Why in the news?
India recorded highest percentage of doping offenders (3.26%), according to the 2022 testing figures released by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA).
More about the news
- India is followed by South Africa and Bangkok in the percentage of doping offenders.
- In 2022, nearly all drug classes saw an increase in the number of individual Prohibited Substances compared to 2021.
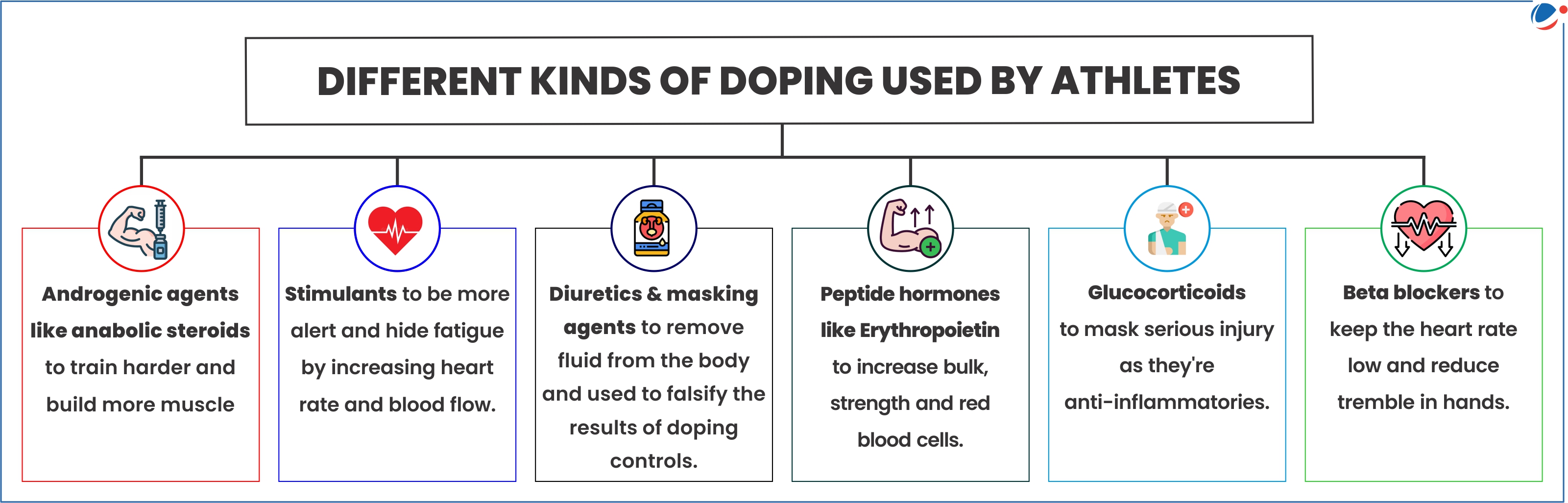
About Doping
- It is the act of consuming banned artificial and often illegal substances to gain an advantage over others in sporting competitions.
- Doping may also include other methods like increasing oxygen in the bloodstream through blood transfusions.
Reasons for high doping incidents in Indian sport
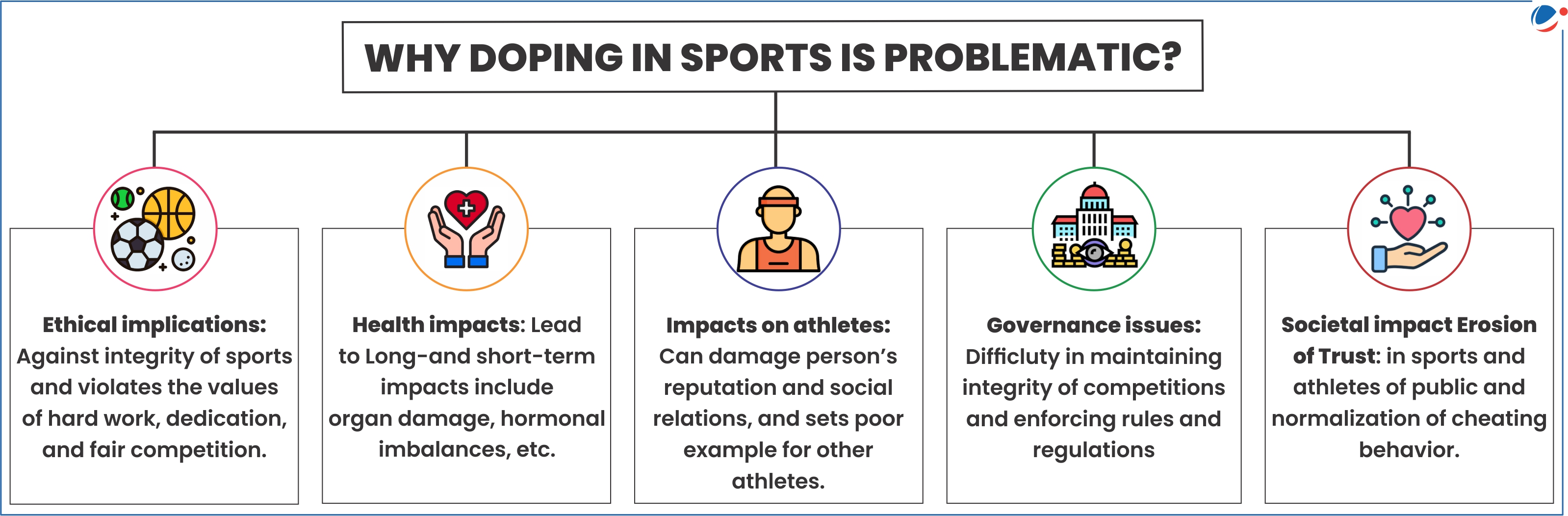
- Recognition and rewards: Winners get instant recognition, financial rewards and government jobs.
- Easy accessibility and availability: Despite regulations and efforts to curb banned substance distribution, these substances remain readily available in various forms.
- Lack of comprehensive education and awareness: Athletes are not well aware of the risks and consequences of doping to the health or integrity of sports, particularly at the grassroots level.
- Lack of sports infrastructure and support: This drives athletes to seek alternative means, including doping, to get an edge over their athletes from better-equipped nations.
- Societal pressure: Sport as a career is often looked down upon in India, making Athletes feel pressured by coaches, family and society to perform well.
- Ineffective testing and monitoring: Smaller competitions in many parts of the country have no anti-doping officials.
Efforts to stop doping in India
|
Way forward to prevent doping in India
- Education: Athletes of all ages need to be educated about the dangers of banned substances.
- Regulating supplements: Food safety and standards Authority of India (FSSAI) can issue certification to supplements that they do not contain banned substances.
- Enhance testing and monitoring: To act as a deterrent, NADA can increase the frequency and quality of doping tests, both in-competition and out-of-competition.
- Strengthening sports infrastructure: Enhancing availability of trained athlete support personnel, along with advanced instruments.
- Developing positive attitude towards sports in society: There is a need to address societal barriers and biases to reduce pressure on athletes.








