98% of Urban Women involved in Household Financial Decisions
- AMFi-CRISIL released a report titled ‘Mutual Growth’ which states that financial decision-making and labour force participation rate (LFPR) of women are rising in India.
Key highlights of the report
- Female Labour Force Participation Rate has increased to 37.0% in 2023 from 23.3% in 2017-18.
- Female LFPR rose to 37% (PLFS of Oct 2023) against 23.3 five years back.
- 47% of women take financial decisions on their own.
- Autonomy of women in taking financial decisions depends on income source, age, and stage of affluence.
Significance of increasing role of women in financial decision-making
- Social: Women’s overall empowerment by addressing gender disparities, reduced domestic violence and conflict, etc.
- Intergenerational impact such as greater proportion of resources allocated towards children’s education, healthcare, etc.
- Economic: Financial literacy and inclusion resulting in better financial planning and wealth management for families and communities.
- Increased financial intermediation and market depth, tapping into talents and skills of women to help drive entrepreneurship and innovation, etc.
Challenges in women’s financial autonomy
- Socio-cultural: Deep-rooted patriarchy, gender stereotypes, etc., which limits women’s financial independence.
- Economic disparities: Lower participation in formal workforce, gender pay gap [share of female labour income was just 18% (World Inequality Report, 2022)], etc.
- ‘Dual-burden’ of work, unpaid and unrecognized domestic and care work by women, etc.
- Tags :
- LFPR
- AMFi-CRISIL
- Labour Force Participation Rate
UNESCO’s “Technology on Her Terms” Report
- UNESCO released 2024 gender report of the Global Education Monitoring Report, titled “Technology on her Terms”.
- The report looks at impact of technology on girls’ education opportunities and outcomes, and role of education on the shape of future technological development.
Impact of technology on girls’ education:
- ICT can overcome barriers to education access for girls in crisis context.
- For instance, in Kenya, M-shule platform delivers education through text message without need for internet connection.
- Digital divide: Girls and women are less able to access technology with 130 million fewer women than men owning mobile phone and 244 million fewer women having Internet access.
- Social media negatively affects well-being and reinforces gender norms. Greater interaction on social media at age 10 is associated with worsening socioemotional difficulties with age among girls.
- Cyberbullying is common and is exacerbated by the danger of deepfakes made using AI.
Role of Education in shaping technological development:
- Average share of STEM is 15% among young female graduates and 35% among young male graduates.
- Underrepresentation in technological design and deployment: In 2022, women held less than 25% of science, engineering and ICT jobs.
- Negative gender stereotypes, reinforced by low expectations from parents and teachers, impact girls’ STEM aspirations.
Recommendations from the report:
- Establish bodies to evaluate education technology and algorithms, to assess where they may be amplifying negative gender stereotypes or negatively affecting well-being.
- Encouraging more girls to study towards scientific careers and promote female leadership in artificial intelligence and technology development.
- Avoid infrastructure-only approaches and invest in gender-responsive education and training programmes to enhance digital literacy and skills for all.
- Tags :
- UNESCO
- Girl Education
State of World Population - 2024 Report
- United Nations Population Fund's (UNFPA) released the State of World Population 2024 report.
- Report is titled "Interwoven Lives, Threads of Hope: Ending Inequalities in Sexual and Reproductive Health (SRH) and Rights".
- Women’s SRHR includes right to be free from torture, right to health, privacy, education, life, and prohibition of discrimination.

Key findings
- India leads globally with an estimated population of 144.17 crore, followed by China (142.5 crore).
- India's population is estimated to double in 77 years.
- 68% of India’s population belongs to age group of 15- 64 years, followed by 10-24 years group (26%),
- India’s Total Fertility Rate i.e. births per woman in reproductive age is estimated at 2.0.
- In India, life expectancy at birth is estimated at 71 and 74 years for men and women respectively.
- Child marriage rates in India was 23% between 2006-2023.
- Women with disabilities experience up to 10 times more gender-based violence than women without disabilities.
- 30 years (1994-2024) of progress in SRH has mostly ignored the most marginalized communities.
Initiatives taken to improve SRH
- India: Janani Suraksha Yojana, Surrogacy (Regulation) Amendment Rules, 2024 etc.
- Global: International Conference on Population and Development Programme of Action in Cairo, Egypt, 1994, Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action, 1995 etc.
