Why in news?
During his visit to Bhutan, the Prime Minister of India was conferred the "Order of the Druk Gyalpo", the highest civilian honor in Bhutan.
More on News
- The "Order of the Druk Gyalpo" award recognizes Indian Prime Minister's contribution to strengthening India-Bhutan friendship and his people centric leadership.
- It also honors India's rise as a global power.
- Indian PM is the first foreign leader to be given this prestigious award.
- Other key developments during the visit:
- India will provide Rs.10,000 crore as financial support to Bhutan over next five years to bolster cooperation in areas like energy, space etc.
- MoUs to establish two rail links including Kokrajhar-Gelephu and Banarhat-Samtse to improve connectivity.
- Both sides look forward to commissioning of 1020 MW Punatsangchhu-II hydropower project in 2024.
Importance of Bhutan for India
|
About the country- Bhutan (Capital: Thimpu)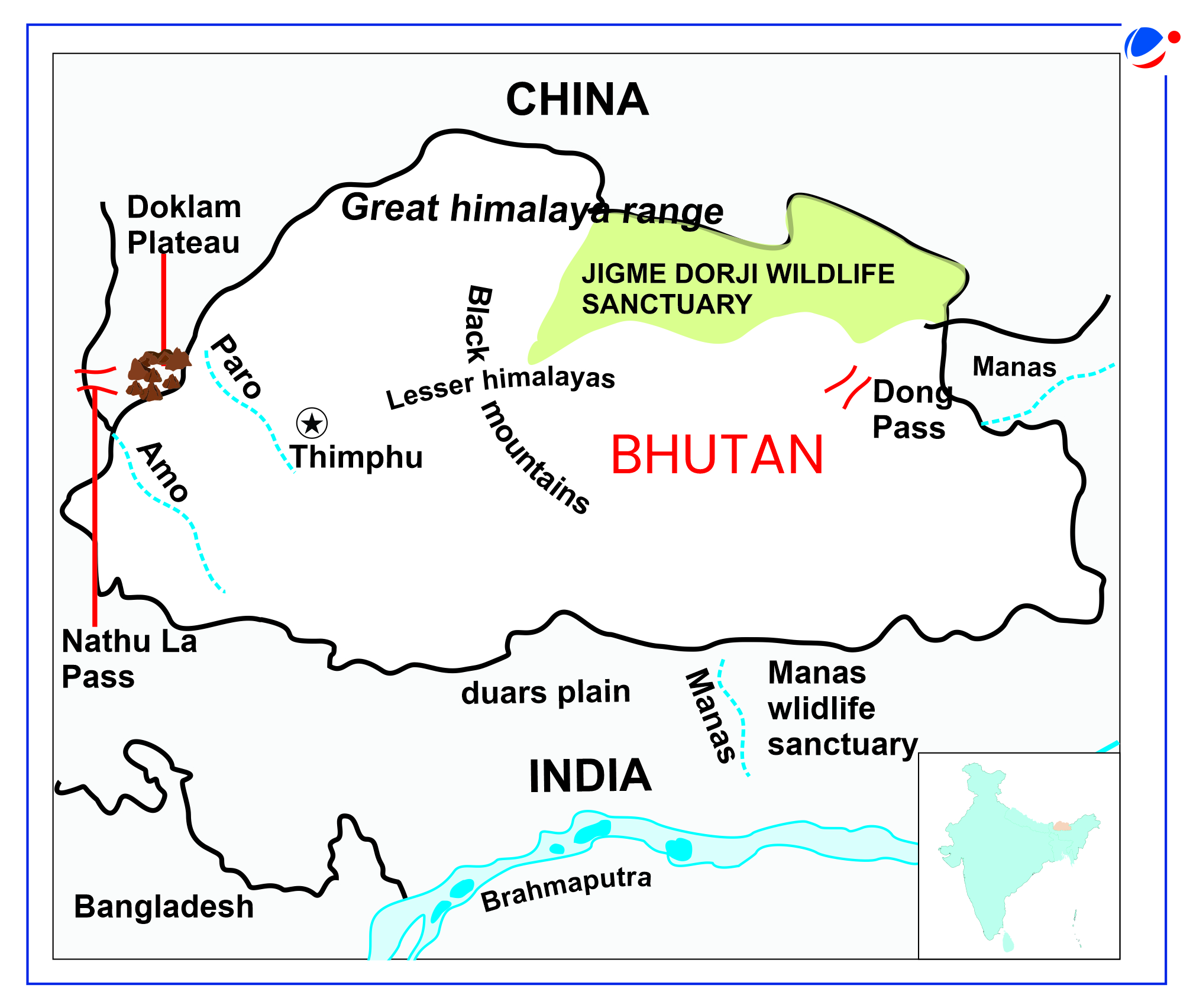
|
Areas of Cooperation between India and Bhutan
- Diplomacy: The basic framework of the relationship is the Treaty of Friendship and Cooperation signed in 1949, which was renewed in 2007.
