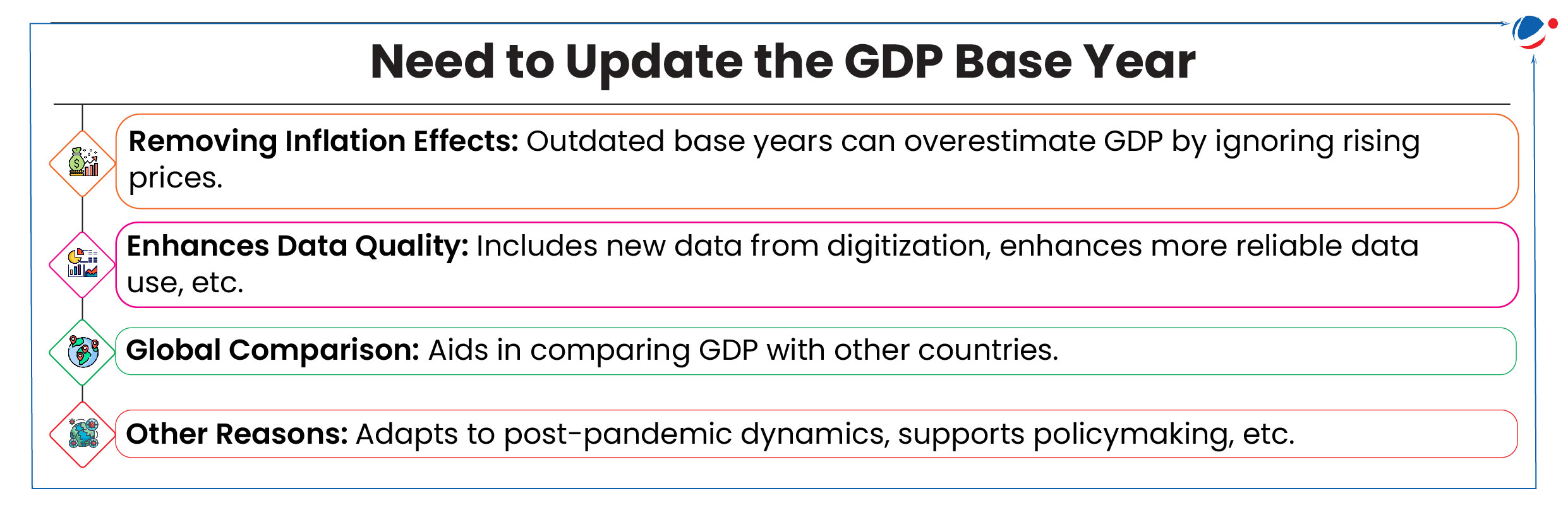
Why in the News?
Government has formed 26-member Advisory Committee on National Accounts Statistics (NAS) to update the GDP base year from existing 2011-12 to 2022-23.
More on the News
- The NAS under chairmanship of Biswanath Goldar has been formed to identify new data sources & refine methodology for compiling NAS.
- Central Statistics Office (CSO) brings out NAS annually which includes GDP estimates from multiple approaches.
- Advisory Committee on NAS will review data sources to align GDP with inflation and industrial indices.
- The previous base year revision in 2015 changed base year from 2004-05 to 2011-12.
- In the new series, CSO did away with Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at factor cost, and adopted the international practice of valuing industry-wise estimates as Gross Value Added (GVA) at basic prices.
What is Base Year?
- A base year is the reference year whose prices are used to calculate the real growth (minus inflation) in national income.
- Thus, Base year is a benchmark used for GDP calculation.
- For example: If 2011-12 is the base year, GDP for other years is adjusted to match 2011-12 prices.
