Inauguration of first trilateral power transaction from Nepal to Bangladesh through the Indian Grid took place.
- The tripartite power sales agreement between NTPC Vidyut Vyapar Nigam, Nepal Electricity Authority(NEA) and Bangladesh Power Development Board was signed earlier.
About Agreement
- To facilitate power transaction from Nepal to Bangladesh, through Indian grid with an export of upto 40 MW of power.
- Commitment towards greater sub-regional cooperation, including in the energy sector, which would lead to increased inter-linkages between the economies for mutual benefit of all stakeholders
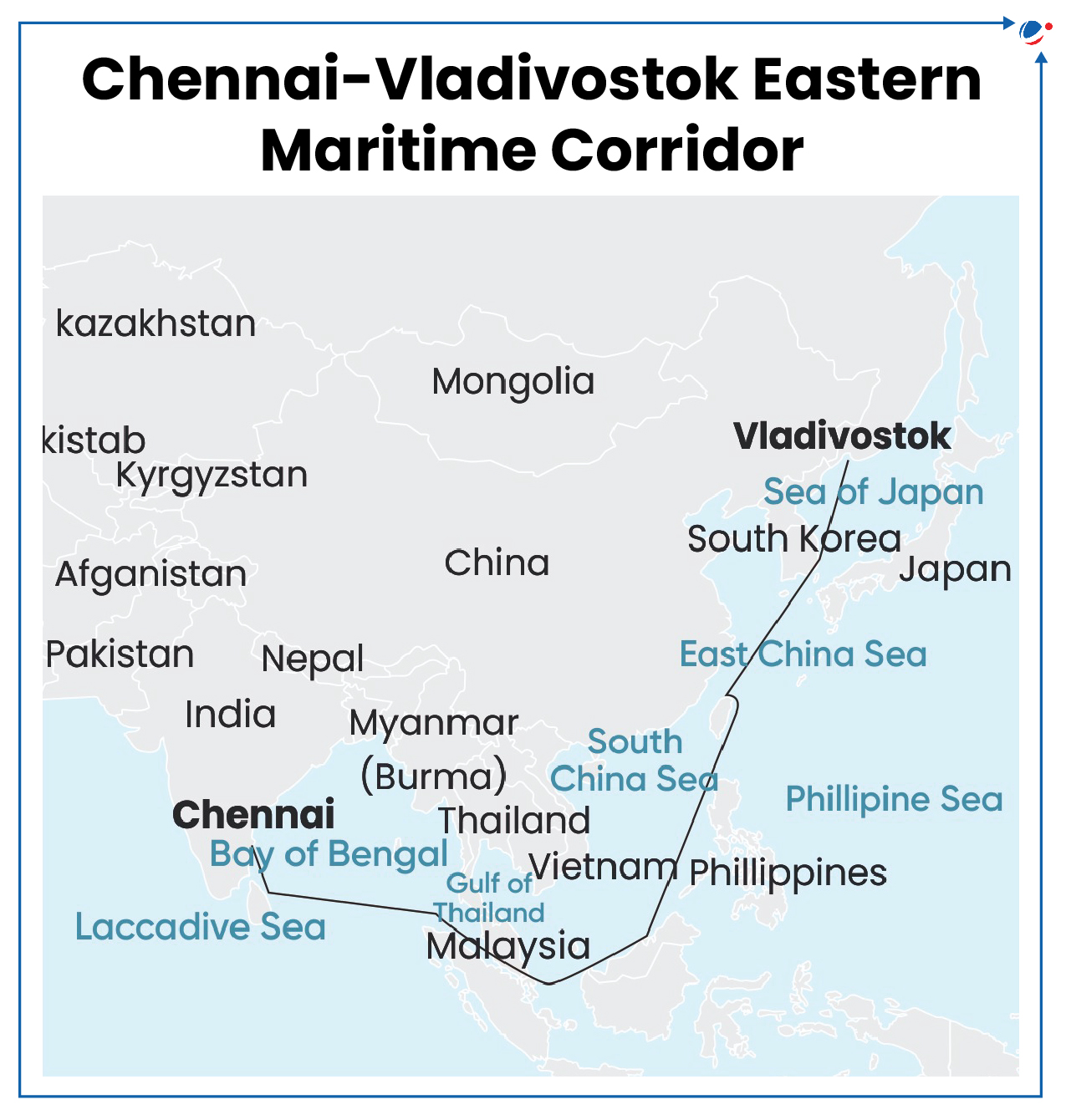
Also known as the Eastern Maritime Corridor (EMC), it is set to boost maritime ties between India and Russia.
