Global Carbon Budget report was published by Global Carbon Project during UNFCCC’s COP29 summit.
- At the current rate of emissions, it is estimated a 50% chance that global average temperatures will exceed 1.5 degrees consistently in about six years.
- This year, possibly, will be the first time the threshold of 1.5 degrees is crossed.
The carbon budget:
It’s the amount of CO2 emissions that will result in limiting global warming to a given level, in this case, the Paris accord’s target of 1.5 degrees C over pre-industrial levels.

Key Findings:
- Globally, fossil-based CO2 emissions are set to touch a record high of 37.4 billion tonnes this year.
- The largest contributions to global fossil CO2 emissions were China (31%), the USA (13%), India (8%), and the European Union (7%), in 2023.
- These four regions account for 59% of global fossil CO2 emissions, while the rest of the world contributed 41%.
- Global emissions from land-use changes like deforestation have dropped 20% over ten years.
- Reforestation and new forests offset about half of permanent deforestation emissions globally.
- The land and ocean CO2 sinks combined took around half of the total CO2 emissions, despite being negatively impacted by climate change.
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) released Adaptation Gap Report 2024 that provides annual assessment on progress in adaptation planning, implementation and finance.
- Adaptation Gap is the difference between actually implemented adaptation (adjustment measures to actual or expected climate) and a societally set goal, reflecting resource limitations and competing priorities.
Key Findings of Report:
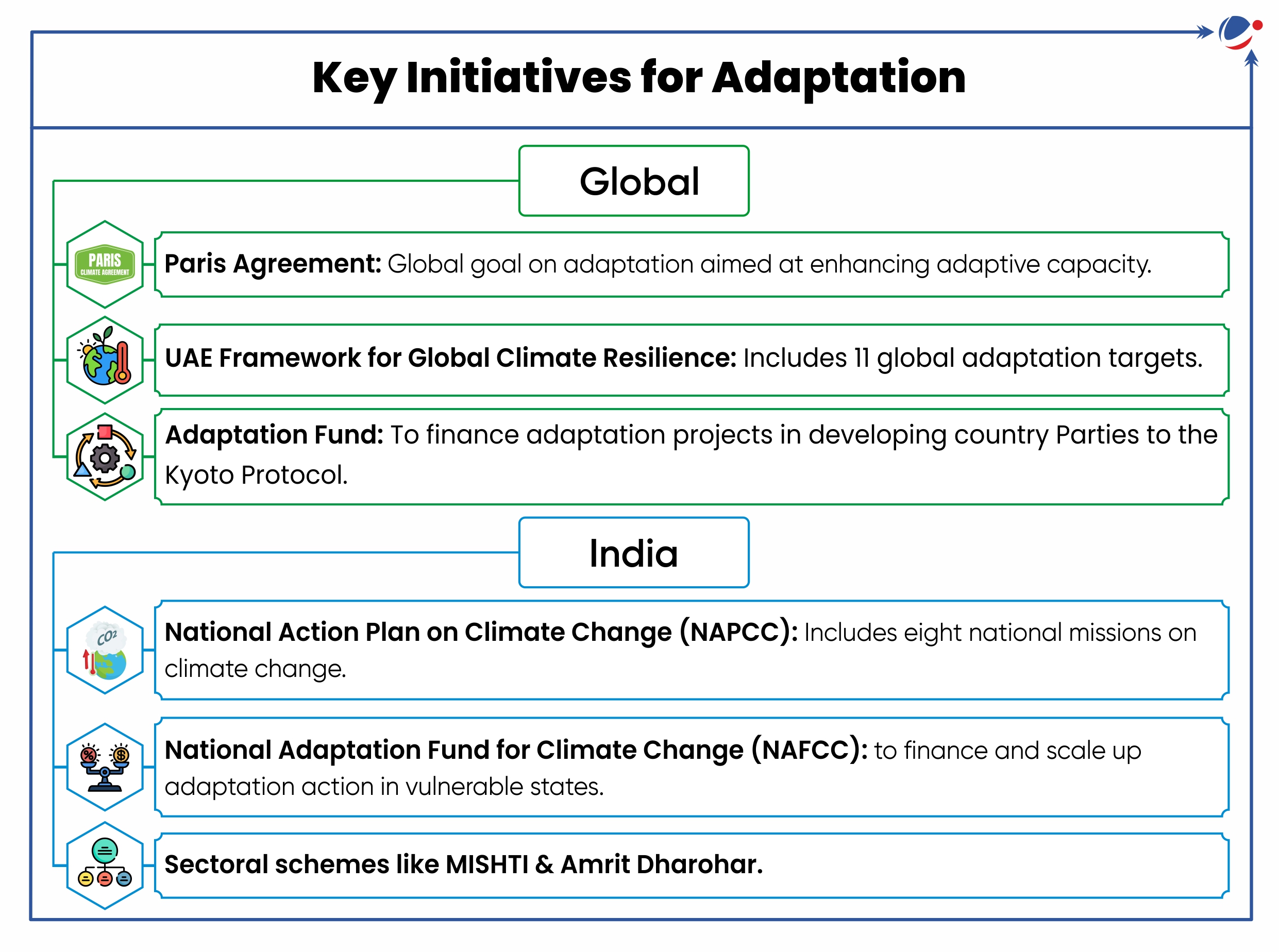
- Adaptation Gap: Adaptation gap is estimated at US$187-359 billion per year.
- Adaptation Progress: International public adaptation finance flows to developing countries increased to US$27.5 billion in 2022.
- This reflects progress towards Glasgow Climate Pact, which urged developed nations to at least double adaptation finance to developing countries from US$19 billion (2019) by 2025.
- Significance of Adaptation: Global climate risk can be halved through ambitious adaptation.
- For instance, US$16 billion invested in agriculture per year would prevent about 78 million people from climate change related starving or chronic hunger.
Recommendations for bridging adaptation gap
- Adopt an ambitious New Collective Quantified Goal for climate finance at COP29.
- Strengthening enabling factors, adapting new financial instruments, capacity building and technology transfer are central.
- Adaptation financing needs to shift from reactive, incremental, project-based financing to more anticipatory, strategic and transformational adaptation.
Report focuses on global emission trends, future projections and what is required from next NDCs to achieve long-term temperature goals of Paris Agreement.
Key Observations:

