Why in the News?
India underscored the need for global climate justice and equitable action during the Second Annual High-Level Ministerial Round Table on Just Transition at COP29.
About Just Transition
- According to International Labour Organization (ILO), a just transition means greening the economy in a way that is as fair and inclusive as possible to everyone concerned, creating decent work opportunities, and leaving no one behind.
- It is a process of shifting from high-carbon, unsustainable systems to low-carbon, sustainable economies in a way that is equitable, inclusive, and fair.
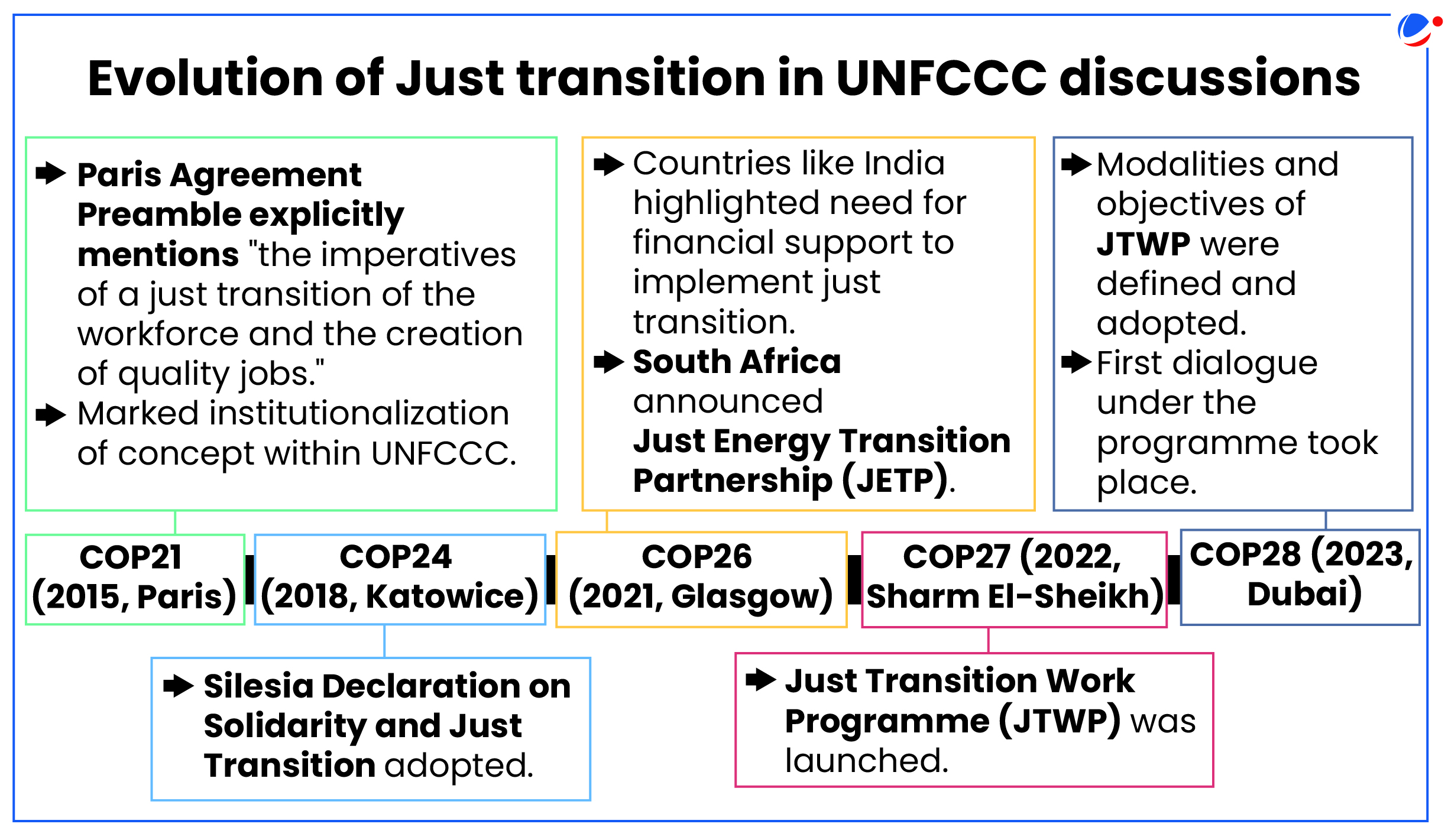
- It was recognised by the Just Transition Declaration agreed at the UN Climate Change Conference in Scotland (COP26).
- Key elements include:
- Equity: Protecting the rights and livelihoods of workers and communities, particularly those dependent on fossil fuels and other high-carbon industries.
- Inclusion: Ensuring that all stakeholders—workers, governments, industries, and civil society—are involved in decision-making.
- Sustainability: Aligning economic and social systems with the goals of reducing GHG emissions and conserving natural ecosystems.
Need of Just Transition
- Impact on Workers: ILO estimates that while 24 million new green jobs could be created by 2030, 6 million jobs in carbon-intensive industries might be lost.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Emission reduction in energy sector plays a significant role in meeting the Paris Agreement target of limiting global warming to 1.5°C.
- GHG emissions must peak before 2025 at the latest and decline 43% by 2030.
- Energy Security: Adoption of diverse renewable energy sources reduces reliance on volatile fossil fuels subject to geopolitical tensions and price fluctuations.
- Avoiding Discontent: E.g., Yellow Vest protests in France (2018) protested against climate measures which disproportionately affected lower-income groups.
Challenges in Just Transition
- High Costs of Transition: For instance, India will require more than a trillion dollars over the next three decades to transition its coal mining and thermal power sectors (Just transition, Just Finance report).
- Regional Disparities: Coal-reliant regions, such as South Africa's Mpumalanga or India's Jharkhand, have limited resources to diversify their economies, exacerbating inequalities in transition readiness.
- Energy security and accessibility: Coal-based power plays a significant role in developing countries for development purposes and enhancing energy accessibility and affordability for their citizens.
- E.g., coal accounts for about 55% of India's commercial energy requirements and coal-based TPPs produce more than 70% of electricity.
- Economic losses: As per International Energy Agency (IEA) stranded fossil fuel assets (i.e., no longer economically viable) could result in losses due to shift toward green transition.
- E.g., Saudi Arabia derived 68% of its 2022 budget revenue from oil.
- Inequitable Impacts: For instance, women are overrepresented in informal and low-carbon jobs, limiting their opportunities in green sectors (UN Women, 2023).
- Other issues: Infrastructure challenges like upgradation of grid infrastructure; lack of adequate technology transfer; etc.
Initiatives Taken for Just TransitionIndia
Global
|
Way Forward
- Set up National Just Transition body to independently monitor coal closure and repurposing and ensure fair distribution of transition benefits and costs.
- Explore sustainable financing through mechanisms like Just Energy Transition Partnership (JETP), green bonds, etc.
- Banks and multilateral institutions should raise commitments by providing more grants, concessional loans, etc.
- Maintain and enhance social infrastructure, e.g., introduce compensation packages to formal workers engaged in low-carbon jobs, such as severance pay, voluntary retirement scheme (VRS), etc.
- Develop strategies to create new, sustainable jobs and provide adequate training, and reskilling programs for workers impacted by the energy transition.
- Foster active participation of all affected groups, especially marginalized and vulnerable communities, in the planning and decision-making process.
- Develop and augment green energy infrastructure by upgrading the transmission and distribution systems.