About EMC
- Envisioned during the Eastern Economic Forum (2019) in Vladivostok, Russia.
- It seeks to develop a sea route between the Indian port of Chennai and Vladivostok through Northeast Asia.
- Covers a distance of around 10, 300 km.
- Passes through the Sea of Japan, the South China Sea, Malacca Strait, etc.
Significance of the Corridor
- Reduced Logistics cost: Due to reduction in transportation time (by around 16 days) and distance (by around 40%).
- Present trade route between Mumbai and St. Petersberg (Russia) via Suez Canal takes around 40 days and covers a distance of around 16, 066 Km.
- Boost India’s maritime sector: The sector handles around 95% (by volume) and 70% (by value) of country’s trade.
- Complement India’s Maritime Vision, 2030 that encompasses more than 150 initiatives from all areas of Maritime Sector.
- Address China’s Dominance: Passes through the South-China Sea.
- Vladivostok is located at a short distance from Russia-China border.
- Boost India’s Act Far East Policy: Offer enhanced access to Russian resources and provide stronger foothold to India in the Pacific trade network.
Other Significant Maritime Corridors
|
Digital Infrastructure Growth Initiative for India Framework (DiGi Framework) seeks to advance cooperation between the United States, Japan, and the Republic of Korea in partnership with India.
DiGi Framework
- Objective: It aims to further their collaboration with the Indian private sector to support digital infrastructure in India.
- Partner Agencies: U.S. International Development Finance Corporation, the Japan Bank for International Cooperation (JBIC), and the Export-Import Bank of Korea (Korea Eximbank).
- Implementation: It will support projects in information and communications technology sector such as 5G, Open RAN, submarine cables, optical fiber networks, data centres, smart city, e-commerce, AI, and quantum technology.
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) in India
- India became the first country to build all three foundational DPIs through India Stack: digital identification (Aadhaar), real-time rapid payment (UPI) and data sharing architecture (Data Empowerment and Protection Architecture).
- Significance:
- Inclusive Development: DPI helped India achieve 80% financial inclusion during 2018-2023 and enabled direct benefit transfers supporting 87% of poor households during Covid-19.
- Economic Growth: India can speed up economic growth by 33% by implementing DPI in financial sector.
- Emission Reduction: DPI in climate sector can accelerate emissions control by 5-10 years through implementing DPI in carbon offsets and trading, land mapping, and weather information and monitoring.
India’s Efforts at Globalizing DPIs
|
India proposed seven key pillars to strengthen ties between India and the Caribbean Community (CARICOM).
- Seven pillars listed by the India form the acronym C-A-R-I-C-O-M.
- Pillars include Capacity Building, Agriculture and Food Security, Renewable Energy and Climate Change, Innovation, Technology and Trade, etc.
- The first-ever India-CARICOM Summit was held in 2019.
About CARICOM
- A regional organization established in 1973 to promote economic integration and cooperation in the Caribbean.
