Why in the News?
2025 marks the Communist Party of India's (CPI) its 100th foundation day.
About Communist Party of India

- Background
- Formation of CPI outside India (1920): A group of seven people including leaders like M.N. Roy, Mohd. Ali, Mohd. Shafiq, etc. met in Tashkent (capital of the then Turkistan Republic of the Soviet Union), to form the Communist Party of India.
- Reason behind the formation: Disappointment and disenchantment caused by the sudden withdrawal of the non-cooperation movement and inspiration from the October revolution of 1917 that had established the first workers' state in the world.
- Formation of CPI inside India: A resolution announcing the formation of CPI was adopted during 'Kanpur Communist Conference' in December 1925 bringing together various communist groups active across British India.
- First President: Malayapuram Singaravelu Chettiar
- In May 1923, the 1st May Day celebration in India was organized under his leadership.
- First general secretaries: S.V.Ghate and J P Bagerhatta
- Founding members of the party: Satyabhakta, M.N.Roy, E.T.Roy, Abani Mukherjee, Mohammad Ali, Hasrat Mohani etc.
- First President: Malayapuram Singaravelu Chettiar
- Prominent Leaders: M.N. Roy, Evelyn Trent-Roy (wife of M.N.Roy), Abani Mukherjee, Rosa Fitingov, Mohmmad Ali, Mohmmad Shafiq, A. K. Gopalan, S.A. Dange, E.M.S. Namboodiripad, P.C. Joshi, Ajay Ghosh and P. Sundarraya etc.
- Ideology: They followed Marxist and Leninist ideas.
- Marxism-Leninism is a political ideology and a system of government based on the ideas of Karl Marx and Vladimir Lenin.
- It combines Marxist socialism with Leninist vanguardism, emphasizing the role of a communist party in leading a revolution to establish a socialist state and eventually a communist society.
- Publications supported by CPI: Ganavani (Bengali weekly), Mehnatkash (Urdu weekly from Lahore) and Kranti (Marathi weekly from Bombay).
- Major goals of CPI: Nationalization of banks, workers and peasants' rights, land reforms, abolition of zamindari, formation of socialist state etc.
- Key events in the history of CPI:
- Ban: British government declared CPI illegal in July 1934 and the ban was lifted in 1942.
- Split: In 1964 following the ideological rift between Soviet Union and China, CPI split into the CPI (pro-Soviet faction) and CPI (Marxist) (pro-China faction).
Role of CPI in Indian Freedom Struggle
- Mobilization of masses: With the CPI led organizations like All India Trade Union Congress (AITUC) in 1920, All India Kisan Sabha (AIKS) and All India Student's Federation in 1936 and Mahila sanghmas, CPI mobilized masses from every section of the society into the Indian Freedom struggle.
- Indian National Movements like non-cooperation, civil disobedience saw huge participation from women, peasants, workers and middle class.
- Social reforms: CPI was actively engaged in social reforms by advocating rights for Dalit equality, unity of Hindu and Muslims and formation of united nation against colonial repression.
- Kerala: CPI leaders like AK Gopalan and P Krishna Pillai led the satyagraha in Guruvayur for entry of Untouchables inside the temple.
- Maharashtra: Under the leadership of R.B. More, communists were the organizers of Ambedkar led Chavdar Lake Satyagraha at Mahad in March 1927.
- Demand for Full Independence: It was the CPI who first sent the manifesto in the shape of an open letter with the demand for full independence to the Ahmedabad session in 1921 and subsequently to the Gaya session in 1922 of Indian National Congress (INC).
- Such resolution was later passed in INC session of Lahore in 1929.
- Ideological Influence: Through organizations like the All India Students Federation and the All India Progressive Writers Association, communists propagated the idea of overthrowing the British rule through the revolutionary activities.
- The British were gravely concerned about the growth and influence of the communists and targeted and arrested communist leaders in Meerut Conspiracy case 1929.
