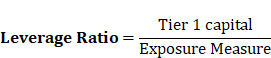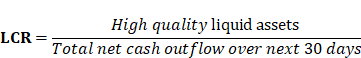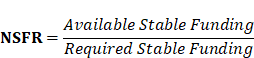
Why in the news?
Consumer Bankers Association (CBA) recently released a White Paper, "The Impact of the Basel III Endgame Proposal on Consumers on the Margins of the U.S. Financial System".
About Basel III Endgame
- The final set of rules of Basel III norms has been called "Basel III Endgame."
- Basel III is a set of measures developed by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision to strengthen the regulation, supervision, and risk management of banks.
- Potential impact of the Endgame includes Globally Systemically Important Banks (G-SIBs) experiencing an increase of 21% in capital requirements.
- Proposed changes are aimed at improving the "strength and resiliency" of the banking system while also improving transparency and consistency in banks' capital frameworks.

Basel Norms (Refer box at the end of this article for key terminologies associated with Basel Norms):
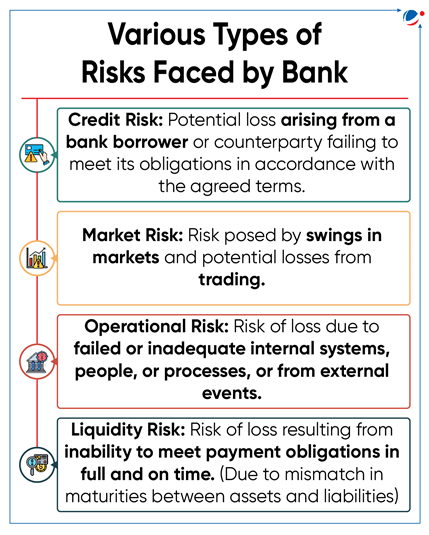
- Description: These rules focus on the amount of capital that banks must have against the credit, operational, and market risk of their business.
- Banks face significant risk primarily due to being one of the most heavily leveraged sectors.
- Heavily leveraged sectors rely extensively on debt for financing their operations and investments.
- Basel I Norms (1987):
- In 1987, the Committee introduced capital measurement system which focused on the credit risk and risk-weighting of assets.
- These norms set minimum level of capital requirements that banks should have.
- Basel II norms (2004):
- These updated norms sought to improve the risk calculation in capital measurement by introducing three important pillars: Minimum capital requirements, Supervisory Review and Market Discipline.
- Basel III Norms (2010):
- Released in response to the financial crisis of 2007-08.
- It aims to build robust capital base for banks and ensure sound liquidity and leverage ratios.
Key Features of Basel I, II and III Compared | ||||
Pillars | Key Components of Pillars | Basel I | Basel II | Basel III |
Pillar I (Capital Requirements) | Minimum Ratio of Capital to RWAs | At least 8% (CAR) | 8% | 8% + 2.5% of Capital Conservation Buffers |
Tier 1 capital to RWAs | At least 4% | 4% | 6% | |
Pillar II (Supervisory Review Process) | No provisions for Supervisory Review | Risk Based Supervision introduced | Enhanced Supervisory Process | |
Pillar III (Disclosure & Market Discipline) | No Provisions related to Market Discipline | Quantitative and Qualitative disclosures prescribed at Quarterly, Half-Yearly and Yearly intervals | Enhanced Disclosure Norms | |
New Banking Capital Requirement Parameters Introduced by Basel III
| ||||
Significance of Basel Norms:
- Development of better risk assessments system: Through capital requirement parameters, it provides an edge over other banks, by focusing on only those target segments, markets and customers who have high risk ratio.
- Robust risk management process: It results in serving the customers better including small and medium sized businesses. It leads to better liquidity for small businesses and help in their growth and expansion needs.
- Improved Corporate Governance: Norms also offer banks with business benefits like improving corporate governance and allocation of capital.
- Stable financial System: New liquidity and leverage framework under Basel norms will not only enhance the risk absorbency of individual banks but also aid in Strengthening soundness of financial system during extreme stress.
- Minimizing Economic Spillovers: These Norms ensure that the banking system as a whole does not crumble and its spill-over impact on the real economy is minimized.
Basel norms implementation in India:
- Basel 1 norms were adopted in India with the announcement by RBI in its Mid-term Review of Monetary and Credit Policy for 1998-99 to raise Capital to Risk Weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR) from 8 per cent to 9 per cent.
- In 2007, RBI announced the final guidelines for implementation of Basel II.
- Draft guidelines for implementation of Basel III capital regulations were issued in Dec 2011.
- The Basel III capital regulations (Pillar I of Basel III Norms) were implemented in India with effect from April 2013 and have been fully implemented as on October 2021.
- As compared to the Basel norms, the RBI's prescribed norms are stricter and more prudential.
Conclusion
The Capital Accord of 1988, which set global standards for regulation and supervision, has emerged as one of the most significant developments. The biggest contribution of the Basel Accord has been to arrive at a common definition of capital, while capital adequacy norms have been adopted in different countries with certain country-specific adaptations.
Important Terminologies related to Basel Norms
|
Important Ratios Related with Basel Norms:
CAR = |