Recently, 10,000 newly established Multipurpose Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (M-PACS), along with dairy and fisheries cooperative societies were inaugurated.
- Union Government aims to establish 2 lakh new PACS within the next 5 years.
About PACS
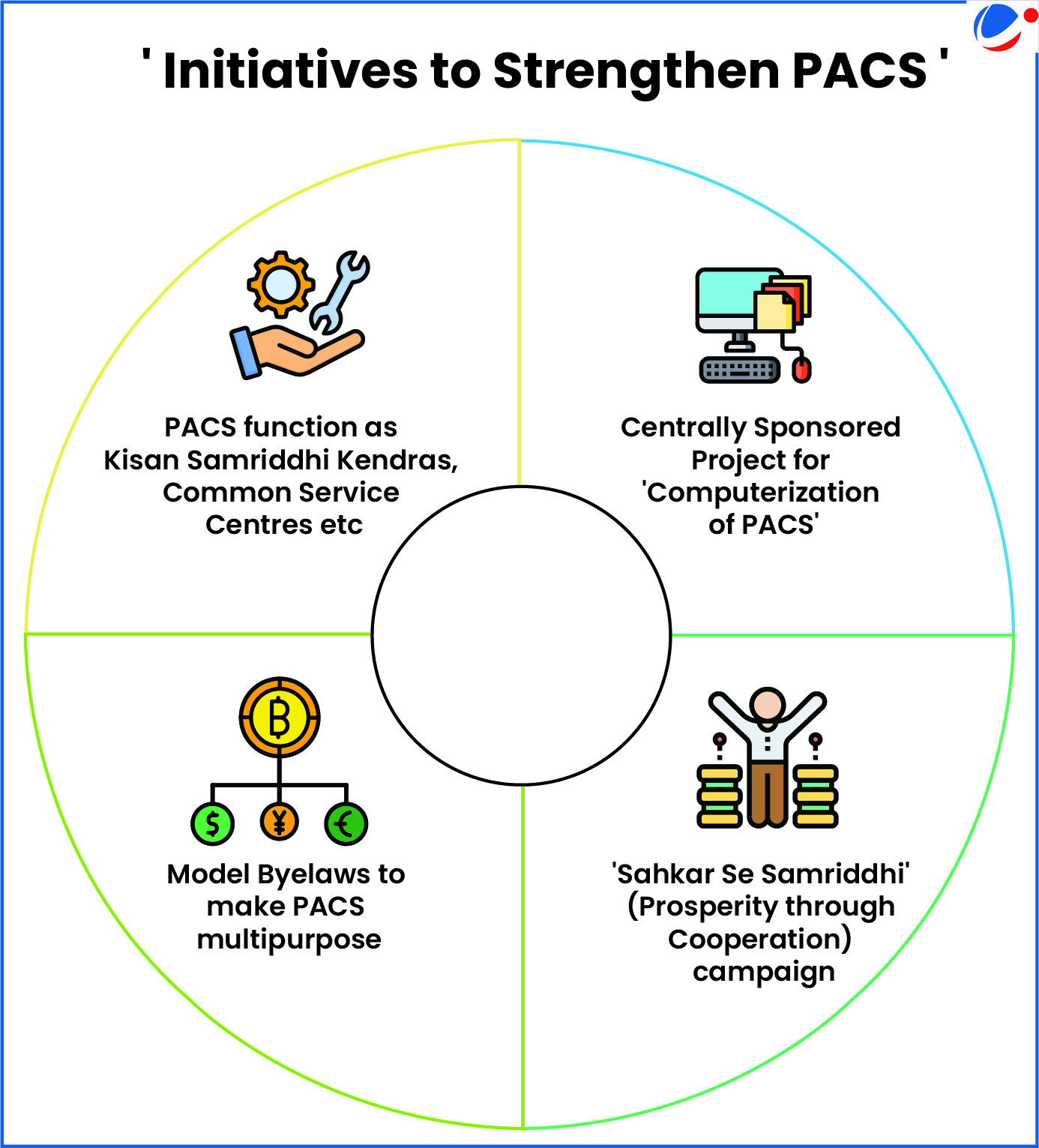
- About: Grass root level credit institution of the short-term co-operative credit structure.
- Functions: Deals with the rural (agricultural) borrowings, collection & repayments of loans, undertaking distribution & marketing functions etc.
- Serves as the final link between the ultimate borrowers and the higher financing agencies (Scheduled Commercial Banks, NABARD, etc.).
- Membership: Individual farmers, artisans, and members of other weaker sections of the society as shareholder.
- Regulation: Registered under Cooperative Societies Act, 1912, and administered by concerned State Registrar of Cooperative Societies (RCS).
- They are outside purview of Banking Regulation Act, 1949 and are not directly regulated by RBI.
- Significance: Promotes financial inclusion; building block of the cooperative banking system; brings farmer communities closer to institutional credit, inputs, market, value addition, etc.
Challenges faced
- Organizational weaknesses in terms of inadequate geographical coverage and weaker credit units.
- Inadequate financial resources in relation to short & medium-term credit needs of rural economy.
- Outstanding large over-dues (NPAs) of more than 40% of demand and credit outstanding.
- Others: Absence of well-trained human resources, lack of digital infrastructure, etc.







