Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) released Nexus Assessment Report
- Report is also known as the Assessment Report on the Interlinkages Among Biodiversity, Water, Food and Health.
- It offers a scientific assessment of complex interconnections among nexus elements – biodiversity, water, food, health and climate change – and explores response options to maximize co-benefits.

Key findings
- Unaccounted-for costs of current economic activity – reflecting impacts on nexus elements – are at least $10-25 trillion per year.
- Existence of such unaccounted-for costs, alongside direct public subsidies, enhances private financial incentives to invest in nature damaging economic activities.
- Biodiversity decline per decade for last 30-50 years is 2-6%, reducing ability of ecosystems to sequester carbon and accelerating climate change.
- In last 50 years, global trends in indirect socio-economic drivers of biodiversity loss such as increasing waste, overconsumption and population growth intensify the direct drivers like land and sea-use change, pollution, invasive alien species etc.
- Unsustainable freshwater withdrawal, wetland degradation and forest loss have decreased water quality and climate change resilience.
- Around 50% of emerging infectious diseases are driven by interconnections between ecosystem, animal and human health.
Way ahead
- Adopting synergistic approaches restoring carbon-rich ecosystems forests, mangroves etc.
- Management of biodiversity to reduce risks of diseases spreading from animals to humans.
- Others: Reliance on urban nature-based solutions, knowledge of indigenous peoples, adopting sustainable agricultural practices, one health approach etc.
Article Sources
1 sourceFAO’s first major assessment of soil ‘Global Status of Salt-Affected Soils’, report released
- Salt-affected soils either have elevated amounts of soluble salts (saline soils) or exchangeable sodium ions (sodic soils) measured in terms of high electrical conductivity, adversely affecting the soil fertility & growth of plants.
Factors increasing salinisation and sodification
- Anthropogenic factors:
- Inefficient agricultural practices: Overuse of fertilizers, poor-quality water & overexploitation of aquifers for irrigation, inadequate drainage systems etc.
- Deforestation: Removal of deep-rooted vegetation (dryland salinization).
- Others: Excessive water pumping in coastal and inland areas, mining activities, etc.
- Natural factors: Climate crisis increasing aridity; permafrost thawing; etc.
Key findings of the report
- Global
- Coverage: ~10% (~1.4 billion ha) of global land area is affected, with probable increment to 24-32%.
- Most affected countries: Australia (area wise), and Oman (percentage wise).
- India specific
- Coverage: ~2.1% (~6.72 million ha) of its total geographic area is affected.
- Most affected states (area wise): Gujarat followed by U.P, Maharashtra, West Bengal and Rajasthan.
- ~17% of irrigated agricultural land due to use of brackish groundwater for irrigation.
- Sustainable management practices includes mitigation efforts like mulching, adaptation efforts like breeding salt-tolerant plants, bioremediation, etc.
The Business 4 Land Forum at COP16 of UNCCD highlights the private sector’s key role in promoting sustainable land use.
- UNCCD (United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification), 1994 is the sole legally binding international agreement linking environment and development to sustainable land management.
About Business 4 Land Forum (2024)
- It is the UNCCD’s main initiative to engage the private sector in sustainable land and water management.
- Aim: Restore 1.5 billion hectares of land by 2030, supporting Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN) and improving drought resilience.
Countries negotiating a legally binding instrument on plastic pollution concluded their fifth session without finalization of a treaty.
- The Treaty being negotiated, has been mandated by a 2022 UN Environment Assembly resolution.
- It seeks to addresses the full life cycle of plastic, including its production, design and disposal.
Factors leading to non-finalization of treaty
- Production Capping: Demand for production cap goals by European union, Latin American and African countries was opposed by countries including India and China.
- Unclear definition: Lack of clear language on elimination of certain plastic chemicals and products.
- Draft text clearly defined plastic and plastic products but did not reflect definitions of microplastics, nanoplastics, primary plastic polymers, and recycling.
India’s stance
- Impact on Development: India stated its inability to support any measures to regulate the production of primary plastic polymers as it could impact development rights of nations.
- Defining Scope: Scope of instrument should be limited to addressing plastic pollution only without overlapping with the mandate of other multilateral environmental agreements.
- Phase out period: India did not support inclusion of any list with phase out dates, at this stage.
- Assistance: Due consideration to national circumstances and capabilities should be given and provision of financial and technical assistance, including technology transfer to developing countries, should be included.
Article Sources
1 sourceUNEP has announced Champions of Earth Award, 2024.