- Revision of base year are also relevant for other metrics such as the Index of Industrial Production (IIPs), the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) and the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
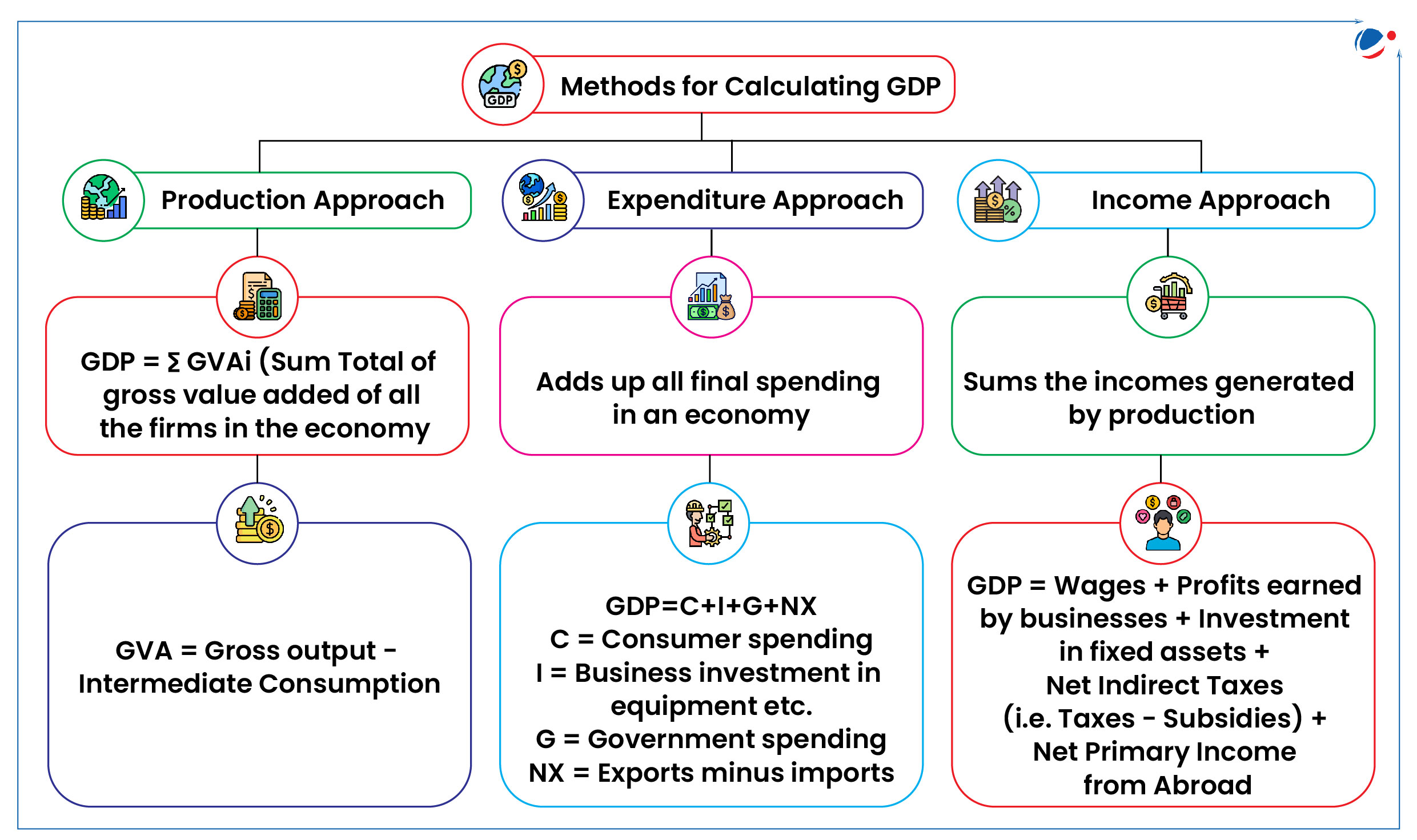
About GDP
- Measurements of GDP: Theoretically, GDP can be measured in three different way, each of which should give the same answer (refer to the infographic)
- Nominal GDP: Measured at current market prices, ignores inflation.
- Real GDP: Adjusted for inflation using base year prices, showing true economic growth.
- Limitations of GDP
- Excludes non-market activities (e.g., household work)
- Ignores income inequality
- Overlooks environmental damage
- Misses informal economy contributions
- Doesn't measure welfare or living standards
Other relevant information on GDPChain-based GDP calculation
GDP Accounting Standard
|







