Why in the News?
Recently, German Chancellor visited India to enhance bilateral relations between India and Germany.
More on the News
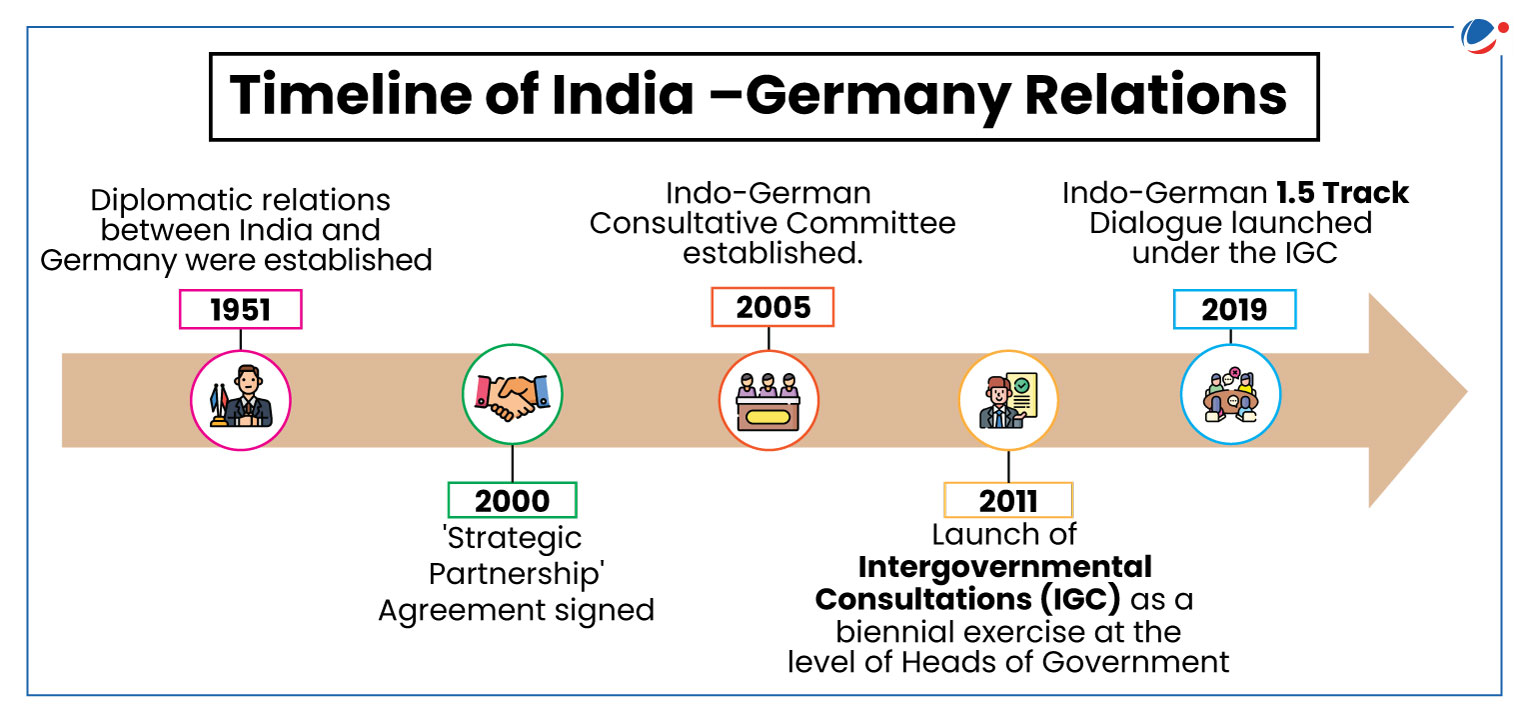
- 2024 marks the 25th anniversary of the strategic partnership (signed in 2000) between India and Germany.
- 2024 also marks the 50th anniversary of the signing of the Inter – Governmental Agreement on Cooperation in Scientific Research and Technological Development.
- During the visit the 7th Inter-Governmental Consultations (IGC) were held and also the 'India-Germany Innovation and Technology Partnership Roadmap' for renewable energy, AI, quantum technologies, and space exploration was launched.
Significance of India-German partnership
- Trade and Investment
- Germany is India's largest trade partner in Europe, with bilateral trade reaching US$ 33.33 billion in 2023.
- Germany is the 9th largest foreign direct investor in India, with a cumulative FDI of US$ 14.5 billion (April 2000 - December 2023).
- Germany gets access to India's large and growing consumer market along with availability of skilled labor and rapid adoption of digital technologies.
- Climate and Sustainability
- Under the Green and Sustainable Development Partnership (2022), Germany committed €10 billion for projects like solar partnerships and agro-ecology.
- Germany is a member of India-led initiatives like the Coalition for Disaster Resilience Infrastructure (CDRI) and the International Solar Alliance (ISA).
- Technology and Innovation: The Indo-German Science and Technology Centre (IGSTC) supports 49 priority projects, including initiatives like Women in Science and Engineering Research (WISER).
- Defense and Security: The 2006 Defence Cooperation Agreement has led to Joint Working Groups on Counter-Terrorism, Cybersecurity, and Defence.
- Also, recently, Germany has shown keen interest in participating in Project- 75I Programme of the Indian Navy for six conventional submarines.
- Joint exercises: Ex MILAN, PASSEX, Ex TARANG SHAKTI-1, etc.
- Diversification of Trade Partners: Reducing dependency on China (China+1) following the EU-China trade tensions by strengthening ties with India.
- In June 2024, the EU imposed tariffs of up to 38.1% on Chinese electric vehicles for unfair trade practices.
Challenges in Bilateral Relations
- Trade and Investment Barriers: Indian companies face non-tariff barriers on their products in Europe such as Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM).
- Similarly, bureaucratic hurdles and a complex tax system have kept German investments in India at around 25 billion euros ($27 billion) in 2022, about only 20% of the volume invested in China.
- Strategic and Geopolitical Differences: India's neutral stance on the Russia-Ukraine conflict contrasts with Germany's strong opposition to Russian aggression.
- China's Role: Germany's economic dependence on China limits its ability to fully support India's position against China unlike the USA and Japan in QUAD.
- Human Rights Criticism: German critiques of India's internal policies (e.g., Kashmir, press freedoms) create diplomatic sensitivities.
Way Forward
- Free Trade Agreement (FTA): Early conclusion of the negotiations between India and the EU to compete with China's almost 300 billion euros trade with Germany alone.
- Indo-Pacific Engagement: Increase Germany's presence in the region through joint naval exercises and infrastructure investments as envisaged in the 7th IGC.
- Collaboration in clean tech and sustainable development with projects like electric mobility, green hydrogen, renewable energy, etc. through initiatives like the Green and Sustainable Development Partnership.
- Supply Chain Resilience: To diversify the production chain of semiconductors, automobile parts, pharmaceuticals away from China, both Germany and India can become partners, also supporting 'Make in India' initiative.







