Introduction
Recently, the Supreme Court ordered all states and union territories to issue ration cards to 80 million migrants and unorganized workers under the National Food Security Act (NFSA) 2013. They need ration cards to claim government food grain, it is considered as a part of their basic need. However, sometimes Governments cannot fulfill basic needs in resource-scarce times presents one of humanity's most fundamental ethical dilemmas.
Different Stakeholders involved in the fulfilment of bare necessities
Stakeholder | Role/Interests | Ethical issues. |
Individuals and Communities |
|
|
Government |
|
|
Civil Society |
|
|
Corporations |
|
|
International Organizations |
|
|
What are Bare Necessities?
Bare necessities are the fundamental requirements that are necessary for human survival and well-being. These needs are essential for maintaining life and ensuring that individuals can function and thrive in their daily lives.
They are not universally defined and vary due to regional, social, economic, and political differences. Economic Survey 2020-21 introduced Bare Necessities Index (BNI) which used 26 indicators based on five dimensions – water, sanitation, housing, micro-environment and other facilities.
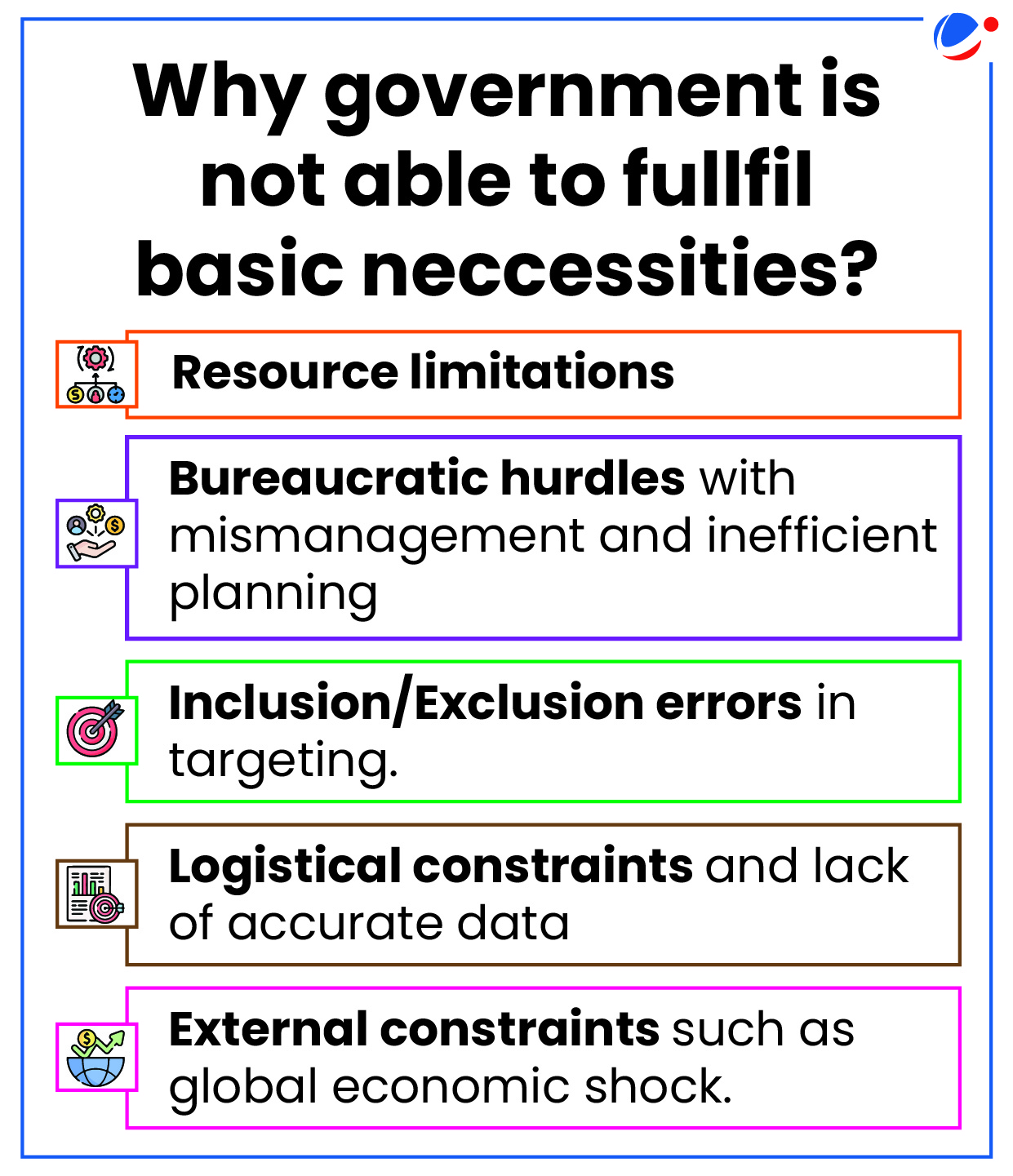
Why government is responsible for providing bare necessities?
- Social Contract theory is about what kind of relationship a government should have with its citizens for instance citizens restrict certain freedoms in exchange for public services and security.
- Constitutional mandate: The Constitution of India mandates the government to fulfil basic necessities and aspirations of its citizens.
- For instance, Article 39(a) requires the State to secure for its citizens the right to an adequate means of livelihood while Article 47 envisions raising level of nutrition and standard of living.
- The Supreme Court has increased the scope of fundamental right. Ex. Right to life has been expanded to include Right against the adverse effects of climate change, Right to Food, etc.
- Expanding Nature of rights: Laws have evolved with the needs of the populace to increase the threshold of bare necessities. For instance, Right to Education, Right to Information, etc
- International commitments: aimed at fulfilling the basic needs of its citizens such as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set forth by the United Nations.
- Pubic goods: The government is capable of providing basic necessities that benefit society as a whole, such as clean water and sanitary infrastructure.
What are the Ethical Approaches for fulfillment of bare necessities by the government?
|
Ways to balance between bare necessities and scarce resources
- Global public goods: The COVID-19 pandemic, refugee crises, climate change—these global problems have shown the need for public goods at the global level.
- Prioritization and efficient allocation: Encourage practices that reduce resource wastage, are sustainable, and promote harmony between nature and human activities.
- Also, resource allocation should focus on the needs of the marginalized and vulnerable population as envisaged by Gandhiji's Sarvodaya.

- Principles to define bare necessities: For defining bare necessities, the principle of provisioning of public goods can be utilized to identify the core set of basic necessities.
- The Netherlands provides a good example of defining the bare necessities through the provision of public goods; these goods should be socially just, economically efficient, and consistent with democratic principles.
- Technological innovation: Advancement and integration of technology in resource management can help in spreading limited resources and their effective utilization.
- Convergence of Resources: Effective resource management requires collaboration between different levels of government, Civil societies, corporate social responsibility fund of industries and international institutions.
Check your ethical aptitudeThe government is providing a new type of health insurance cards of up to 5 lakhs. The program has the potential to benefit a large section of society by providing them security via reducing the cost of health and also promoting the right to health. While the program has been successful in protecting the poor, critics argue that the increasing financial burden strains the government's budget, potentially limiting resources for other essential services. On the basis of the above case study, answer the following questions:
|