- Tags :
- United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA)
Longevity India Initiative (LII)
- Indian Institute of Science (IISc) has launched the ‘Longevity India’ Initiative to support ageing research in India.
About LII
- Seeks to enhance understanding of ageing through both fundamental and applied research, and to develop solutions that can improve quality of life.
- Brings together a multidisciplinary team of experts from academia, and industry to promote healthy ageing across India.
- Research focus includes identifying early disease indicators, investigating ageing biomarkers, and developing new therapeutics and technologies to aid in healthy ageing.
- Tags :
- Indian Institute of Science (IISc)
- Longevity
Panel for Queer Community Notified
- Ministry of Law and Justice notifies panel to address issues related to the queer community.
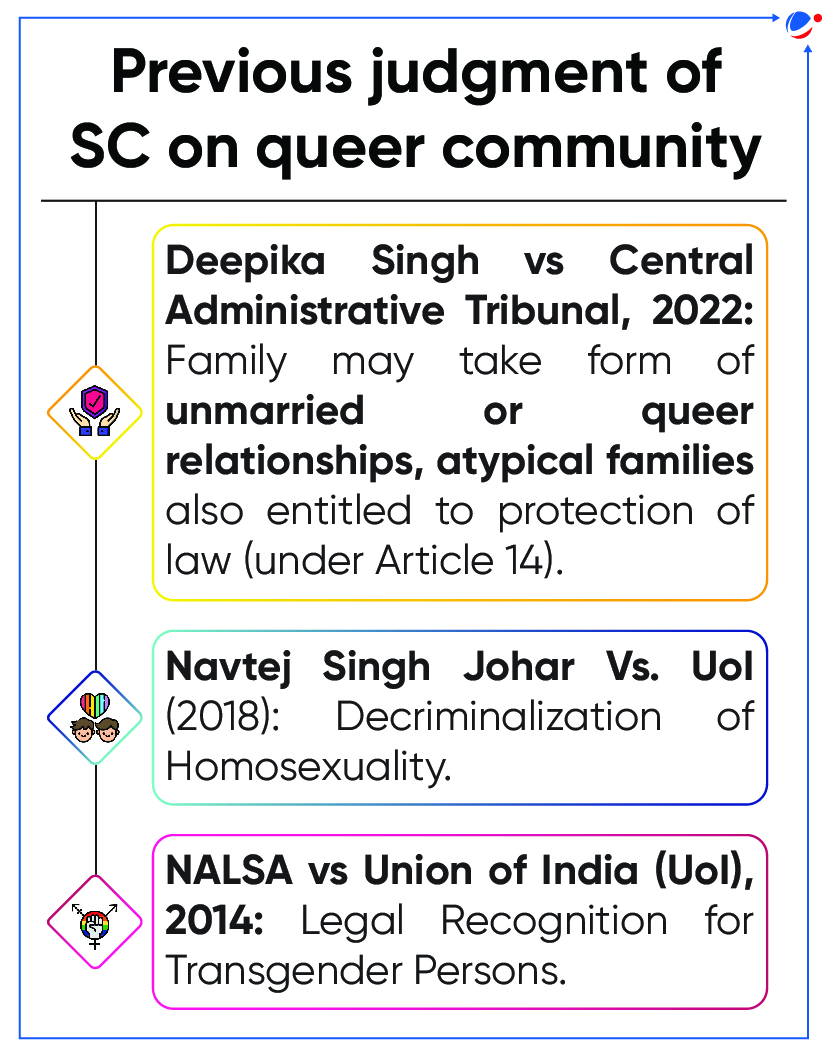
- The committee headed by Cabinet Secretary was constituted in compliance with the direction of the Supreme Court (SC) in Supriyo v Union of India case (2023).
- In this case, SC had refused to grant legal recognition for same-sex marriages observing that it was a matter for the Parliament to decide
- Committee will recommend measures to ensure
- no discrimination in access to goods and services for the queer community
- queer people are not subjected to involuntary medical treatments, violence, coercion, etc.
Queer community
- It refers to people who identify themselves as (or LGBTQ+ (lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer and intersex)
- Many such people face issues like Social Exclusion, homelessness, low education, low accessibility to health care, etc.
- Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019 provides for the protection of their rights and their welfare.
