55th GST Council Meeting
55th Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council meeting was held in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan.
- The meeting resulted in several significant decisions aimed at tax rate changes, trade facilitation, and compliance streamlining under GST.
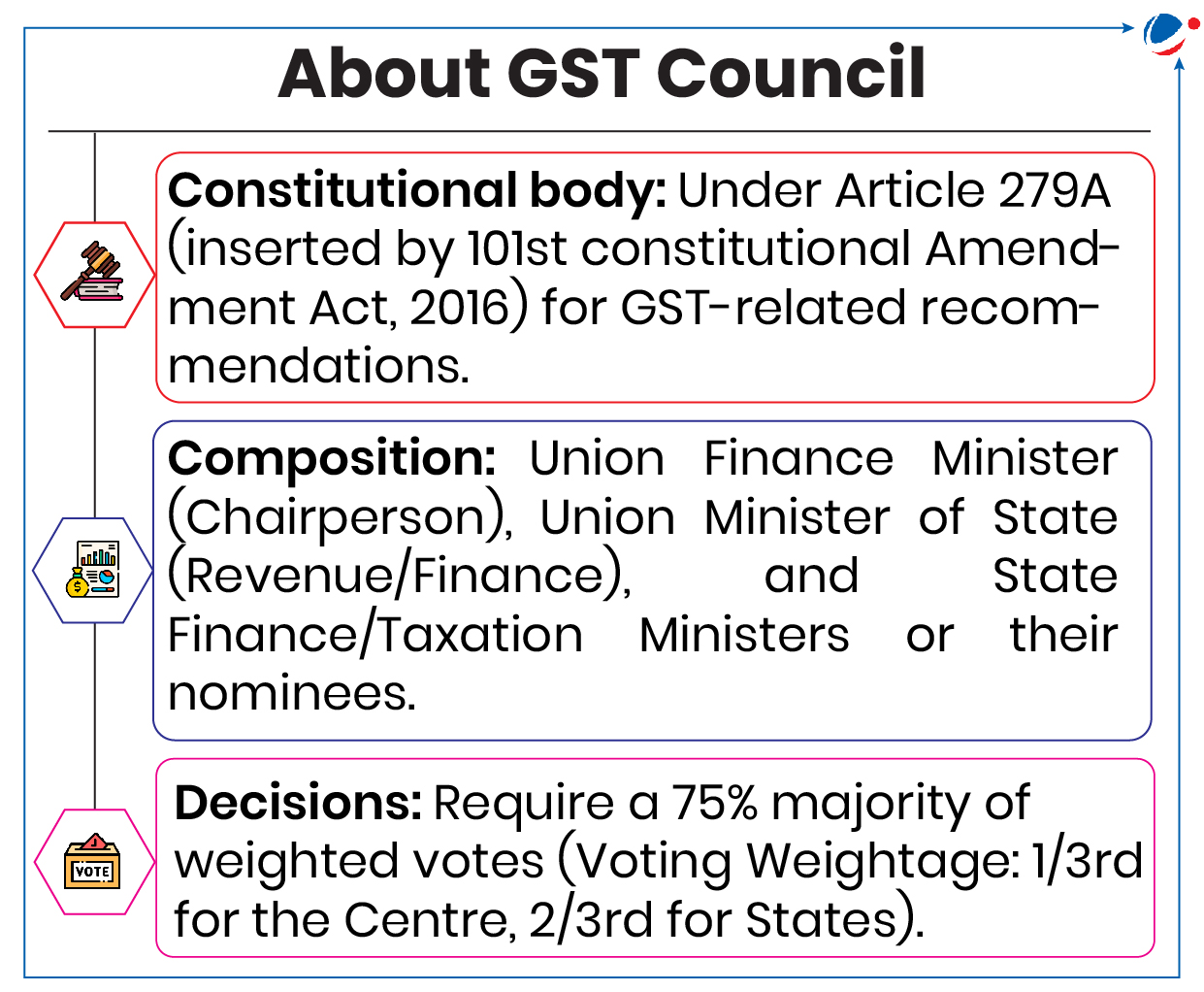
Key-recommendations by GST Council
- Full exemption of GST on gene therapy.
- Exemption of GST on contributions by general insurance companies from third-party motor vehicle premiums for Motor Vehicle Accident Fund.
- Reduction in the GST rate on Fortified Rice Kernel (FRK) to 5%
- Others
- Pepper: whether fresh green or dried and raisins when supplied by an agriculturist is not liable to GST
- Popcorn: when popcorn is mixed with sugar (e.g. caramel popcorn), it would attract 18% GST.
