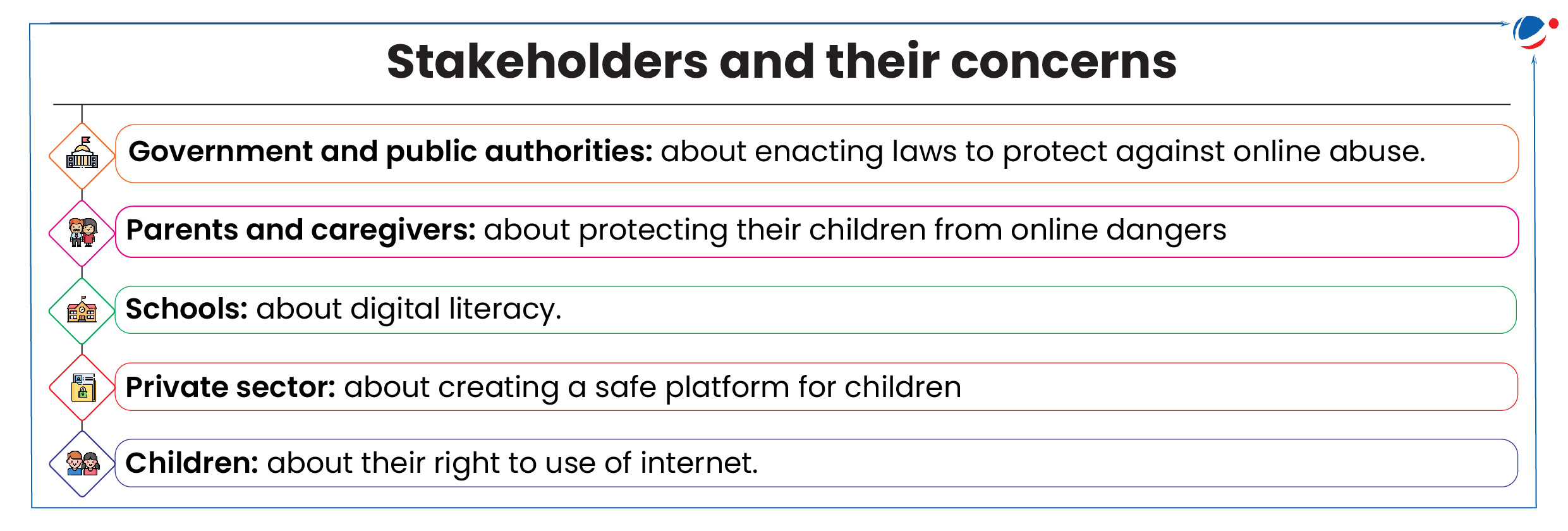
Why in the news?
Australia has become the first country to pass a law banning social media use for children under the age of 16.
Key Provisions of the Online Safety Amendment (Social Media Minimum Age) Bill 2024
- Minimum Age Requirement: Require age‐restricted social media platforms to take reasonable steps to prevent Australians under 16 years old from having accounts.
- Responsibility of Social Media Providers: Companies are responsible for ensuring children under the minimum age cannot access their platforms.
- Fines for Non-Compliance: Impose maximum penalties of up to $49.5 million for a breach of the minimum age obligation.
Reasons for Childs addiction to Social Media
- Peer Influence: Children are influenced by peers and social media's validation system (likes, comments, shares).
- Instant Gratification: Social media offers immediate rewards, releasing dopamine, which can lead to addictive behavior as children crave these instant rewards.
- Parents: In modern society, especially in urban society where both parents are working, parents are unable to provide adequate attention to a child, leading to a modern phenomenon of the "iPad kid".
- Escapism: Children turn to social media to escape real-world issues like loneliness and stress, developing emotional dependency on the platforms.
- Algorithm-Driven Engagement: Algorithms tailor content to keep children engaged longer, making it harder to stop using social media.
Arguments supporting and opposing the ban
Supporting the ban | Opposing the ban |
|
|
Government initiative to protect children online
- Section 67B of the Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000: Provides stringent punishment for publishing, transmitting, or viewing Child sexual abuse material online.
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023: Requires data fiduciaries to collect "verifiable parental consent" for processing personal data of children under 18.
- The National Commission of Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR): It has established an online complaint management system.
Global steps to protect children online
Country | Policy/Regulation | Details |
United States | Children's Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) (1998) & Children's Internet Protection Act (CIPA) (2000) |
|
European Union | General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) | Parental consent is required for the processing of personal data for children under the age of 16, though the member states can lower that limit to 13. |
UK | Online Safety Act (2023) | Sets tougher standards for social media platforms such as Facebook, YouTube and TikTok – including on appropriate age restrictions. |
Way ahead
- Safety-by-Design
- Privacy by Default: Tech companies must provide default privacy settings for minors, especially regarding data collection. For example, the UK's Age Appropriate Design Code.
- AI Detection of Harmful Content: Use AI tools to identify and remove harmful interactions or inappropriate content in children's feeds.
- Regulations:
- Accountability for Tech Companies: Instead of banning, tech companies can be held accountable for creating safer, child-friendly spaces.
- Social media platforms like Meta set age limits (13+) to ensure children's safety online.
- Investing in a Children's Internet: Governments could create a "Children's Internet" – a safe, educational space free from mainstream social media risks.
- Accountability for Tech Companies: Instead of banning, tech companies can be held accountable for creating safer, child-friendly spaces.
- Improving Digital Skills and Education:Educate children and parents about responsible online behavior, digital literacy, and self-regulation.
- For E.g., Kerala's Digital De-Addiction (D-DAD) centres offer free counseling for kids struggling with digital addiction.
- Parental Involvement and Control:
- Create Accounts Together: Set up social media accounts with your child to ensure proper privacy settings, strong passwords, and content limitations.
- Establish Screen Time Limits: Implement tools to manage screen time, promoting healthier digital habits.
- Enable Activity Reports: Regularly review detailed reports on your child's social media activity to identify any concerns early.
- Protect Personal Information: Teach your child to keep personal details (address, phone number) private to avoid online dangers.
- Report and Block Unwanted Interactions: Teach your child how to report or block harmful accounts to protect against cyberbullying and harassment.
Related News: Brain RotThe term "brain rot" has been named the Oxford Word of the Year 2024. About Brain Rot
|