- Tags :
- Ministry of Law and Justice
- LGBTQIA+
UNHRC adopted First Resolution of its kind for Intersex Rights

- Resolution is adopted at the 55th Session of the United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC).
- Resolution calls on states:
- To combat discrimination, violence and harmful practices against persons with innate variations in sex characteristics and
- Address their root causes as well as help intersex people ‘realize the enjoyment of the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health’.
- Intersex people are born with sex characteristics (such as sexual anatomy, reproductive organs, hormonal patterns and/or chromosomal patterns) that do not fit typical binary notions of male or female bodies.
- They may have any gender identity or sexual orientation.
- Experts estimate that up to 1.7 % of the population are born with intersex traits.
- Intersex people are different from transgenders.
- Transgenders are born with a body that has unambiguous sexual characteristics (either male or female) but they don’t match the person's gender identity.
- Key issues with Intersex People: They are subjected to human rights violations because of their physical characteristics.
- Society has created harmful stereotypes and pathologization (treating intersex persons as necessarily ill or disordered) towards them.
- They face issues like Infanticide, forced and coercive medical interventions, discrimination in different sphere, legal recognition, etc.
- Tags :
- United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC)
IOM released “A decade of documenting Migrant Deaths” Report

- International Organization for Migration (IOM) released a report “A Decade of Documenting Migrant Deaths”.
- Report was released on completion of ten year of IOM’s Missing Migrants Project (MMP).
- MMP was launched in 2014 to document deaths and disappearances of people in migration process towards an international destination.
- IOM, Established in 1951, is leading intergovernmental organization in field of migration.
- Headquartered at Geneva (Switzerland) and consists of 175 member states (including India).
Key findings
- More than one in three migrants whose country of origin could be identified comes from countries in conflict.
- More than two-thirds of those whose deaths were documented through IOM’s MMP are unidentified.
- Major causes of death: Drowning; Vehicle accidents; Suffocation due to fuel inhalation, Inadequate shelter, healthcare etc.
Migration
- Migration refers to movement of persons away from their place of usual residence, either across an international border or within State.
- Factors behind Migrations: Urbanisation, Marriage, Economic disparities, Political instability, Impacts of climate change, etc.
- Consequences of migration
- Intermixing of diverse cultures and evolution of composite culture.
- Overcrowding in cities led to their haphazard growth and slum development.
- Changes resource- population ratio.
- Brain drain i.e. skilled people migrate from poorer countries to developed countries for better economic opportunities.
- Tags :
- Missing Migrants Project (MMP)
Food Waste Index Report 2024
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) Launched Food Waste Index (FWI) Report 2024.
- Report co-authored with WRAP (Waste and Resources Action Programme) was published ahead of International Day of Zero Waste (observed annually on 30 March).
- FWI tracks global and national generation of food and inedible parts wasted at retail and consumer (household and food service) levels.
- It supports the goals of two indicators of SDG 12.3 which is to be achieved by 2030 i.e.
- SDG 12.3.1 (a), Food Loss Index (FLI), reduce food losses along production and supply chains, including post-harvest losses. Food and Agriculture Organization is custodian of FLI.
- SDG 12.3.1 (b), FWI, halve per-capita global food waste at retail and consumer levels. UNEP is custodian of FWI.
- It supports the goals of two indicators of SDG 12.3 which is to be achieved by 2030 i.e.
Key findings
- Households across all continents wasted over 1 billion meals a day in 2022, while 783 million people were affected by hunger and a third of humanity faced food insecurity.
- Food Waste generates an estimated 8–10% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Issues
- Due to lack of robust cold chains, hotter countries generate more food waste per capita in households.
- Insufficient Data for retail and food service sectors, particularly in low and middle-income countries.
- Fragmented food system.
About WRAP
Suggestions for reducing food waste through collaborative approach
|
- Tags :
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
The Global Network against Food Crises (GNAFC)
- The GNAFC launched the Global Report on Food Crises (GRFC) which is produced annually by the Food Security Information Network (FSIN).
About GNAFC
- It was launched in 2016.
- By the European Union, the UN’s Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Food Programme (WFP).
- It seeks to better link, integrate and guide existing initiatives, partnerships, programmes and policy processes to address the root causes of food crises.
- It brings together governments, international organisations, and NGOs to improve humanitarian responses and reduce the number of people facing acute food insecurity.
- Tags :
- Global Report on Food Crises (GRFC)
- GNAFC



