Why in the news?
Various initiatives have been taken for the expansion and modernization of PACS.
More on the news
- Initiative for expansion: Foundational stone for an additional 500 PACS for construction of godowns & other agri-infrastructure was laid down.
- Initiatives for modernization of PACS:
- Project for computerization in 18,000 PACS across the country was inaugurated.
- Under ‘centrally sponsored project for computerisation of PAC’ scheme, government aims to computerise 63,000 functional PACS. This will help in improving their operational efficiency, ensuring speedy disbursal of loans, lowering of transaction costs and increasing transparency.
- National Cooperative Database (NCD) was inaugurated by Ministry of Cooperation.
- NCD provides all information about the cooperative sector like number of co-operatives in states/UTs.
- Project for computerization in 18,000 PACS across the country was inaugurated.
About PACS
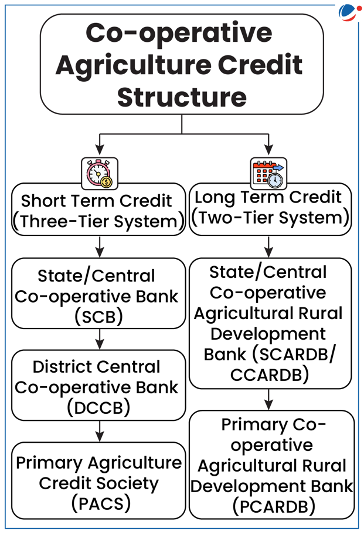
- Definition: PACS are the grassroot level arms of short-term co-operative credit structure (refer to infographics).
- Regulation:
- PACS are registered under Cooperative Societies Act and are administered by concerned State Registrar of Cooperative Societies (RCS).
- SCBs/DCCBs are also registered under provisions of State Cooperative Societies Act of State concerned and are regulated by RBI. However, PACS are outside purview of Banking Regulation Act, 1949 and are not regulated by RBI.
- PACS are registered under Cooperative Societies Act and are administered by concerned State Registrar of Cooperative Societies (RCS).
- Refinancing: They are refinanced by NABARD through DCCBs and SCBs.
- Functions:
- Gives short-term credit loans and collects repayment from rural borrowers.
- They can also provide other input services, like seed, fertilizer, and pesticide distribution to member farmers.
- Significance: PACS play a key role in financial inclusion.
- PACS account for 41 % of the KCC loans given by all entities in the Country and 95 % of these KCC loans through PACS are to the Small and Marginal farmers (2022).
- Current Status: There are more than 65000 functional PACS across country.
Issues faced by PACS
- Infrastructure: Absence of digital infrastructure, such as computerized accounting systems, poor access to internet connectivity limits their ability to streamline operations and also hampers public trust in them.
- Financial: PACS suffer from inadequate capital, low levels of deposits, and high non-performing assets (NPAs).
- Debt waiver schemes and interest subvention schemes also have adverse impact on balance sheet of PACS.
- Human resource: Lack of trained staff and insufficient managerial skills among members of PACS hinders their functioning.
- Governance: PACS are managed by a body elected from local village groups which results in political Interference.
- Other governance issues, such as lack of transparency, and inadequate accountability mechanisms have also undermined the effectiveness of PACS.
- Regional disparity: PACS are largely concentrated in western and southern states (Maharashtra, Gujarat, Karnataka etc.).
Initiatives to strengthen PACS
|
Way Forward
- Encourage adoption of technology: Implementation of Common Accounting System (CAS) and Management Information System (MIS), establish common hubs that can provide technological and other support services to PACS.
- Also, incentivize PACS for promoting adoption of mobile banking, and e-governance platforms, etc.
- Financial strengthening: Introduced a risk-based lending model and implement effective recovery measures to address NPA issue.
- Enhance capital base of PACS through access to external funding sources, diversifying their business portfolio, etc.
- Human Resource: Implement capacity-building programs, provide better compensation and career progression opportunities to skilled staff to retain them.
- Improving governance:
- Regular audits, and strict disclosure norms to ensure transparency and accountability.
- Implement measures to insulate PACS from undue political influence and ensure their autonomous functioning.






