spotted on Mars and Saturn’s moon Titan.
- Researchers from IIT Madras developed a method for treating bauxite residue (known as Red Mud) using phosphoric acid to extract valuable materials from it.
- Some such materials like ceramic have dielectric and optical properties, with potential applications in electronic components and energy storage.
- Red Mud is a byproduct of aluminium production.
- It contains heavy metals such as arsenic, lead, cadmium, chromium, vanadium and mercury.
- Its high alkalinity makes it extremely corrosive and damaging to soil and life forms.
- Researchers discovered four gigantic seamounts in the deep sea off the coast of Peru and Chile.
- About Seamounts
- A seamount is an underwater mountain with steep sides rising from the seafloor.
- Most seamounts are remnants of extinct volcanoes and are typically cone shaped.
- Seamounts with large flat summits are called guyots.
- Seamounts are found in every world ocean basin.
- Seamounts function as oases of life or biological hotspots with higher species diversity and biomass on and around it.
- World’s highest seamount is Hawaii's dormant volcano Mauna Kea.
- International Commission on Stratigraphy rejected proposal to declare the start of the Anthropocene Epoch in geologic time.
- Anthropocene Epoch is an unofficial unit of geologic time.
- It describes the most recent period in Earth’s history when human activity started to have a significant impact on Earth’s climate and ecosystems, particularly since industrialization.
- Current epoch is called the Holocene which began 11,700 years ago after the last major ice age.
- Currently, on geological time scale, we are living in the Phanerozoic Eon, Cenozoic Era, Quaternary Period, Holocene Epoch, and the Meghalayan Age.
- Border Road Organisation has connected strategically important road from Manali (Himachal Pradesh) to Leh (Ladakh) through Darcha and Nimmu on Kargil–Leh Highway.
- Road is not only shorter, but crosses only one pass—Shinkun La (approx. 16,500 feet).
- Shinku La Pass connects Lahaul and Spiti in Himachal Pradesh with Zanskar Valley in Kargil, Ladakh.
- This will result in road having all weather connectivity to Ladakh region.
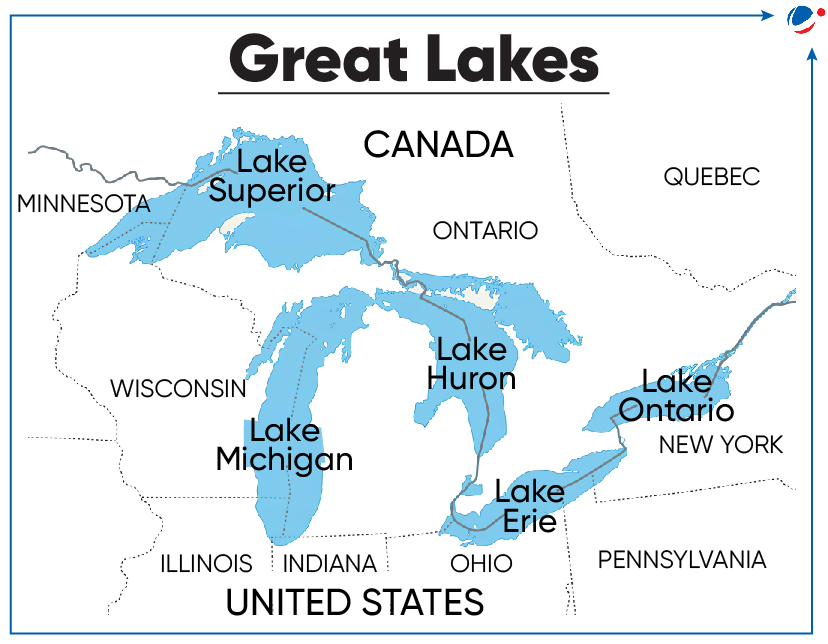
- North America’s Great Lakes have recorded significantly below-average ice cover for the second consecutive year in a row.
- Great Lakes
- Great Lakes — Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie and Ontario — form the largest fresh surface water system on Earth.
- Except for Lake Michigan, the lakes provide a natural border between Canada and United States.
- Water in the Great Lakes flows from Lake Superior, via Lake Huron, Lake Michigan, Lake Erie, into Lake Ontario, and into the Atlantic Ocean through the Saint Lawrence River.