Why in the News?
Recently, Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI) released 'Smuggling in India' report 2023-24.
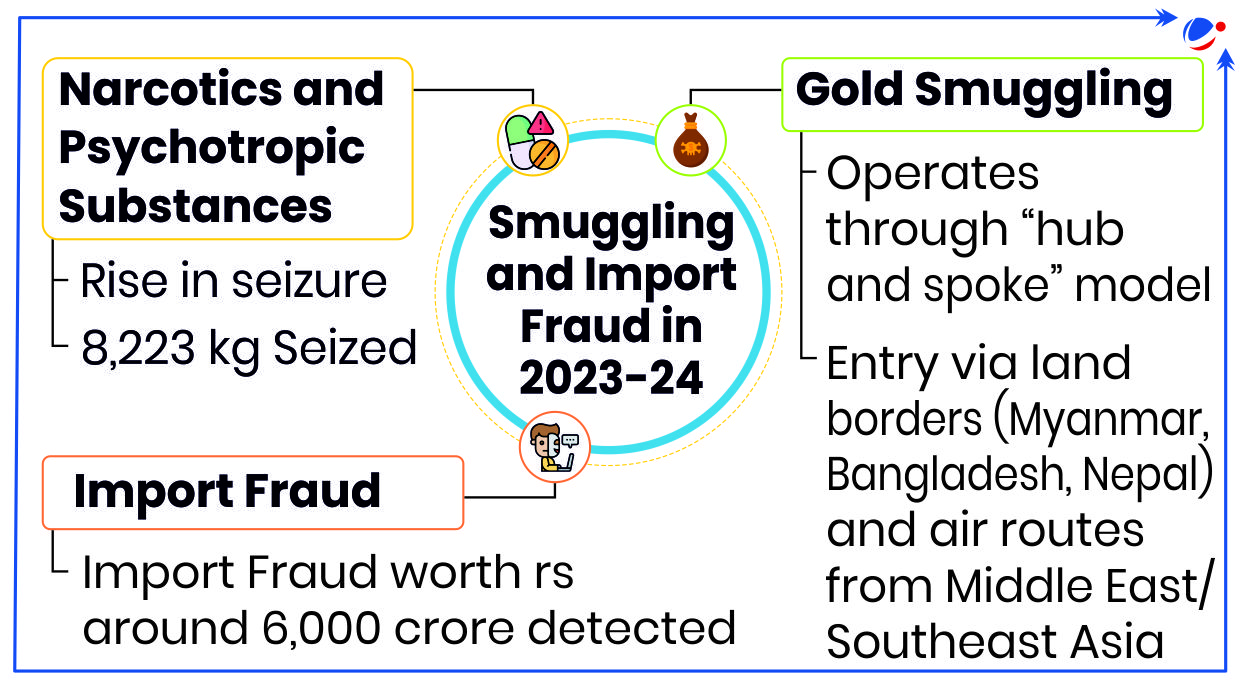
Key Highlights of the Report
- The report provides insights into trends, challenges, and measures in combating smuggling.
- The DRI's interception of illegal drugs, wildlife products such as elephant tusks (~53 kg), foreign currencies, insecticides, etc. showcases a rising trend of smuggling activities (refer to the infographics).
Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI)
|
Reasons behind increased cases of Smuggling in India
- Geography and Borders: India's extensive coastline and porous borders with Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Nepal create multiple entry points for smugglers.
- India's North-Western borders to Death Crescent (Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan) and North-Eastern borders to the Death Triangle (Myanmar, Laos, Thailand).
- Market Demand: High demand for items like gold, especially from Gulf states like UAE and Saudi Arabia, drives illegal trade.
- Sophisticated Techniques: Smugglers use advanced concealment methods such as hiding drugs in machinery parts, ingestion by carriers (known as 'mules') etc.
- Moreover use of technologies such as Darknet, and Crypto Currencies leveraging anonymity complicates law enforcement efforts.
- E.g. Anti-national elements/smugglers are using drones for smuggling of Arms/Narcotics across India-Pakistan border in Punjab State
- Misuse of legal loopholes: E.g. Smugglers exploit Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) and produce Invalid Certificates of Origin and Misrepresentation of goods and causes loss to the government
- Transnational Networks: Smuggling is challenging to detect and dismantle due to intricate international networks.
Nexus of Smuggling and India's Security Risks
India faces multiple security challenges due to smuggling activities that threaten both national security and social stability:
- Narco-Terrorism: India's location between the Death Crescent and Death Triangle makes it particularly vulnerable to narco-terrorism, where drug smuggling directly funds insurgent activities.
- Terrorist organizations rely on smuggling drugs, weapons, gold, and counterfeit currency to finance their operations.
- Financial instability: Foreign currency smuggling weakens India's financial system, while money laundering and tax evasion distort markets and undermine economic stability.
- These activities allow criminal enterprises to expand their operations while depriving the government of legitimate revenue.
- Commercial Fraud: It includes misuse of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs), misclassification of goods, and undervaluation of imports leading to significant revenue losses for the government.
- Wildlife and Environmental Crimes: Smugglers trade in endangered species, traffic hazardous materials and e-waste, and engage in illegal logging of valuable trees like Red Sanders, all of which threaten India's biodiversity.
- Human Trafficking: Smuggling often overlaps with human trafficking, as smugglers use the same transportation routes, document forgery networks, and safe houses for multiple illegal operations.
- This creates a complex web of organized crime that poses significant challenges for law enforcement and border security.
Steps Taken to prevent smuggling and associated crimes
|
Conclusion
As current trend points towards increased sophistication and modernization of crime, it calls for multifaceted response by enforcement agencies such as use advanced detection technologies (Artificial Intelligence, Machine learning, Advance data analytics and use of Open-Source Intelligence) coupled with traditional methods of gathering and generation of actionable intelligence.
Related News: UN Commission On Narcotic Drugs (UNCND)Recently, India has been chosen to chair the 68th Session of the UNCND for the 1st time. About UNCND
|