- Tags :
- Gene Therapy
- GST Council
- GST on popcorn
Articles Sources
All-India House Price Index (HPI)
Reserve Bank of India released its quarterly House Price Index (HPI)
- HPI: Increased by 4.3% year on year in quarter 2: 2024-25, up from 3.3% in the previous quarter.
- Bengaluru saw the highest growth at 8.8%, while Kanpur experienced a decline of -2.0%.
About All-India Home Price Index (HPI)
- Base: 2010-11 = 100
- Data Source: Transaction-level data from registration authorities in 10 major cities.
- Cities Covered: Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, Chennai, Delhi, Jaipur, Kanpur, Kochi, Kolkata, Lucknow, Mumbai
- Tags :
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
- House Price Index (HPI)
Consumer Confidence Survey (CCS)
Latest RBI survey shows weakened consumer confidence in India’s economy, employment, and spending.
About CCS
- It is an economic indicator reflecting optimism or pessimism about the economy and personal finances.
- It gauges the economy’s health from the consumer’s perspective. High confidence typically leads to increased consumer spending.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) measures it through a bi-monthly CCS.
- CCS responses are measured through two indexes:
- Current Situation Index (CSI): Consumer sentiment about the economy, employment, and prices compared to a year ago.
- Future Expectation Index (FEI): Expectations about the economy, employment, and prices a year ahead.
- Tags :
- CCS
- FEI
SFBs To Extend Credit Line Through UPI
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently decided to permit Small Finance Banks (SFBs) to extend pre-sanctioned credit lines through Unified Payment Interface (UPI).
Credit Line through UPI by SFBs
- Under this facility, payments through a pre-sanctioned credit line issued by a Bank to individuals, with prior consent of the individual customer, are enabled for transactions using UPI System.
- Previously, in September 2023, RBI allowed operations of pre-sanctioned credit limits through UPI by Scheduled Commercial Bank to individuals.
- Significance: Aims to deepen financial inclusion and enhance formal credit, particularly for ‘new to credit’ customers.
About SFBs
- Origin: Announced in Union Budget 2014-15.
- Objective: To further financial inclusion by –
- provision of savings vehicles primarily to unserved and underserved sections of the population, and
- supply of credit to small business units; small and marginal farmers; micro and small industries; and other ocusingio sector entities, through high technology-low cost operations.
- Registration: As a public limited company under Companies Act, 2013.
- Licensed under: Section 22 of Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
- Regulated by: RBI.
- Applicability of CRR and SLR: Similar to CRR and SLR requirements for Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs).
- Capital requirement: Minimum paid-up voting equity capital of ₹200 crore (except for such SFBs which are converted from Urban Cooperative Banks).
- Priority Sector Lending (PSL) norms: Required to extend 75% of its Adjusted Net Bank Credit (ANBC) to the priority sectors, as classified by RBI.
- Tags :
- UPI
- Unified Payment Interface (UPI)
- SFB
Unified Payments Interface (UPI) Lite
RBI has revised transaction limits to ₹ 1,000 from ₹ 500 earlier for UPI Lite to encourage use of UPI.
- RBI also raised the total limit for offline transactions on UPI Lite to ₹ 5,000 from ₹ 2,000.
About UPI Lite
- It is a payment solution that leverages trusted NPCI Common Library application to process low value transactions without utilizing a Remitter bank’s core banking systems in real-time, while providing adequate risk mitigation.
- With the consent of its UPI registered customer, an issuing bank can create an escrow on the customer’s account up to a set limit.
- Tags :
- Unified Payment Interface (UPI)
- UPI Lite
Index Of Eight Core Industries (ICI)
The Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI) increased by 3.1% in October 2024 compared to October 2023.
About ICI
- The ICI measures combined & individual performance of production of eight core industries viz. Coal, Crude Oil, Natural Gas, Refinery Products, Fertilizers, Steel, Cement & Electricity.
- The Eight Core Industries comprise 40.27 % of the weight of items included in Index of Industrial Production (IIP).
- The Office of Economic Adviser, Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Union Ministry of Commerce is responsible for Compiling and releasing monthly ICI.
- Tags :
- Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI)
World Bank Released Annual International Debt Report (IDR) 2024
The IDR features external debt statistics and analysis for low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) that report to the World Bank’s Debtor Reporting System (DRS).
