Why in the news?
Recently, core-loading process in the indigenous Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR) was initiated at Madras Atomic Power Station in Kalpakkam, Tamil Nadu.
More on news
- PFBR has been designed and constructed indigenously by Bharatiya Nabhikiya Vidyut Nigam Ltd or BHAVINI with significant contribution from more than 200 Indian industries.
- Core loading is the process of placing nuclear fuel assemblies inside the core of a nuclear reactor.
- The completion of core loading will effectively mark the first approach to ‘criticality’.
- Criticality means the initiation of a self-sustaining nuclear fission reaction that will eventually lead to the generation of power by the 500-megawatt electric (MWe) FBR.
Bharatiya Nabhikiya Vidyut Nigam Ltd or BHAVINI
|
Thorium reserves in India
|
What is Fast Breeder Reactor?
- Fast Breeder Reactor (FBR) is a nuclear reactor that uses fast neutron to generate more nuclear fuel than they consume while generating power.
- FBR will use Uranium-Plutonium Mixed Oxide (MOX) fuel.
- The Uranium-238 “blanket” surrounding the fuel core will undergo nuclear transmutation to produce more fuel, which is why they are termed "breeders."
Significance of FBR
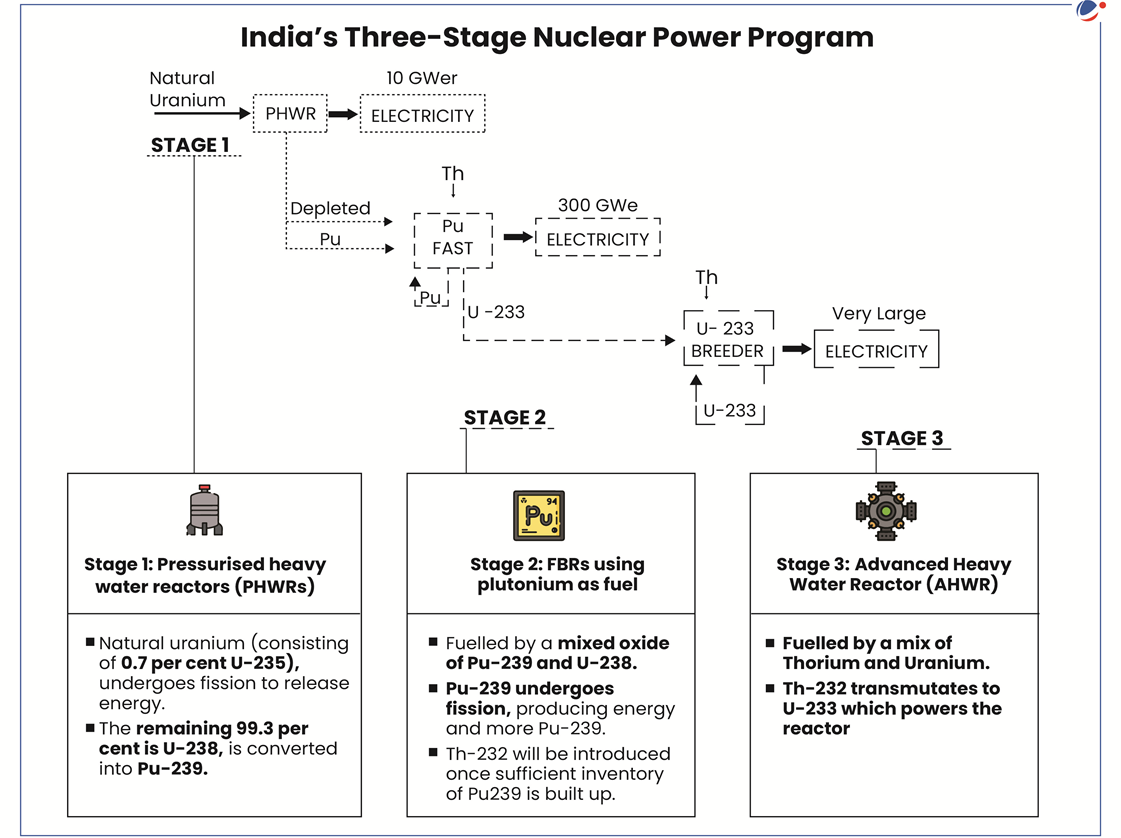
- Beginning of Stage 2 of nuclear programme: The operationalisation of PFBR will mark the start of stage II of India’s three-stage nuclear power programme.
- Paves way for third stage: In FBR, Thorium-232(Th-232) will also be used as blanket.
- By transmutation (conversion of one element to another), Thorium will create fissile U-233 which will be used as fuel in the third stage.
- FBR is thus a steppingstone for third stage of nuclear power program paving the way for the eventual full utilisation of the country’s thorium reserves.
