Why in the News?
India unveiled its updated NBSAP for 2024-30 at CoP-16 to the UN Convention on Biological Diversity (UNCBD) reinforcing its commitment to biodiversity conservation through targeted actions.
About NBSAP
- Article 6 of the UNCBD requires every party to the convention to prepare NBSAPs.
- It is the primary tool for mainstreaming biodiversity and implementation of the UNCBD at the country level.
- It provides a framework for biodiversity conservation, enables focus on sustainable use of biological resources, and ensures fair and equitable sharing of benefits derived from them.
Key highlights of the updated NBSAP 2024-30
- Approach: Adopts a 'Whole of Government' and 'Whole of Society' approach aligning itself with KMGBF to halt and reverse biodiversity loss by 2030, with a longer-term vision of living in harmony with nature by 2050.
- National Biodiversity Targets (NBTs): 23 NBTs focused on 3 themes – reducing threats to biodiversity; ensuring sustainable use of resources; and enhancing tools for implementation.
- Acknowledges environmental challenges: Outline strategies to address them through ecosystem restoration, species recovery programmes, community-driven conservation efforts etc.
- Implementation framework: Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) serves as the central agency advocating a collaborative governance model, promoting a bottom-up approach engaging local communities and various sectors.
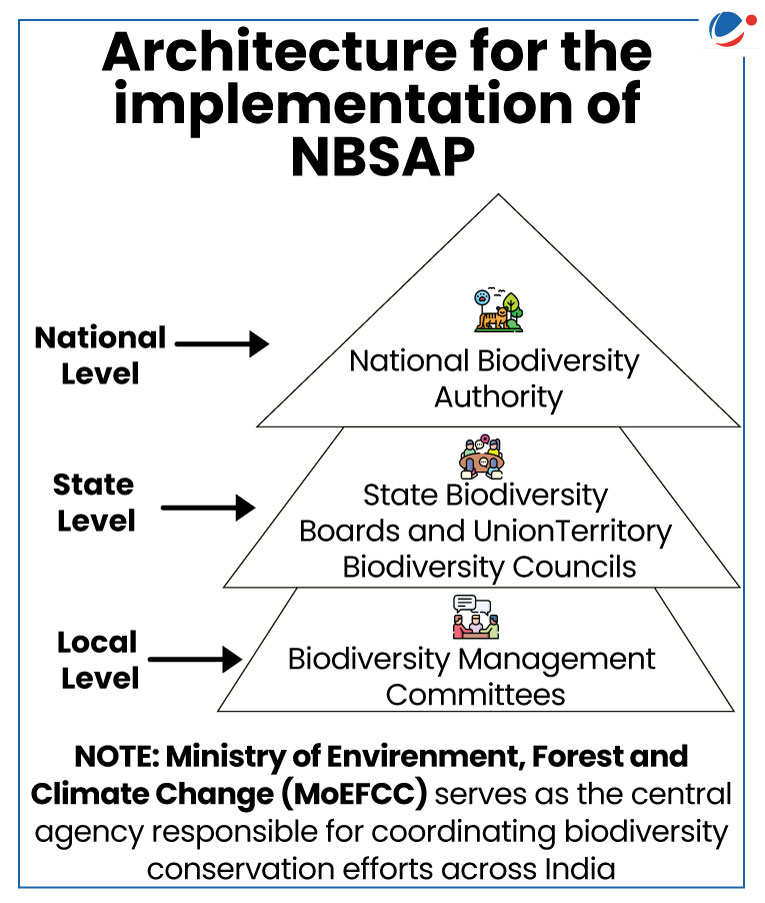
- Enactment of Biological Diversity Act, 2002 developed a multi-tier governance structure (refer infographic).
- Capacity building: Through need & gap assessment; target group identification; Identification of experts/ environmentalists; and training for the acquisition of knowledge, skills etc.
- Resource mobilization: Recognizes India among the leading countries for implementation of Biodiversity Finance Initiative (BIOFIN) at national level.
- BIOFIN is a global partnership launched by UNDP and the European Commission to support countries to enhance their financial management of biodiversity and ecosystems.
- Other features: Emphasized upon adoption of transformative approach focusing on ecosystem-management based bottoms-up approach for implementing and mainstreaming biodiversity.
Biological Diversity Act, 2002 (last amended in 2023)
*SBBs are not constituted for Union Territories (UTs). NBA exercises the powers and performs the functions of a SBB for the UT. |
Conclusion
India's updated NBSAP adopts a comprehensive approach to biodiversity conservation, integrating traditional practices with modern governance & collaborative strategies while addressing contemporary environmental challenges. However, achieving the 23 NBTs and ensuring sustainable development will require continued efforts in capacity building, resource mobilization, effective monitoring, etc.
Related News: Biological Diversity Rules, 2024
|