Key highlights
- Rising External Debt: Total external debt of LMICs rose by 2.4% in 2023, reaching $8.8 trillion.
- Factors Driving Indebtedness
- High Interest Rates: Tight monetary policies in high-income countries pushed interest rates to a 20-year high.
- Bangladesh and India experienced over 90% increases in interest payments in 2023.
- Other Factors: Inflation, depreciating currencies, and global economic uncertainty due to armed conflicts and trade fragmentation.
- High Interest Rates: Tight monetary policies in high-income countries pushed interest rates to a 20-year high.
- Impact of rising debt: Budget strain impacted critical sectors like health, education, and environmental programs.
Way Ahead
To promote sustainable and inclusive debt solutions, the UN Trade and Development earlier proposed the following measures:
- Global Financial Reforms: Comprehensive reforms to prevent a widespread debt crisis and create an inclusive financial system.
- Mitigating Predatory Lending: Increase concessional financing and reduce information asymmetry (between lender and borrowers) and discourage exploitative lending practices.
- Crisis Resilience: Implement climate-resilient debt clauses and standstill rules to pause repayments during crises.
- Improved Restructuring Mechanisms: Establish automatic restructuring rules and a Global Debt Authority to guide and coordinate sovereign debt management.
- Tags :
- International Debt Report (IDR) 2024
Articles Sources
Tax Justice Network Released ‘State of Tax Justice 2024’ Report
Report highlights tax losses to global tax abuse and provides assessment of global tax reforms.
Key Observations of Report
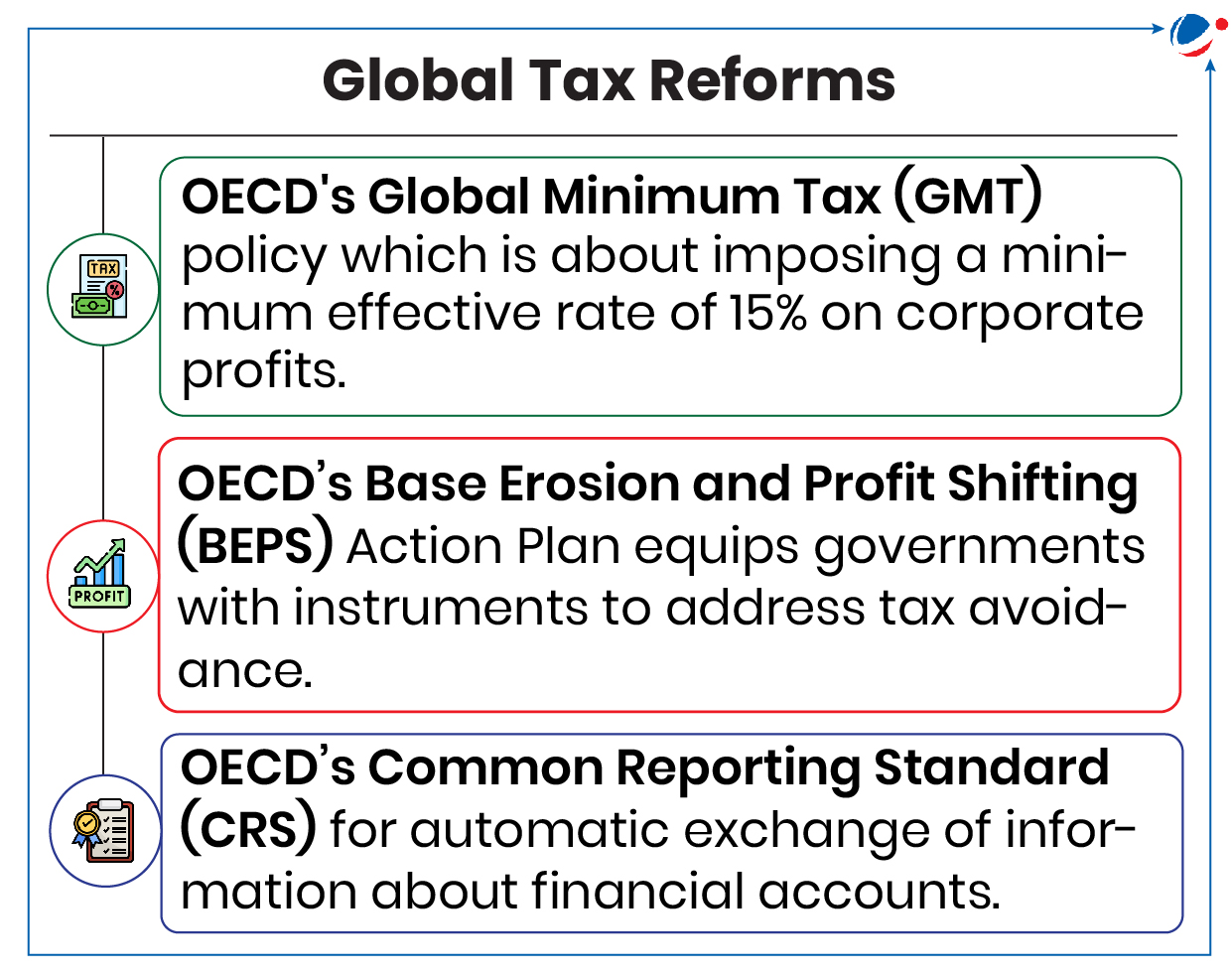
- Countries are losing US$492 billion a year to global tax abuse.