- Technological advancement: Once commissioned, India will be second country after Russia to have a commercial operating FBR.
- China has a small programme on fast breeders; programmes in countries such as Japan, France, and the United States were shut down amid safety concerns.
- Reduced waste: As FBR uses the spent fuel from the first stage, it will also lead to significant reduction in nuclear waste, thereby avoiding the need for large geological disposal facilities.

India’s 3 stage Nuclear Power Programme
- India holds only about 2-3% of the world's uranium reserves, but it possesses one of the largest shares of global thorium reserves.
- Dr Homi J Bhabha, father of India’s nuclear programme, therefore, devised a three-stage nuclear power programme in 1950s to make the most of India's limited uranium reserves and abundant thorium reserves.
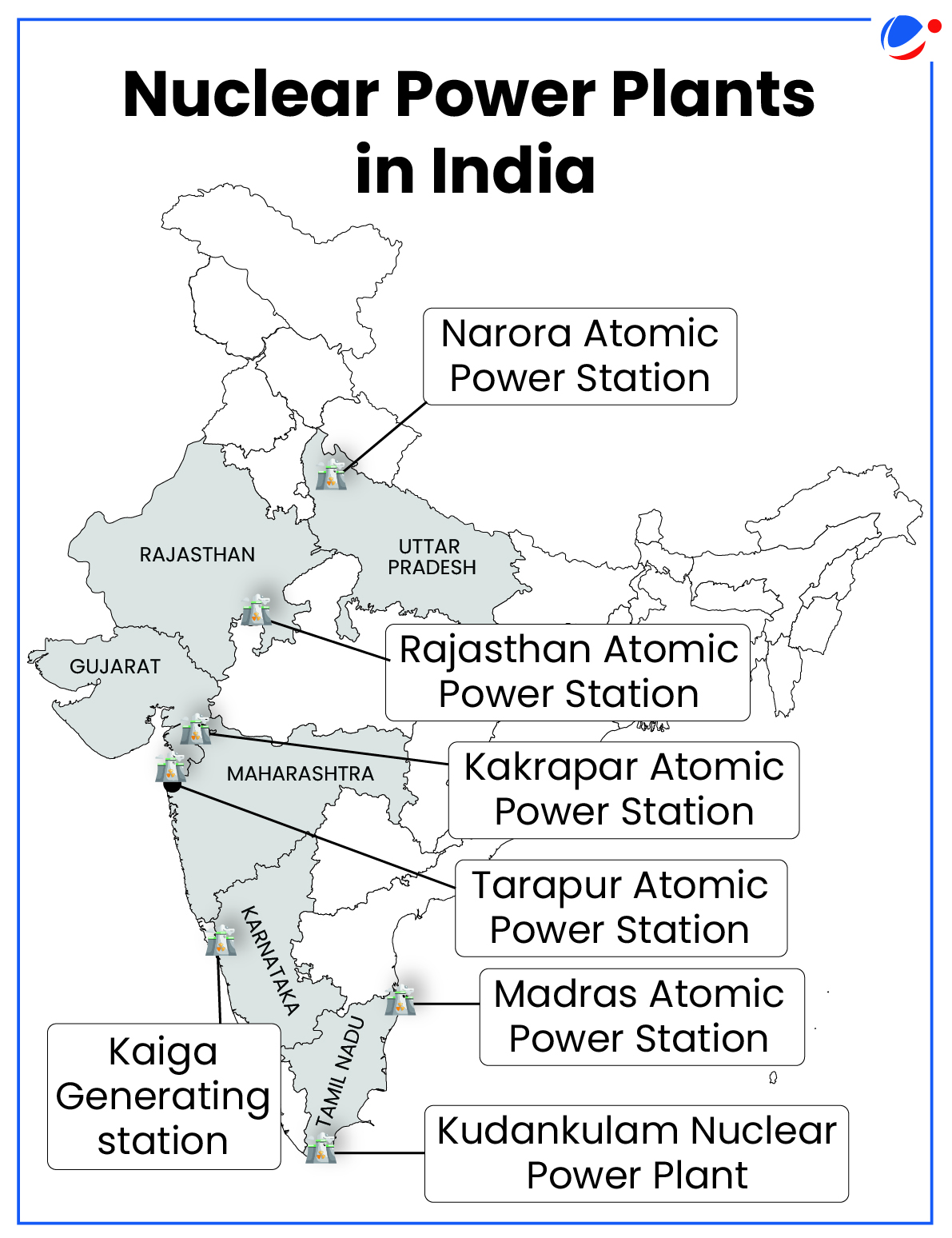 Nuclear Power generation in India
|
Related news: Nuclear Energy Summit
|






