Why in the news?
India has conducted the first human clinical trial of gene therapy for Haemophilia A (FVIII deficiency) at Christian Medical College (CMC) Vellore (Tamil Nadu).
About Gene Therapy
- Definition: It is a technique that uses a gene(s) to treat, prevent or cure a disease or medical disorder.
- In most gene therapy, a normal gene is inserted into the genome to supplement an abnormal disease-causing gene and restore the target cell to a normal state.
- Vectors: Vector refers to the carrier used for delivering the therapeutic gene to the patient’s target cells. It is of two types:
- Viral vector (viruses like adenoviruses, retroviruses, adeno-associated viruses, etc. are used).
- Non-Viral vector where in chemical and physical methods are used to insert DNA into cells.
- Particle bombardment, use of liposomes, polymers, Nanoparticles etc. are used in this method.
- Application: Both inherited genetic diseases (e.g., haemophilia and sickle cell disease) and acquired disorders(e.g., leukaemia) could be treated with gene therapy.
Methods of Gene therapy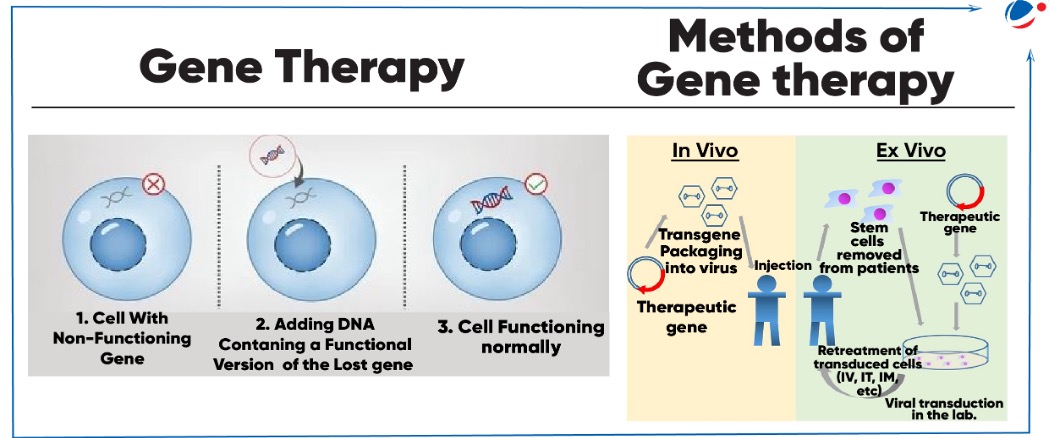 NOTE: National Guidelines for GTP Development and Clinical Trials (2019) issued by Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and ICMR broadly specifies the ethical, scientific, regulatory procedures for conducting clinical trial on gene therapy products (GTP) in India. |
Types of Gene Therapy
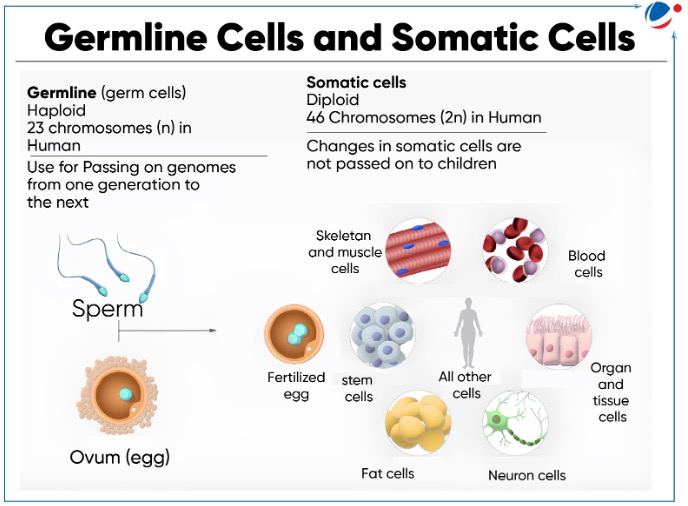
- Germline gene therapy: In germline gene therapy, the Germline Cell (egg or sperm) are modified by the introduction of functional genes, which are integrated into the genome.
- Somatic cell gene therapy: In this, therapeutic gene are transferred to a patient’s somatic cells (cells other than germline cells). Any modification and any effects are restricted only to that patient and are not inherited by future generation.
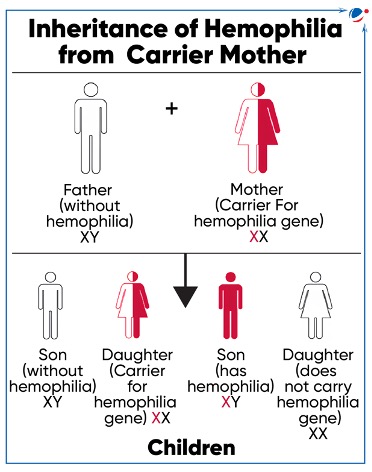
About Haemophilia
|