- Out of this, two-third (US$347.6 billion) is lost to multinational corporations shifting profit offshore to underpay tax.
- Remaining one-third (US$144.8 billion) is lost to wealthy individuals hiding their wealth offshore.
- Nearly half the losses (43%) are enabled by the eight countries (all OECD members) that remain opposed to a UN tax convention: Australia, Canada, Israel, Japan, New Zealand, South Korea, UK and US.
- Countries of Global North lose largest amount of tax revenues in absolute terms while countries of Global South endure the deepest losses as a share of their tax revenues.
- Such tax loss results in foregone public services, increased inequalities between countries, and limited domestic businesses.
Policy recommendations
- Adopt a UN tax convention, which would establish globally inclusive international tax rules, combat cross-border tax evasion, and restore the potential for progressive national taxation.
- A UN framework convention on international tax cooperation will be negotiated from 2025-2027.
- Having excess profits and wealth taxes as it can reduce economic inequality, limit monopoly power, and ensure that those who benefit most from society contribute proportionately to the social good.
- Tags :
- BEPS
- tax justice network
Articles Sources
Global Wage Report Released By ILO
Global Wage Report (2024-25) by International labour organization (ILO) provides detailed look at wage trends across the globe highlighting changes in wage inequality and real wage growth.
Key Findings
- Trends in wage growth
- Global: After falling in 2022, global real wage growth recovered in 2023.
- Regional: Average wages are increasing faster in Asia and the Pacific, Central and Western Asia, and Eastern Europe compared to the rest of the world.
- Around 9.5% of the Indian workers are low paid wage workers

- Trends in labour income inequality
- Wage inequality: Overall it has witnessed a declining trend globally.
- However, it is highest in low-income countries and lowest in high-income countries.
- Informal Economy: Women and workers are overrepresented at the low end of the wage distribution.
- Moreover, informal employment has increased in absolute terms due to insufficient formal job creation
- Wage inequality: Overall it has witnessed a declining trend globally.
- Labour Productivity (1999-2024): It has increased more rapidly in high-income countries than real wages.
Way forward
- Increased research: Robust data and statistics should be used for measuring and estimating change in inequality.
- National strategies to reduce wage inequality: Wages should be set with consideration of economic factors as well as needs of workers and their families and should promote gender equality, equity and non-discrimination
- Redistribution of Income through system of taxes and social transfers: It should be followed with policies promoting productivity, decent work and the formalization of the informal economy.
- Tags :
- Global Wage Report
Windfall Tax
Government abolishes windfall tax on crude oil, ATF, petrol, and diesel exports.
About Windfall Tax
- A windfall tax is a tax imposed by governments on certain industries that experience significantly above the average profits due to favorable economic conditions.
- E.g., India imposed windfall tax on domestic crude oil production in July 2022, following a sharp rise in global crude oil prices.
- These taxes are designed to capture a portion of these unexpected gains to fund public projects, reduce deficits, or redistribute wealth.
- Tags :
- Windfall Tax
Atmanirbhar Clean Plant Programme (CPP)
Asian Development Bank (ADB) and India signed a $98 million loan agreement for developing regulatory framework and institutional systems to effectively implement the CPP for horticulture.
About CPP
- Genesis: Approved under the Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH).
- MIDH is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme for the holistic growth of the horticulture sector covering fruits, vegetables, root & tuber crops, etc.
- Purpose: Provide farmers access to virus-free, high-quality planting material, leading to increased crop yields.