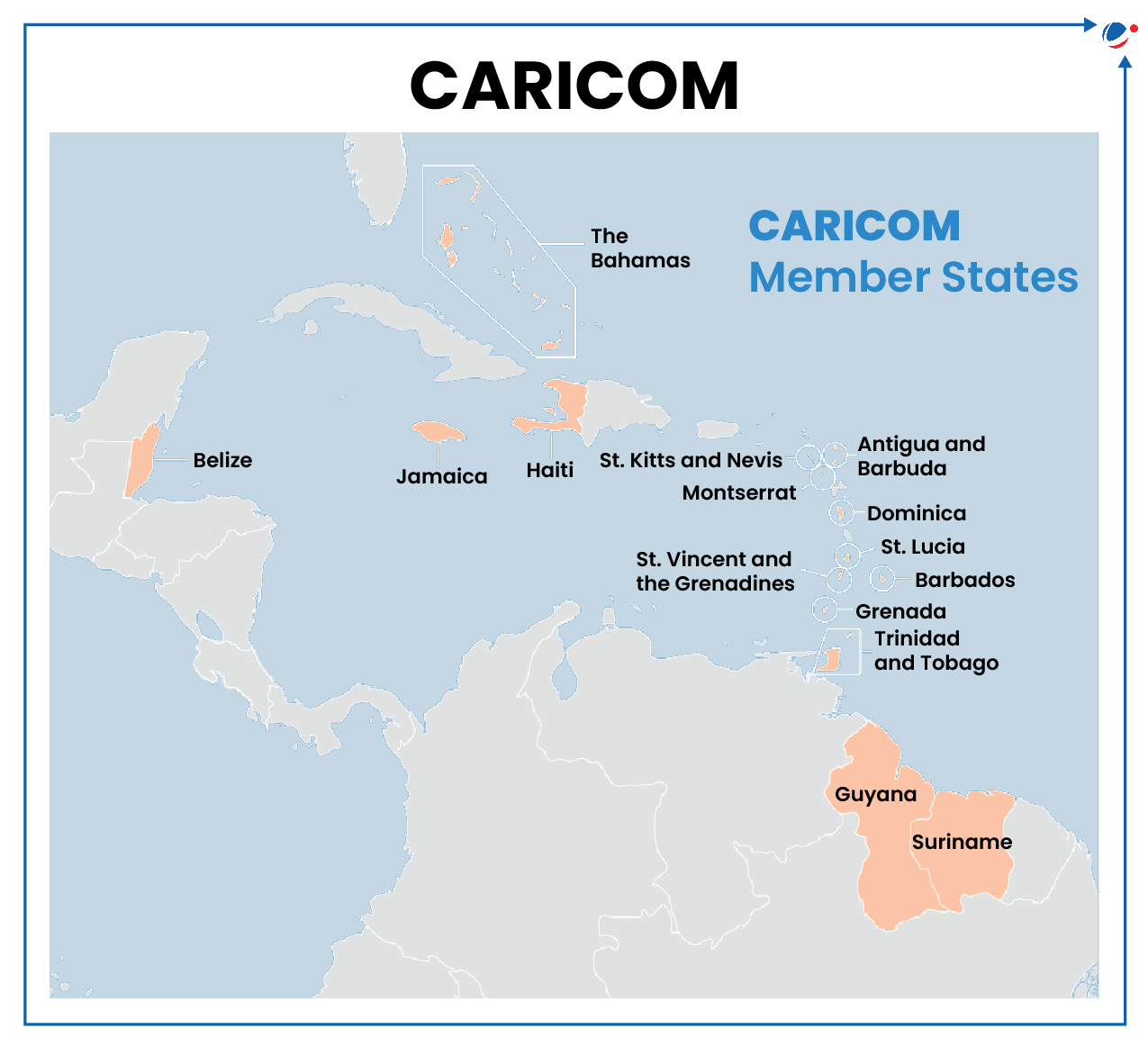
- Consists of 21 countries (fifteen Member States and six Associate Members) including Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, etc.
Significance of CARICOM for India
- Partnership in Multilateral Forums: Many CARICOM countries such as Antigua and Barbuda support India’s position in international forums. E.g. Support for permanent membership in the UNSC.
- South-South Cooperation: Countries from group participated in 3rd Voice of Global South Summit, 2024, organised by India.
- Defence Export: E.g. Recently, HAL delivered two Dornier 228 planes to Guyana.