- Trade:
- India is Bhutan's top trade partner both as an import source and as an export destination, with the balance of trade in India's favour.
- India is the leading source of investments in Bhutan, comprising 50% of the country's total FDI.
- Trade, Commerce, and Transit Agreement (2016) establishes a free trade regime between the countries.
- Development Partnership:
- Bhutan has been the biggest beneficiary of India's external aid in the budget for 2023-24.
- Bhutan has decided to become a 'high-income' nation by 2034. India committed to stand for 'Brand Bhutan' and 'Bhutan Believe'.
- Connectivity: Bhutan is planning to build an international city- Gelephu Mindfulness City- that will connect its border with Assam.
- Hydropower: India constructed four major hydroelectric projects in Bhutan which are supplying electricity to India- Kurichhu, Tala, Chukha and Mangdechhu.
- The 720 MW Mangdechhu was handed over to Bhutan in 2022.
- Cultural Relations:
- Buddhism connects both countries on similar ideologies.
- The India-Bhutan Foundation, established in 2003, aims to enhance people-to-people exchanges in the cultural field.
- Security:
- The Indian Military Training Team (MTRAT) is permanently based in western Bhutan and assists and trains the Royal Bhutan Army.
- India's Border Road Organisation (BRO) has built the majority of roads in Bhutan under project 'DANTAK'.
- New initiatives of Cooperation:
- Launch of RuPay, and BHIM app in Bhutan, collaborating on a number of technology initiatives such as 'Digital Drukyul'.
- ISRO and Bhutan agency jointly developed satellite 'India-Bhutan SAT', launched by ISRO.
- India is also helping Bhutan to fill the shortages of STEM teachers in schools of Bhutan.
- Under the Vaccine Maitri Initiative, India gifted 5.5 lakh doses of the Made-In India Covishield vaccines to Bhutan.
Major Challenges in India-Bhutan Relationship
- Issues in hydropower trade: India's past changes in power purchasing policy, not able to fairly negotiate power tariff delay in completion of projects (E.g. Punatsangchhu I & II) by India.
- Hideout for militants: India's North-East Militant outfits like the United Liberation Front of Assam (ULFA), National Democratic Front of Bodos (NDFB), etc. uses Bhutan for the hideout.
- BBIN initiative: The Bangladesh Bhutan lndia Nepal (BBIN) Motor Vehicle Agreement is on hold by Bhutan due to environmental concerns.
- Increased financial burden on Bhutan as India moved away from 60:40 model (60% grant, 40% loan) to 30:70 model.
- China's presence: Bhutan's border disputes with China like Doklam raises security concerns for India.
Way Forward
- Diversifying economic engagements: Strengthening collaboration in fields such as fintech, space tech, and biotech can lead to a stronger partnership.
- India will need to sustainably invest in Bhutan's services sector in line with its philosophy of Gross National Happiness (GNH).
- India shall leverage the Gelephu project as an opportunity to deepen its partnership with Bhutan and counter Bhutan's growing engagement with China.
- Initiating Trilogue with China: Opening such communication channels can minimize uncertainties with regard to border disputes.
- Improving people-to-people ties: Soft power diplomacy can be induced through Buddhism and by encouraging more tourist activities.
- Security measures: Establish contact points between two countries and mechanisms for real time sharing of information regarding militant outfits.
India-Bhutan-China TriangleIt reflects the complex geopolitical dynamics as a result of India's close ties with Bhutan, China's rising influence in Bhutan, Bhutan's border disputes with China, and the broader India-China rivalry. China's rising influence in Bhutan
Implications of increasing China's role in Bhutan for India
|