- Key Components
- 9 world class state-of-the-art Clean Plant Centers (CPCs) equipped with advanced diagnostic therapeutics and tissue culture labs.
- Certification Framework, supported by a regulatory framework under the Seeds Act 1966.
- Support for large-scale nurseries for the development of infrastructure.
- Implementing Agencies: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare through the National Horticulture Board (NHB) and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research.
- It will be Implemented from 2024-30 with 50% assistance from ADB.
Other Key Initiatives for Horticulture Sector
- Coordinated programme on Horticulture Assessment and Management using Geoinformatics (CHAMAN), develop and firm up scientific methodology for estimation of area and production under horticulture crops.
- Kisan Rail services, for transporting perishables including fruits and vegetables.
- Capital Investment Subsidy Scheme by NHB.

- Tags :
- Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- Clean Plant Programme (CPP)
Articles Sources
RBI Increases Limit For Collateral-Free Agricultural Loan
The move aims to provide enhanced financial access to farmers, ensuring they have sufficient resources to meet their operational and developmental needs without the burden of providing collateral.
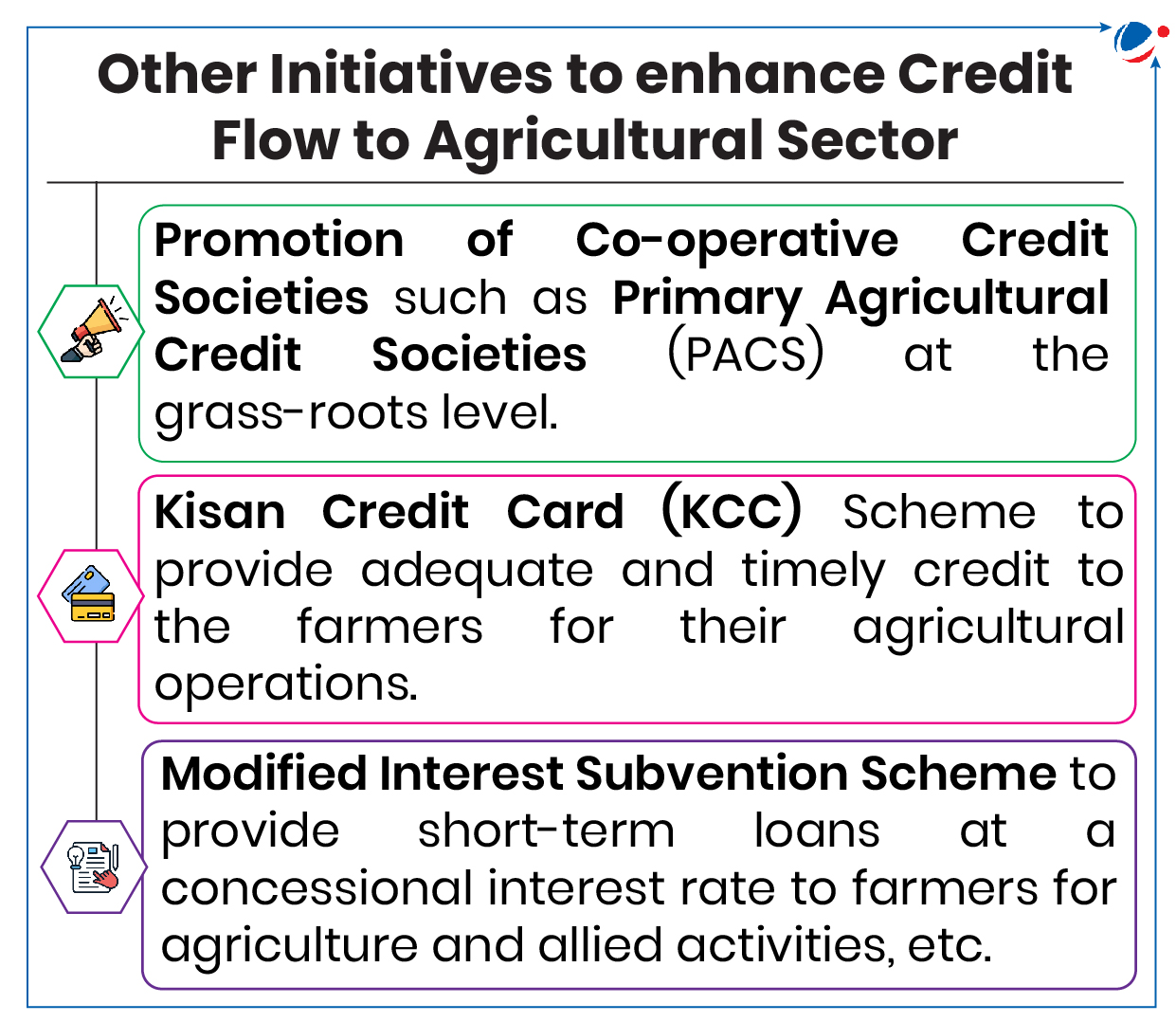
Key directives to banks include:
- Enhanced limit for collateral-free agricultural loans, including loans for allied activities, from the existing loan limit of ₹1.6 lakh per borrower to ₹2 lakh.