- 2024 Lifetime Achievement category is awarded to Indian ecologist Madhav Gadgil for protecting people and planet through research and community engagement.
- He is renowned for his work in ecologically fragile Western Ghats region of India, a unique global biodiversity hotspot.
About Champions of Earth Award
- Awarded annually since its inception in 2005, it is UN’s highest environmental honour.
- In 2024, UNEP honours individuals and organizations working on innovative and sustainable solutions to restore land, enhance drought resilience, and combat desertification.
- Given in categories like Policy leadership; Inspiration and action; Entrepreneurial vision; Science and innovation.
Article Sources
1 source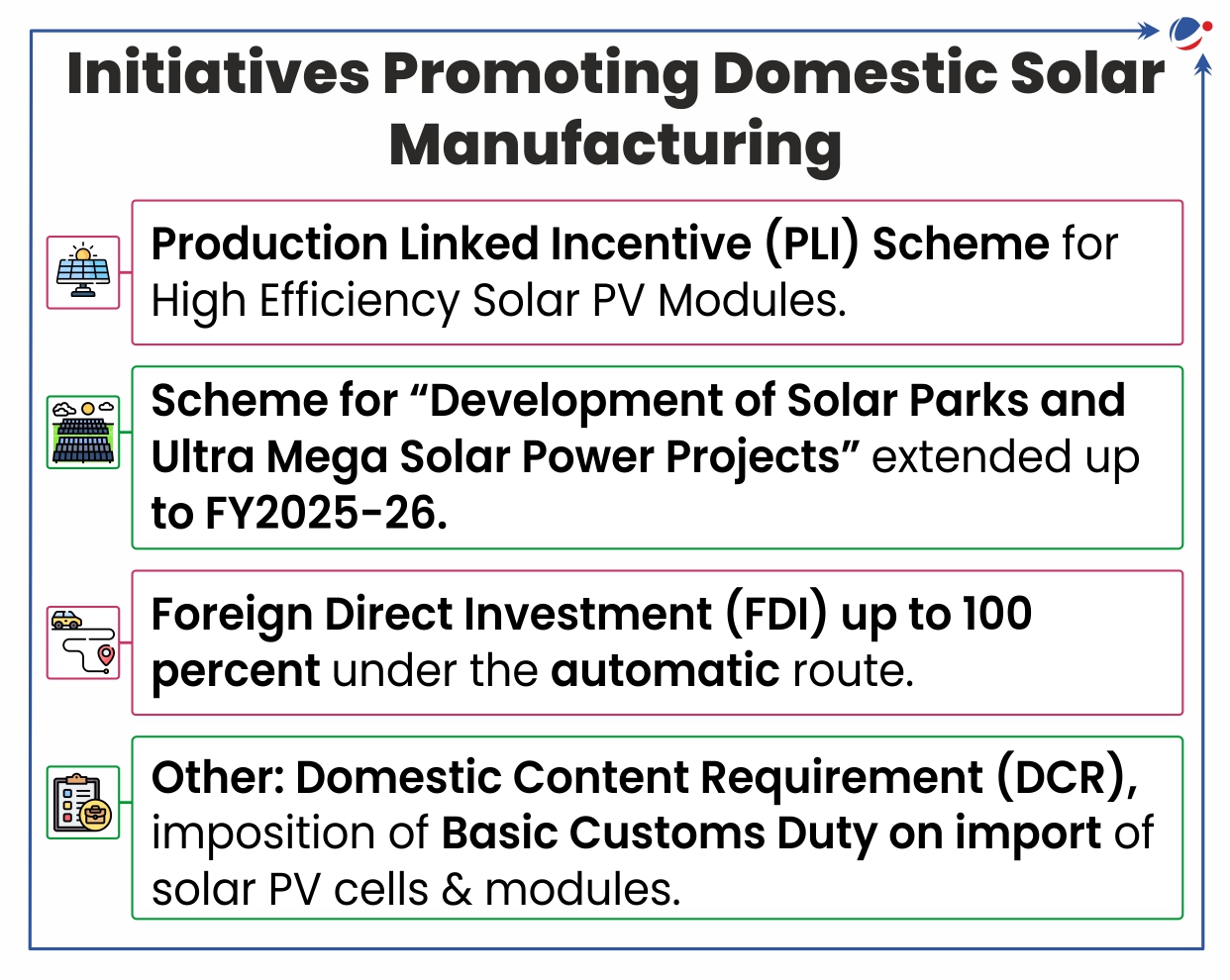
Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) approved amendment to ALMM Order, 2019
- The amendment to the Approved Models and Manufacturers of Solar Photovoltaic Modules (ALMM) Order, 2019 aimed at boosting domestic solar manufacturing.
