Why in the news?
Department of Biotechnology (DBT) announced the completion of GenomeIndia project.
About GenomeIndia Project
- Launched: by DBT under Ministry of Science and Technology (2020).
- India had announced its first complete human genome in 2009.
- Aim: To collect 10,000 genetic samples from citizens across India and create a Reference Genome for Indian Population.
- Human genome reference sequence is an accepted representation of the human genome sequence, made up of a combination of several people’s DNA.
- About the mission:
- Comprises researchers from 20 national institutes led by Centre for Brain Research Bengaluru.
- Datasets generated will be stored at Indian Biological Data Centre in Faridabad.
- It was inspired by the Human Genome Project (HGP), the First international research effort to determine entire human genome DNA sequence.
- HGP was launched in 1990, completed in 2003 and covered ~92% of total human genome sequence.
- It was led by the 'International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium' which involved scientists from 20 institutions in six countries: France, Germany, Japan, China, the UK and the US.
- It will create a database representative of India’s diverse population, in addition to the other benefits offered by genome sequencing.
Other Initiatives for Genome sequencing
|
What is genome and genome sequencing?
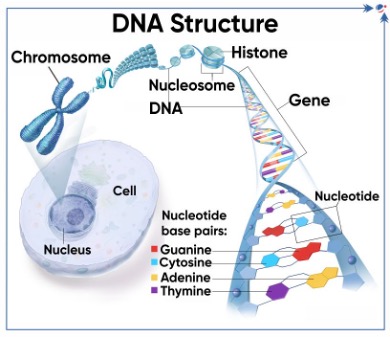
- The genome is a complete set of genes of an organism and includes all the chromosomes, which house the DNA and genes.
- A gene is a basic unit of heredity made up of a sequence of nucleotides in DNA or RNA.
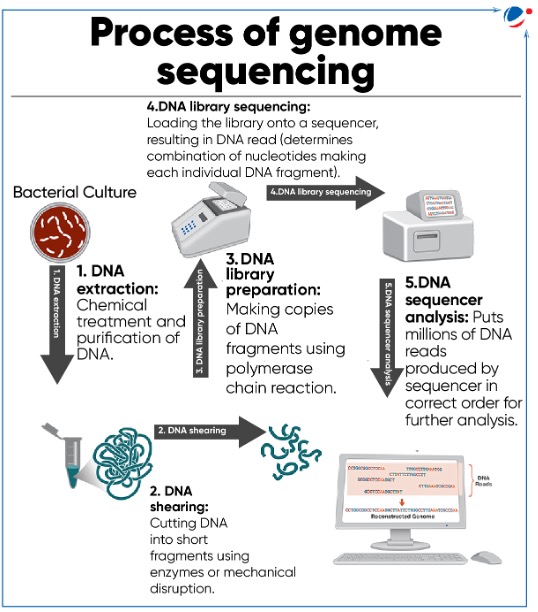
- Genome sequencing means determining the exact order of base pairs in a strand of DNA in an individual.
- DNA molecules are polymers of long chains of nucleotides, which are sugar molecules attached to a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base.
- DNA bases are Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), and Thymine (T).
- Human genome contains approximately 3.2 billion nucleotides and 23,500 genes.
Significance of Genome sequencing
- Enable treatments for genetic diseases: Genome sequencing is useful in-
- Prenatal screening to identify genetic disorders in foetuses.
- Liquid biopsies to diagnose cancer early.
- Pharmacogenetics- study of how genes affect a person's response to drugs to prevent adverse drug reactions.
- Development of Predictive diagnostics and personalized healthcare: Through customised drugs and gene therapies based on genome sequencing.
- Facilitate Advanced Analytics and Artificial Intelligence integration: To enhance understanding of genetic causative factors and develop disease treatments.
Challenges related to genome sequencing
- Lack of regulatory framework: It limits quality and proficiency standards and leads to misuse of data.
- Instances of samples from India sequenced and analysed abroad have been observed due to inadequate regulation.
- Privacy and data issues: Due to technology involving sensitive information such as personal data, medical history, and family history with diseases.
- Fragmentation of genetic data: With data remaining in silos, it prevents its access to public health decision-making.
- Ethical issues:
- Inequity and low diversity: Unregulated market forces may create barriers to better healthcare access, especially for the poor and ethnic minorities.
- Discrimination based on genetic information: It may prevent access to health benefits such as insurance.
- Technological challenges: Cyber threats, Problems of sample contamination and viable run quality etc.
- Other issues:
- Financial constraints in establishing and maintaining sequencing facilities.
- Limited skilled personnel for sequencing facilities.
Way Forward
- Establish clear regulations for fair competition and stakeholder trust.
- Prioritize genomic research funding and establish centralized sequencing facilities
- Develop advanced training programs for researchers at both experimental and computational levels
- Improved access of up-to-date genomic data through collaboration with scientific publishers and open access publication models.
- Utilize modern sequencing technologies to minimize infrastructure requirements
- Follow best practices to curb data misuse and ensure ethical technology use, E.g. Genetic Information Non-discrimination Act in the U.S.A.