- Timely implementation (from January 01, 2025) of revised guidelines to ensure swift financial assistance.
- Awareness campaigns to inform farmers and stakeholders of the new directive.
Significance of the Enhanced Limit
- Enhanced Credit Accessibility: Increases access to loans, particularly for small and marginal farmers (over 86% of the sector).
- Streamlined Loan Disbursement: Simplifies the loan process, encouraging higher uptake of Kisan Credit Card (KCC) loans.
- Promotion of Financial Inclusion: Expands formal financial access to the rural farming community and fosters credit-driven economic growth, aligning with the government’s long-term vision for sustainable agriculture.
Key issues in disbursement of Agricultural Credit: Skewed focus on short-term crop loans, rising fiscal burden due to loan waivers, over-reliance on non-institutional credit, etc.
- Tags :
- Agriculture Credit
Credit Guarantee Scheme For E-Nwr Based Pledge Financing (CGS-NPF) Launched
It allows farmers to avail loans against electronic Negotiable Warehouse Receipts (e-NWRs) after depositing their commodities in Warehousing Development and Regulatory Authority (WDRA) accredited warehouses.
About e-NWRs
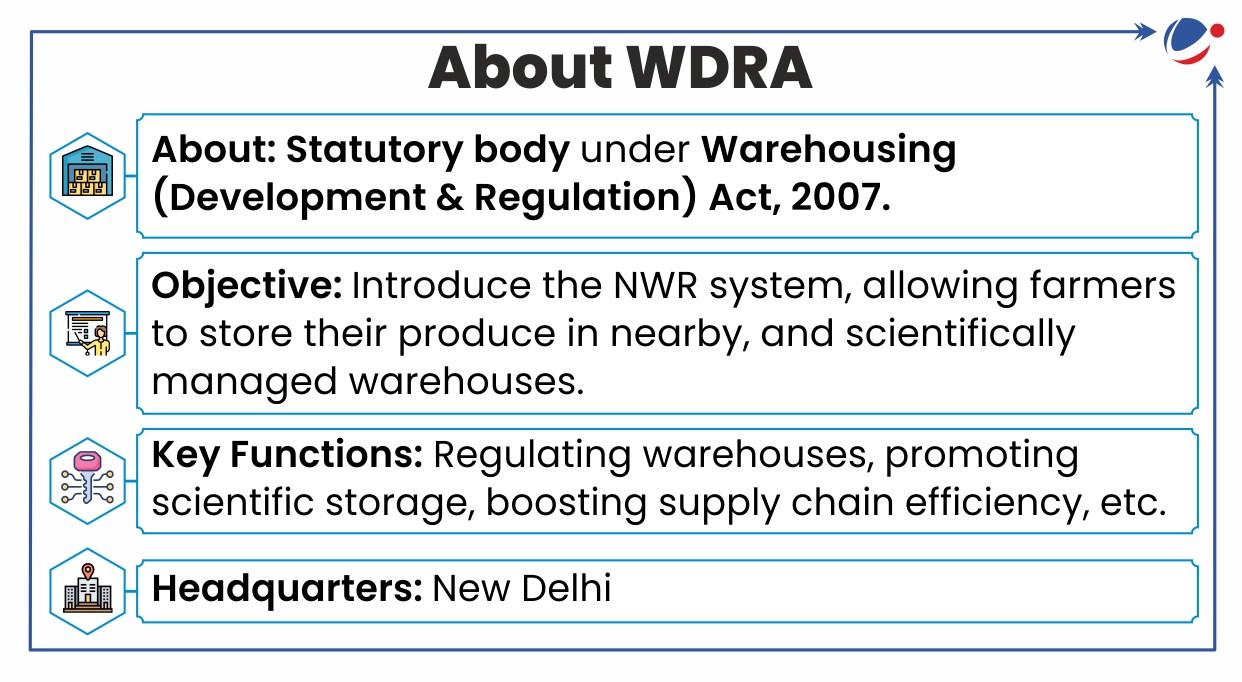
- It is a digital version of the traditional warehouse receipt, governed by the Warehousing (Development and Regulation) Act of 2007.