Key Highlights of Amendment:
- Introduction of ALMM List-II (Solar PV Cells): All solar PV modules used in government-backed projects, net-metering projects, & open-access renewable energy initiatives must source their solar cells from ALMM List-II.
- List I under ALMM framework was issued in 2021 mandating to source PV modules from models & manufacturers included in ALMM List I.
- Exemption: Projects that have already been awarded/completed their bidding process before the issuance of this order.
- Promoting Technology Innovation: Thin-film solar modules manufactured in integrated solar PV module manufacturing units will be considered in compliance with requirement to use solar PV cells from List-II.
- Implementation: From 1st June 2026.
Challenges for India’s solar Manufacturing Sector:
- Inadequate manufacturing capacity: India imports solar equipment from China (62%), Vietnam, Malaysia etc.
- Limited access to affordable technology for mining & processing of critical minerals hampers solar cell & module production.
- Other: Low R&D, difficulties of sourcing of raw materials, skilled labour shortage etc.
Centre is likely to impose penalties on some carmakers in violation of Corporate Average Fuel Efficiency (I) norms.
About I Norms
- These norms were first notified by the Government in 2017, under the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
- Aim: mitigate fuel consumption by lowering CO₂ emissions, reduce oil dependency and air pollution.
- I norms relate the gasoline equivalent corporate average fuel consumption (in litres/100 km) to the corporate average kerb weight of all the cars sold by any original equipment manufacturer (OEM) in a fiscal year.
- Applicability: for petrol, diesel, liquefied petroleum gas, CNG, etc with gross vehicle weight less than 3500kgs.
Taxonomy (or classification) was launched by the Union Ministry of Steel.
Key features of Green Steel Taxonomy
- Definition of Green Steel: Steel with CO2 equivalent emission intensity of less than 2.2 tonnes of CO2e per tonne of finished steel.
- Star Rating System (based on greenness): The threshold limit for star ratings will be reviewed every three years. And the current threshold is
- Five-star green-rated steel: Emission intensity lower than 1.6 tonnes.
- Four-star green-rated steel: Emission intensity between 1.6 and 2.0 tonnes.
- Three-star green-rated steel: Emission intensity between 2.0 and 2.2 tonnes.
- Nodal Agency: National Institute of Secondary Steel Technology (NISST) will be nodal agency for measurement, reporting, and verification (MRV) and issuance of greenness certificates (issued annually) and star ratings.
Importance of Green Steel Taxonomy
- Advancing National Mission on Green Steel: A proposed ₹15,000 crore mission under the upcoming ‘Green Steel Policy’ to support ocusingional of steel industry.
- Boosting Global Competitiveness Helps Indian steel remain competitive amid global policies like the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CABM). Positions India as a leader in green steel manufacturing.
- Promoting Innovation and Growth: Represent a transformative framework in steel production that will foster innovation, and create a market for low-carbon products in India.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe tagging exercise has been conducted under Project Dolphin.
- Tagging involves attaching a device, marker, or tag to an animal for identification or tracking.
About the Tagging initiative
- Objective: It will help in understanding their migratory patterns, range, distribution, and habitat utilization, particularly in fragmented river systems.
- It was conducted by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC), and implemented by the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) in collaboration with the Assam Forest Department.
- It was funded by the National CAMPA Authority.
- National CAMPA Authority, established under the Compensatory Afforestation Fund (CAF) Act, 2016, manages the National Compensatory Afforestation Fund (under the Public Account of India).
- It was funded by the National CAMPA Authority.
About Project Dolphin
- A MoEFCC-funded project launched in 2020 modelled after Project Tiger.
- It aims at conserving the Ganges River dolphins and the riverine ecosystem.
About Ganges River dolphin (Platanista gangetica)
- It is India’s National Aquatic Animal and is endemic to the Indian sub-continent.
- Habitat: Restricted to freshwater (Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna and Karnaphuli-Sangu river systems of Nepal, India, and Bangladesh)
- Presently, India houses about 90% of the global population of the dolphins.
- IUCN Status: Endangered

Article Sources
1 sourceRatapani Wildlife Sanctuary declared as the 8th Tiger Reserve of Madhya Pradesh
- The other tiger reserves in Madhya Pradesh are Kanha, Satpura, Bandhavgarh, Pench, Sanjay Dubri, Panna and Veerangana Durgavati.
