Why in the news?
An incident in the Red Sea has resulted in damage to three submarine cables-Asia-Africa-Europe-1, Europe India Gateway, and Tata Global Network.
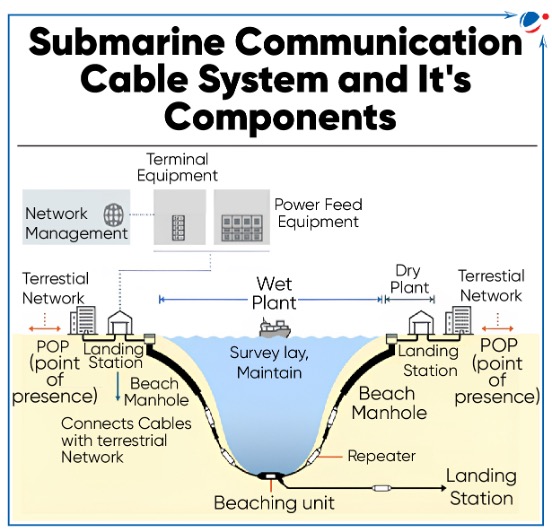
About SMCs
- SMCs are fibre optic cables laid on the ocean floor that connect countries across the world to provide internet and telecommunications.
- They are laid using ships that are modified specifically for this purpose.
- Significance:
- International cables carry around 99% of the world's international Internet traffic.
- United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) in 2010 described SMCs as a "critical communication infrastructure".
- Other threats to SMCs: Fishing and anchoring; Environmental factors like earthquakes, Damage by marine animals, etc.
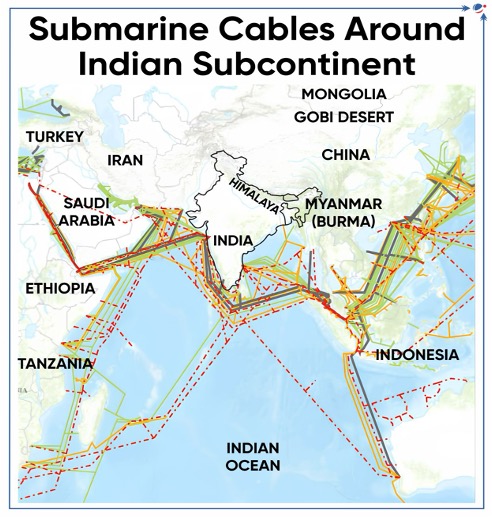
SMC connectivity in India
- India has 17 International SMCs, landing at 14 Cable Landing Stations (CLS) in 5 cities near the coast.
- Mumbai and Chennai have the maximum concentration of SMCs.
- India also has domestic submarine cables such as:
- Chennai-Andaman and Nicobar Island Cable (CANI) connecting Port Blair along with seven other Islands of Andaman & Nicobar
- The Kochi-Lakshadweep Island (KLI) cable system for a direct communication link between Kochi and 11 Islands of Lakshadweep.
- Regulation: Department of Telecommunications (DoT) issues International Long-Distance (ILD) licenses.
- ILD licensees, with prior approval of DoT, are authorized to set up their CLS and to lay submarine cables in India.
 Internet Service Licensees under Unified license is also allowed to install operate and commission International Internet Gateway using submarine cable as medium.
Internet Service Licensees under Unified license is also allowed to install operate and commission International Internet Gateway using submarine cable as medium.
About Optical Fibre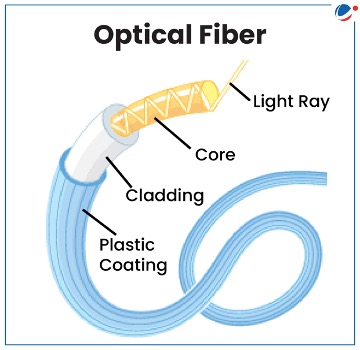
|