- It allows goods deposited in a registered warehouse to be transferred or sold through endorsement.
- Since 2019, WDRA has made the issuance of NWR mandatorily in electronic form.
Key Features of the Scheme
- Ministry: Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution
- Total Corpus: Rs 1,000-crore for post-harvest finance
- Coverage: Loans up to Rs. 75 lakhs for agricultural purpose and up to Rs. 200 Lakhs for non-agricultural purpose.
- Eligible Institutions: All scheduled banks and cooperative banks.
- Eligible Borrowers: Small and marginal farmers, women, SC/ST/PwD farmers, MSMEs, traders, FPOs, and farmer cooperatives.
- Risks Covered: Credit and warehouseman risks.
- Guarantee coverage: 85% for loans up to Rs. 3 lakh and 80% for loan between 3 to 75 lakhs for small and marginal farmers/women/SC/ST/PwD.
- 75% for other borrowers.
Significance of the Scheme
- Minimise distress selling by farmers: Ensuring availability and accessibility of finances for the targeted beneficiaries.
- Instill confidence in bankers, addressing the default arising out of both credit and warehouseman risk.
- Tags :
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for e-NWR
Articles Sources
Kisan Pehchan Patra
Centre has advised states to adopt a ‘camp-mode approach’ to facilitate inclusive, efficient, and rapid farmer registration.
About Kisan Pehchan Patra
- It is an Aadhaar-linked unique digital identity that is linked dynamically to state’s land records, besides having information e.g. demographic, crops sown and ownership details.
- ID will form the core of the ‘Farmers Registry’, one of the three registries under the ‘Agri Stack’.
- Agri Stack is one of the components of the Digital Agriculture Mission, Other being Krishi Decision Support System
- Agristack Consists of 3 databases: Farmers’ Registry, Geo-referenced Village Maps, and Crop Sown Registry.
- Tags :
- Kisan Pehchaan Patra
- land records
Kisan Kavach
Scientists affiliated to the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) have developed an Indigenous ‘anti-pesticide’ suit called Kisan Kavach.
About Kisan Kavach
- Developed by BRIC-inStem, Bangalore, it is designed to protect farmers from the harmful effects of pesticide exposure.
- The kit consists of a trouser, pullover, and a face-cover made of ‘oxime fabric’.
- Oxime fabric can chemically breakdown any of the common pesticides that get sprayed onto cloth or body during spraying operations
- Tags :
- Kisan Kavach
National Legal Metrology Portal (eMaap)
Department of Consumer Affairs is developing eMaap to integrate State Legal Metrology Departments and their portals into a unified National System.
- Presently, State Governments are using their own portals for registration of packaged commodities, issue of licenses and verification/stamping of weighing & measuring instruments
About eMaap
- Aim: Streamline processes for issuing licenses, conducting verifications and managing enforcement and compliance.
- Benefits:
- Foster ease of doing business and Transparency in trade practices by minimizing compliance burdens, reducing paperwork under Legal Metrology Act, 2009.
- Enables data-driven decision-making, streamlines enforcement activities, and facilitates policy formation, ensuring a robust and efficient regulatory framework.
- Tags :
- eMaap
Articles Sources
Merchant Shipping Bill, 2024
Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways introduced Merchant Shipping Bill, 2024 in Lok Sabha.
- Bill seeks to repeal Merchant Shipping Act, 1958.
- Bill aims to consolidate and amend law relating to merchant shipping to ensure compliance with India’s obligation under maritime treaties and international instruments to which India is a party.

Key Highlights of Bill
- Establishment of National Shipping Board: To advise Central Government on matters relating to Indian shipping.
- It shall have power to regulate its own procedure for conduct of its business.
- Maritime Administration: Central Government appoint a person to be Director-General of Maritime Administration.
- Registration of Vessels: Ownership allowed by
- Citizen of India including Non-Resident Indian or an Overseas Citizen of India;
- Company/ body established by any Central Act or State Act having its registered office of business in India.
- Transfer of Indian vessel or share: No person shall transfer/acquire any Indian vessel at any time during which India’s security or any part of territory is threatened by sanction, war or external aggression and proclamation of emergency.