About Ratapani Wildlife Sanctury

- Location: Situated in Raisen and Sehore district of Madhya Pradesh.
- Major sites: Encompasses a World Heritage Site “Bhimbetka Rock Shelters” and many other sites like Ginnourgarh Fort, POW camp, Keri Mahadeo, Jholiyapur dam etc.
- Flora and Fauna:
- The forest in Ratapani is dry deciduous and moist deciduous type, with 55 percent of area covered by teak.
- Major animals are tigers, leopard, sloth bear, hyena, spotted deer, sambar deer etc.
Process of declaring Tiger Reserves in India
- Tiger Reserves are notified by State Governments as per provisions of Section 38V of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 on the advice of the National Tiger Conservation Authority.
- The following steps are involved in the notification:
- The proposal is obtained from the State.
- In-principle approval is communicated from the National Tiger Conservation Authority, soliciting detailed proposals under section 38V of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- National Tiger Conservation Authority recommends the proposal to the State after due diligence.
- The State Government notifies the area as a Tiger Reserve.
Article Sources
1 sourceNational Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) approves Madhav National Park as the newest Tiger Reserve of Madhya Pradesh.
- NTCA is a statutory body constituted under WPA, 1972, as amended in 2006 to administer Project Tiger.
About Madhav National Park
- Location: Situated in northern part of Madhya Pradesh in Shivpuri District (Upper Vindhyan Hills).
- Background: Park was hunting ground of Mughal emperors and Maharaja of Gwaliora and got the status of a National Park in 1958.
- Fauna: Antelopess (Nilgai, Chinkara), Deer (Chital, Sambar and Barking Deer), Leopard, Wolf, Jackal, Fox, Wild Dog, Wild Pig etc
- Flora: Represents Northern Tropical dry deciduous mixed forest as well as Dry thorn forest.
- Other Feature: Sakhya Sagar and Madhav Sagar are the two lakes in the park.
- Madikhera dam is situated in the North Western part of the Park.
Article Sources
1 sourceThe emerging concept and construction of “sponge cities” is an effective approach to solving urban floods.
About Sponge city:
- A sponge city refers to sustainable urban development including flood control, water conservation, water quality improvement and natural ecosystem protection.
- E.g., green roofs, constructed wetlands, increased tree cover etc.
- Benefits: Sponge cities increase air humidity, regulate urban microclimates, and reduce public health risks.
- Sponge cities around the world: Tirana in Albania is creating a ring forest to clean the air; Berlin’s use of green roofs and vertical gardens
New research shows that three sites spread along Denali Fault were once a smaller united geologic feature.
- Location: It is a major strike-slip fault located in Alaska, USA, part of broader tectonic dynamics of Pacific Ring of Fire.
Fault and its Types:
- A fault is a sharp break in the Earth’s crustal rocks.
- Types:
- Normal fault: When two plates, one on top of other, slide past each other
- Reverse faults: When one plate slides under the other, creating a vertical offset.
- Strike-slip faults: When two plates move horizontally past each other.
- Oblique slip fault: Two blocks on either side of fault move in two different directions simultaneously, combining both normal or reverse faulting with a strike-slip component.
Article Sources
1 sourceRecently, Kilauea volcano erupted on Hawaii’s Big Island.
- 99% of gas molecules emitted during a volcanic eruption are Water Vapor (H2O), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), and Sulfur Dioxide (SO2).
- Remaining 1% is comprised of small amounts of hydrogen sulfide, carbon monoxide, hydrogen chloride, hydrogen fluoride etc.
About Kilauea volcano
- About: Among one of world’s most active volcanoes.
- Location: Southeastern part of the island of Hawaii, Hawaii state, U.S.
- Features:
- The Volcano’s summit has collapsed to form a caldera, a broad shallow depression.
- Its slopes merge with those of the nearby volcano Mauna Loa (present in Hawaii’s Volcanoes national park).
Article Sources
1 sourceRecently, India along with 7 other countries launched a new initiative with respect to the fashion and construction industries.
About the Initiative
- It will be funded by Global Environment Facility (GEF)-funded Integrated Programme on Eliminating Hazardous Chemicals from Supply Chains launched for 6 years.
- Members: Cambodia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, India, Mongolia, Pakistan, Peru, and Trinidad and Tobago.
- Objectives: To transform fashion (textile) and construction industries to reduce their environmental impact by reshaping supply chains.
- This effort will promote regenerative design, the replacement of non-renewable materials, resource-efficient production, etc.






