Introduction
Recent emphasis on the idea of P2G2 or Pro-People Good Governance in India and the creation of a new Department of Government Efficiency in USA indicates the growing realization towards better and people-oriented governance. In this light, it is essential to revisit the India's age old traditions that had the idea of Rajadharma imbibed in them dealing with justice, fairness, and welfare of the people.
About Good Governance
- Governance was defined as the manner in which power is exercised in the management of a country's economic and social resources for development.
- It provides a comprehensive framework that ensures that the voices of the most vulnerable are heard and that decisions are made to address both current and future needs.
- According to the United Nations, good governance has eight major characteristics, viz, participatory, consensus-oriented, accountable, transparent, responsive, effective, equitable, and inclusive, all while adhering to the rule of law.
- Challenges to Good Governance: Corruption, lack of accountability, judicial delays, poor law implementation, inadequate public service delivery etc.
Indic Idea of Good Governance
- Brihadaranya Upanishad: It stresses on the duty of the king to protect Dharma, the public good, so that all citizens get equal opportunity and that the weak are not exploited.
- Mundaka Upanishad: It includes the phrase "Satyamev Jayate" that translates to Truth alone triumphs, a basic part of good governance.
- Epic Ramayana: It talks about Ram-Rajya or ideal governance and offers essential insights into the crucial art of leadership. According to Ram Rajya, a leader is expected to look after everyone who need help and support instead of accumulating wealth for himself.
- The Ayodhya Kanda of Ramayana is a treatise on the issues related to good governance. In Ram Rajya, there was no starvation, soreness or discrimination among the people

- Bhagwat Gita: Talks about the concept of Adhishthan, which is an important element at the foundation of everything, including governance.
- Adhisthan, or the seat of action, relates to good governance by ensuring decisions are made with responsibility and stability, fostering a transparent, accountable, and effective administrative system.
- Atharvaveda: Atharvaveda contains a hymn known as the Bhumi Suktam, dedicated to the Earth. This hymn venerates the Earth as the universal mother who nourishes all creatures, and it emphasizes the need to live in harmony with nature.
- Thirukural: It deals with the orderly development of the society, including regulation to ensure reasonableness of prospecting and exploitation of resources and protection of the environment.
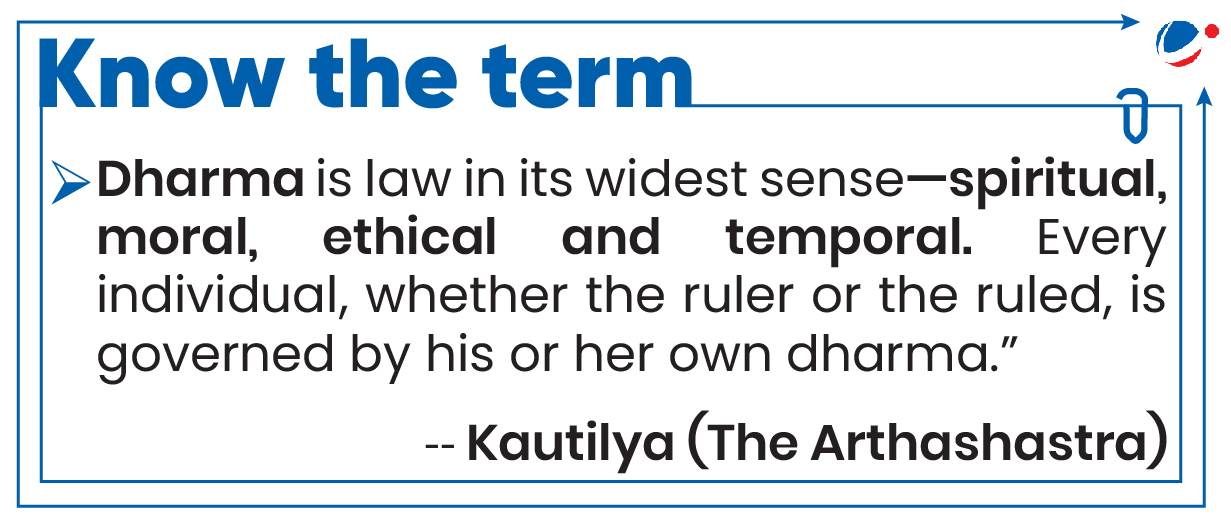
- Kautilya's Arthashastra: It deals with Yogakashema, or the welfare of the citizens, and Raj Dharma describing king as the servants of the citizens who looks after the sick, children, old, etc.
- Antyodaya: It is based on the ideas of Mahatma Gandhi that implies welfare of all through the weakest of the society to achieve Sarvodaya or 'development of all'.
Relevance of the Indic Ideas of Good Governance
- Adapting to Globalisation: Globalisation has limited the authority of government with the rise of various transnational organizations and supranational organizations. Hence, reviving the Indic ideas of good governance may fill up the vacuum in the areas of public order and welfare.
- Philosophies like Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam (the world is one family) promotes global unity and inclusivity.
- Sustainable living: Indic principles as mentioned in Atharvaveda underline the importance of sustainable development practices, as seen in India's commitment to SDGs and Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE).
- Preserving Democracy: By ensuring cooperation between the government and civil society/citizens.
- Karmayogi project for building capacities of government is governed by the same impulse.
- Welfare for All: Concept of Antodaya aligns with the modern concept of inclusive development.
- It is seen in programs like MGNREGA, Public Distribution System (PDS), and Ayushman Bharat aimed at uplifting marginalized communities.
- Improving Diplomatic Relations: Ideas of Kautilya, ocusing on pragmatism assess the strategic opportunities, threats and risks while dealing with foreign countries.
- Conflict Resolution: The Nyaya system of jurisprudence, which focuses on justice, fairness, and mediation, offers an alternative to adversarial legal systems.
- Modern governance could adopt elements of this approach to resolve conflicts more amicably, reducing the burden on judicial systems.
Conclusion
Basic features of the modern day concept of good governance resonates well with the thought process and the administrative structure postulated by the ancient scriptures. The primary objective of the authority in both the cases essentially is the happiness of the people. Therefore, there is a strong need to dive into the seas and oceans of Ancient Scriptures and gain pearls of wisdom necessary to build SMART (simple, moral, accountable, responsive and transparent) administration.
Check your Ethical aptitudeYou have recently taken charge as the District Magistrate of a remote district X. On interacting with the public and the officials there, you find out that the district has a very poor governance track record with corruption among officials, poor service delivery, and complacent attitude among officials. On further inquiry you find that both the officials and the citizens are quite traditional in their beliefs and do not connect with modern governance ideas. Therefore, you feel the urgent need to revamp the administrative strategy by linking it with Indic ideas of Good Governance so that it not only resonates with the beliefs of the people but also the officials ensure their implementation with full spirit. On the basis of the above case study, answer the following questions.
|