- Climate Action Collaboration/ Energy Security: E.g. Suriname joined International Solar Alliance (ISA)
- Other: Act as a gateway to Latin America, Cooperation in disaster resilience (E.g. Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure), Home to Indian Diaspora (Trinidad and Tobago), etc.
11th ADMM-Plus held recently at Vientiane, Lao PDR.
About ADDM-Plus
- It comprises of 10 ASEAN Member States and 8 Dialogue Partners (Australia, China, India, Japan, New Zealand, Republic of Korea, Russia and US).
- Inaugural ADMM-Plus was convened in Hanoi, Vietnam in 2010.
- Since 2017, ADMM-Plus Ministers meet annually to further dialogue and cooperation amongst ASEAN and Plus Countries.
- Its purpose is to strengthen security and defence cooperation for maintenance of peace, stability, and development in the region.
- Focuses on seven areas of practical cooperation: Maritime Security, Counter-terrorism, HADR, Peacekeeping Operations, Military Medicine, Humanitarian Mine Action and Cyber Security.
The 2024 OPCW-The Hague Award was conferred upon the Indian Chemical Council (ICC)
- The Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) Hague award acknowledges ICC contributions to chemical safety, compliance with Chemical Weapon Convention (CWC).
- This is the first time that the Award recognises the efforts of a chemical industry body.
- Hague Award was established in 2014 to honor OPCW’s contributions to Chemical Weapons Conventions (CWC) goals.
About Chemical Weapon Convention (CWC)
- Genesis: It came into force in 1997, and presently has 193 States Parties.

- India is an original signatory to the Convention.
- Aim: To eliminate an entire category of weapons of mass destruction by prohibiting the development, production, acquisition, stockpiling, retention, transfer or use of chemical weapons by States Parties.
- Implementation: OPCW is the implementing body, with a mission to achieve a world free of chemical weapons.
- OPCW was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 2013.
- Chemical Weapon is a chemical used to cause intentional death or harm through its toxic properties.
- Munitions, devices and other equipment specifically designed to weaponise toxic chemicals also fall under the definition of chemical weapons.
- Implementation in India: National Authority Chemical Weapons Convention (NACWC) is responsible for implementing the Convention in India.
- NACWC was established under the Chemical Weapons Convention Act, 2000.
World Urban Forum (WUF) concluded its twelfth edition, held in Cairo (Egypt), with the adoption of 10-point Cairo Call to Action.
- WUF, established in 2001 by UN, is the premier global conference on sustainable urbanization.
Cairo Call to Action
It calls for:
- Urgent action to address the global housing crisis, sharing urban spaces inclusively, and urban planning to deliver better local outcomes.
- Achieving global goals through local action, representation of local actors at all levels, and building alliances to scale local impact.
- Unlocking finance for cities and communities, and ensuring equity and justice.
- Leveraging local and grassroots data for decision-making.
- Harnessing culture and heritage as an asset for sustainability.
Article Sources
1 sourceInternational Cooperative Alliance (ICA) Global Cooperative Conference is being organised in India for the first time in the 130 year long history of ICA.
- Theme "Cooperatives Build Prosperity for All" aligns with the Indian Government’s vision of “Sahkar Se Samriddhi” (Prosperity through Cooperation).
About ICA
- Founded: In 1895, London.
- It is a global organization that unites, represents, and serves cooperatives around the world.
- Members: 306 member organizations across 105 countries.
- It serves as the apex body for the cooperative movement, providing a global platform for collaboration, knowledge exchange, and coordinated action.
