Why in the news?
The "UN World Water Development Report: Water for Prosperity and Peace" report was released on World Water Day (22nd March), at UNESCO Headquarters in Paris.

More about the news
- The United Nation’s annual flagship report on water is published by the UNESCO World Water Assessment Programme (WWAP) on behalf of the UN-Water.
- UN-Water is a ‘coordination mechanism’, which comprises of United Nations members and international organizations working on water and sanitation issues.
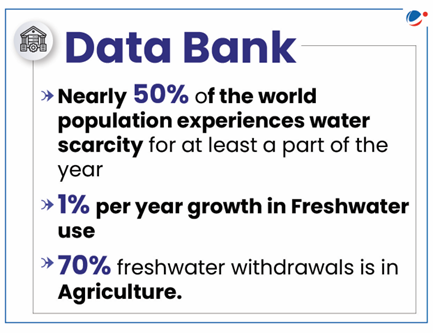
- While the SDG 6 aims to “ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all” None of the SDG 6 targets are appearing to be on track.
- Around 2.2 bn people were without access to safely managed drinking water in 2022.
- The latest report highlights how developing and maintaining water security and equitable access to water services is essential to ensuring peace and prosperity for all.
Water and Prosperity | Water and Peace |
|
|
Challenges related to Water in Prosperity and Peace
- Water–prosperity paradox: While middle- and lower income countries require water to develop their economies, they require economic growth in order to finance water requirement.
- Evolution of Water Pollution: Water pollution does not disappear with the development of a country but evolves in form.
- While wastewater treatment issues affects the water quality in low income countries, runoff from agriculture affects high income countries water resources.
- Data Deficiency: Lack of data and information on various parameters of water like surface and groundwater, soil moisture, and associated hydro meteorological parameters.
- Lack of ambient water quality data indirectly affects the health of nearly 3 bn people in the low and lower-middle income countries.
- Trans-boundary Water Management: Lack of trans-boundary agreements and international basin establishment for the efficient management of trans-boundary rivers
- Only 32/153 countries with trans-boundary waters have an operational arrangement to efficiently manage the water through a trans-boundary basin.
- Water demand from emerging technologies: Increased water consumption with new age technologies as large volumes of water are used in the liquid cooling systems of computers that run AI programmes.
- It is estimated that AI currently requires 500 ml of water to answer 10–50 queries.
Recommendations of the Report
- States to focus on responsible governance of water, ensuring that all have secure and adequate access to water resources, irrespective of their locality.
- Leverage WASH (Water, Sanitation and Hygiene) as a ‘politically neutral’ service system and act as a platform for communal collaboration and partnerships between citizens and government.
- Decouple water from industrial productivity, and replace the existing relationship between water and production in industries by encouraging water reuse and zero discharge.
- Trans-boundary water management, through equitable agreements and establishment of joint operational bodies for the river basins.
- Equitable benefit sharing of water resources, by moving away from mere volumetric water sharing to sharing the outcomes of the resource.