- Prevention and containment of pollution: Every vessel shall comply with provisions of international conventions, as applicable, namely MARPOL Convention; Anti-Fouling Systems Convention; etc. to prevent pollution.
- Tags :
- Merchant Shipping Bill, 2024
Coastal Shipping Bill, 2024 introduced in the Lok Sabha
Bill’s purpose is to consolidate and amend laws governing coastal shipping (Uniformity in regulation), promote coastal trade, connectivity and encourage domestic participation.
- Coastal shipping in India holds great potential owing to its vast coastline (~ 7,500 km) and proximity to important global shipping routes.
Key Highlights of Bill
- Prohibition of coasting trade: Prohibition of trade in coastal water without license by vessels other than Indian vessels.
- Permitting Inland vessels to engage in coastal trading.
- National Coastal and Inland Shipping Strategic Plan: For development, growth and promotion of coastal shipping.
- National Database of Coastal Shipping: To ensure transparency of procedures and aid in information sharing.
- Licensing of chartered vessels: Empower the Director-General to issue a license after taking into consideration certain factors including citizenship of crew and building requirements of vessel.
- No license granted shall be suspended, revoked or modified, unless the license has been given a reasonable opportunity of being heard.
- Other Provisions: Provision for compounding of certain offences and imposition of penalty by the principal officer; and provision for empowering the Director-General to call for information in respect of certain matters.

- Tags :
- Coastal Shipping Bill, 2024
‘Jalvahak’ Scheme to boost Inland Waterways
Union Government unveiled ‘Jalvahak’ Scheme which aims to encourage business enterprises with safe and timely delivery of cargo through inland waterways, in a cost effective manner.
Scheme aims to incentivize cargo movement via inland waterways, promoting sustainable and cost-effective transportation across National Waterways (NW)-1, NW-2, and NW-16.

About the Jalvahak scheme
- Ministry: Union Ministry of Ports, Shipping & Waterways.
- To be jointly implemented by the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) and Inland & Coastal Shipping Ltd (ICSL), a subsidiary of the Shipping Corporation of India.
- Aim: Schemes aim at Incentivizing Modal Shift of 800 Million Tonnes KMs with an investment of ₹95.4 crores.
- Time frame: Valid for an initial period of 3 years.
- Route: Fixed Day Scheduled Sailing Service will ply vessels between Kolkata – Patna – Varanasi – Patna – Kolkata stretch of National Waterways (NW)-1, between Kolkata and Pandu in Guwahati on NW 2, and NW 16 via Indo Bangladesh Protocol Route (IBPR).
- Incentive: Offers reimbursement upto 35% of total operating expenditure incurred while transporting cargo.
- Criteria: Provides direct incentive to transport their goods via inland waterways for a distance of more than 300 km.
- Significance: Reduced logistics costs, decongestion of road and railways, and adapting to a sustainable mode of transportation.
- Tags :
- ‘Jalvahak’ Scheme
First Ever Auction of Minerals in Offshore Areas
Ministry of Mines Launched first ever tranche of auction of mineral blocks in offshore areas
- It is a major step forward in exploring India’s extensive offshore mineral resources within its Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
Key Details of the Offshore Mining Auction
- Mineral Blocks: Auction includes 13 mineral blocks spanning across the Arabian Sea and Andaman Sea.
- Types of Mineral and corresponding Region: Construction sand (Off the coast of Kerala, Arabian Sea), lime-mud (Off the coast of Gujarat, Arabian Sea) and polymetallic nodules and crusts (Off Great Nicobar Islands, Andaman Sea).
Offshore Mining or Deep Sea Mining
- It is the process of retrieving mineral deposits from the deep seabed, at a depth of more than 200 meters.
- Geological Survey of India (GSI) has identified about six lakh sq. kms of offshore area having potential for offshore mining.
Significance of Offshore Mining for India
- India’s offshore mineral reserves include gold, diamond, copper, nickel, cobalt, copper, manganese, and rare earth elements essential for development.
- Offshore mining will increase availability of minerals (Atmanirbharta in critical minerals), unlock India’s blue economy and reduce dependence on imports.
- These minerals are critical for infrastructure development, high-tech manufacturing and green energy transition.
Challenges in Offshore Mining
- Lack of private participation, requirement of highly skilled labour and capital, environmental challenges like habitat destruction, disruption of marine ecosystems etc.

- Tags :
- Minerals in Offshore Areas



