Why in the news?
A recent study has highlighted that Baseflow has contributed significantly to the flooding of rivers in peninsular India
More on news
- The study examined six major river basins of peninsular India namely Narmada, Tapi, Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, and Cauvery.
- It used discharge data from river basins to improve understanding of the influence of process-based factors (rainfall, soil moisture, and baseflow) on riverine floods.
- The study revealed that catchments with higher baseflow lead to an increased likelihood of rapid runoff with incoming rainfall events in shorter time lags.
What is Baseflow?
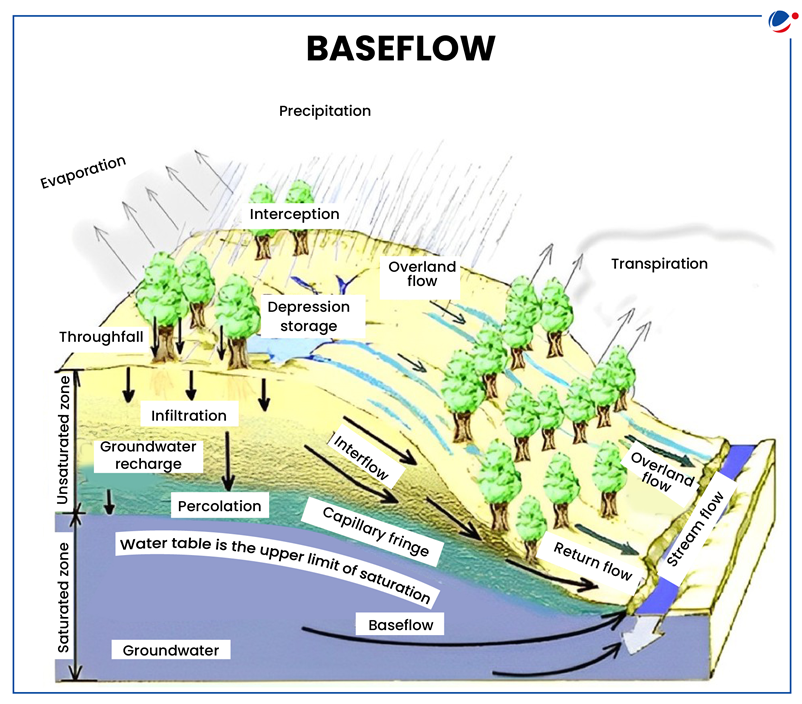
- Baseflow refers to the portion of stream flow that originates from groundwater discharge seeping into the stream or river over an extended period.
- Groundwater discharges into the water bodies when the water table intersects the surface of the ground along rivers or wetlands, contributing to their flow.
Factors influencing Baseflow
- Topography of the land: affects the movement of water across the surface and the subsurface, thereby influencing the infiltration and flow process.
- Nature of the Soil: influences the rate of infiltration, hydraulic conductivity and groundwater recharge.
- Hydraulic conductivity is a measure of how easily water can pass through soil or rock.
- Land use pattern: The conversion of forest to urban land increases baseflow owing to the presence of impervious surfaces in urban areas.
- Climate Change: Changes in precipitation volume and timing can alter infiltration and groundwater levels, which in turn affect the baseflow discharge.
Environmental significance of Baseflow
|
Potential effects of change in Baseflow
- Increases Flood Risk: Catchments with higher baseflow reflect more wet conditions, which increases the chances of rapid runoff during heavy rainfall.
- Alternatively, prolonged periods of below-average precipitation and high temperatures lead to a decrease in the groundwater recharge rate leading to a situation known as baseflow droughts.
- Affects the riverine ecosystem: Reduced baseflow leads to stagnant condition of water in river beds which also leads to depletion of dissolved oxygen thereby threatening the riverine species.
- Affects the water temperature: As the groundwater is cooler than the surface water, reduced inflow of baseflow water in a stream increases its temperature.
- Other effects include alteration in downstream flow, water utilization patterns and increased silt accumulation among others.
Conclusion
Baseflow of a river can be effectively managed through integrated water management approaches like optimal land use policies, recharging of groundwater, continuous monitoring and assessment of the river basins among others.