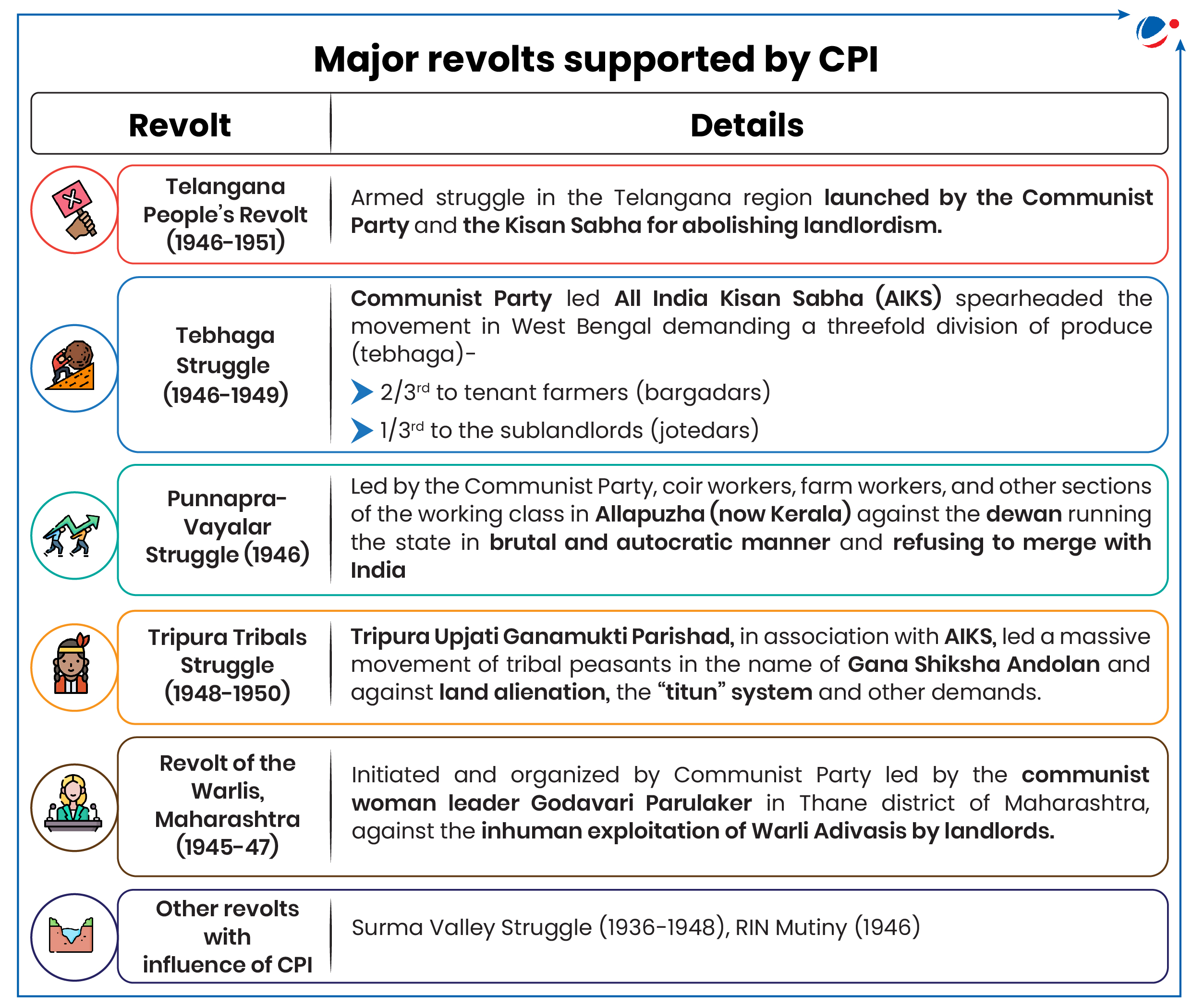
- Support to struggles: CPI and its leaders supported several major peasant and worker struggles in India. (see infographic)
- Role of CPI in Constitution making
- Idea of constitution: It was M.N. Roy who formally proposed the idea of constitution in 1934, similarly CPI also put forth the idea of a constituent assembly.
- Ideals of Constitution: CPI significantly influenced the ideals of secularism, justice, equality, universal suffrage, minority rights, land reforms etc. which are incorporated in the Constitution.