Article Sources
1 source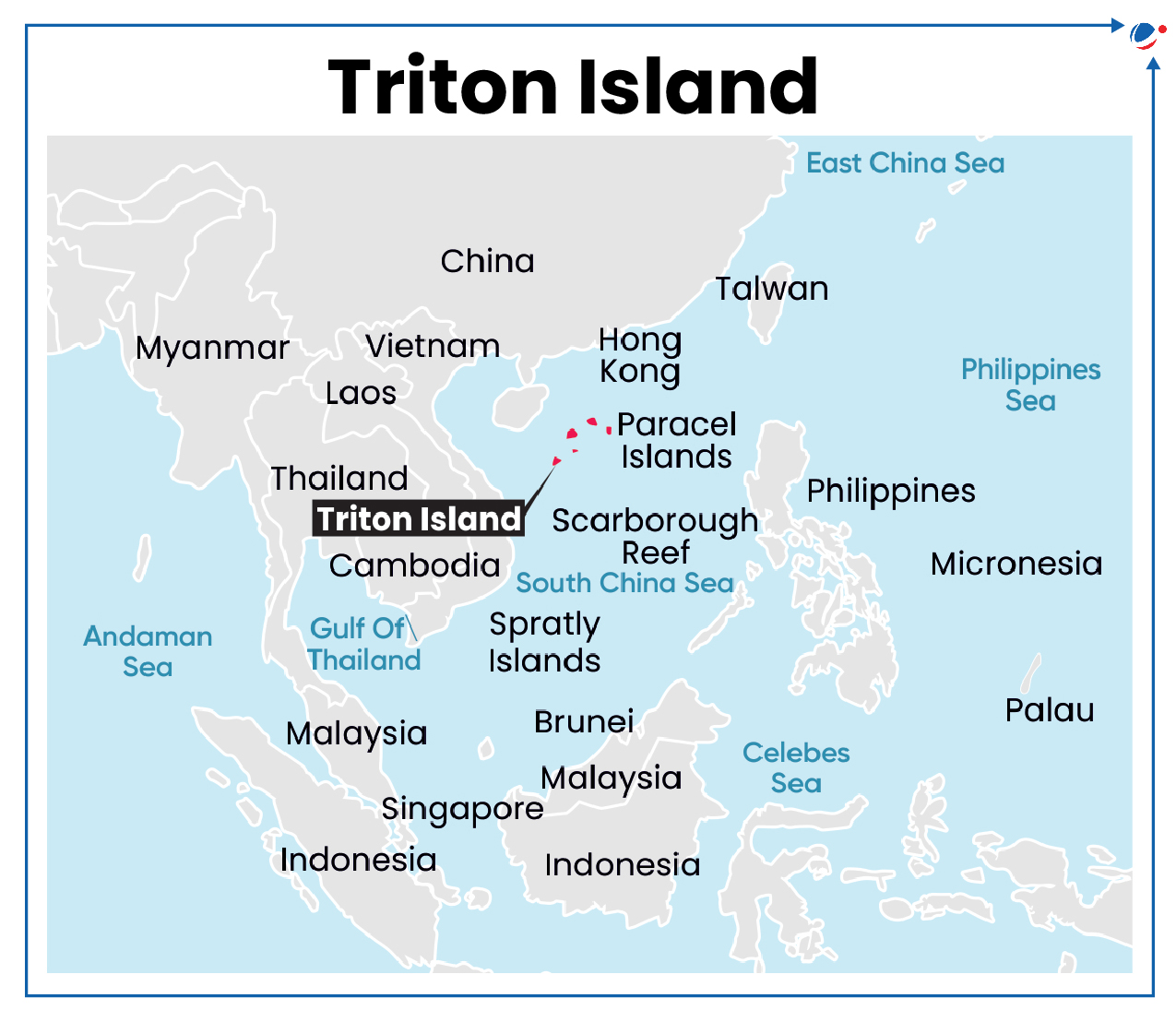
Recent satellite imagery reveals a significant military buildup by China on Triton Island.
About Triton Island
- Located in the Paracels (South China Sea) is also known as Xisha Islands in China.
- It is effectively controlled by China but is also claimed by Vietnam and Taiwan.
- China took control of the Paracels from South Vietnam following a 1974 naval clash.
- Military buildup on Triton Island represents a significant escalation in China’s strategy to establish military dominance in the South China Sea.