- Greenhouse-gas (GHG) emissions rose to a new high of 57 gigatons(Gt) of CO2 equivalent in 2023 (1.3 % increase from 2022).
- India ranks 3rd in total GHG emissions with 4,140 MtCO2e compared to China (1st) & US (2nd).
- Large disparities in Current and historic GHG emissions: Six largest GHG emitters accounted for 63 % of global GHG emissions while least developed countries accounted for only 3%.
- Similarly, India’s historical CO2 emissions (1850–2022) are much lower i.e. 83 GtCO2 than China (300 GtCO2) & US (527 GtCO2).
- Missing NDC targets: Adoption of more stringent policies is required across countries to achieve NDC targets for 2030.
Recommendations for limiting global warming to 1.5°C:
- Nations must collectively commit to cut 42 % off annual greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 and 57 % by 2035 in next NDCs.
- NDCs must include all gases listed in Kyoto Protocol, cover all sectors, and set specific targets.
- Increased deployment of solar photovoltaic technologies and wind energy could deliver 38 % of total emission reduction potential in 2035.
Article Sources
1 sourceUN Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre (UNEP-WCMC) and IUCN released Protected Planet Report 2024.
About Protected Planet Report 2024

- It is first report to assess global status of Protected and Conserved Areas (PCA) in context of Target 3 of Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF).
- Protected Area is geographically defined area which is regulated and managed to achieve specific conservation objectives.
- Conserved Areas are areas outside Protected Areas that are managed to conserve biodiversity, ecosystem services, and local values.
- Target 3 aims to expand global network of PCA to 30% coverage in a way that is equitable and respects rights of Indigenous Peoples and Local communities (IPLC).
Key findings
- Global coverage of PCAs has reached 17.6% of terrestrial and inland waters and 8.4% of marine and coastal areas.
- Over two-thirds of Key Biodiversity Areas are now partially or fully covered by PCAs, but 32% remain unprotected.
- Only 8.5% of land is both protected and connected.
- Data on effectiveness of management is limited with only 4% of protected areas are governed by IPLC.
Way ahead
- Recognition and support to Indigenous and Traditional Territories: These territories cover 13.6% of global land and should be included in conservation efforts.
- Provide international financing to developing countries to fund expansion of PCAs: Under GBF, countries committed to increase investment in biodiversity from all sources to atleast USD 200 billion per year by 2030.
Article Sources
1 sourceFourth edition of ‘An Eye on Methane: Invisible but not unseen’ Report launched by United Nations Environment Programme’s (UNEP) International Methane Emissions Observatory (IMEO).
About IMEO
- IMEO, a core implementing partner of Global Methane Pledge, provide open, reliable, and actionable data on methane emissions.
- IMEO collects and publishes data through rigorous industry reporting via the Oil and Gas Methane Partnership 2.0 (OGMP 2.0), from satellites via the Methane Alert and Response System (MARS), from global methane science studies, and from national emissions inventories.
Key Findings of Report
- Global Warming: Human-caused methane emissions are responsible for roughly one-third of the planet’s current warming.
- Emissions from Oil and Gas Sector: UNEP’s OGMP 2.0, which require its members to report their emissions, covers only 42% of global production.
- Emissions in Steel Supply Chain: Production of metallurgical coal for steel production accounts for one-tenth of energy sector methane emissions and can be mitigated at a minimal cost.
- Poor Response to Emissions: Through MARS, IMEO alerts countries of major emissions but only 1% of such alerts received any substantive response.
Initiatives taken to reduce Methane Emissions
- Global: Global Methane Pledge, Climate and Clean Air Coalition, Global Methane Alliance etc.
- India: National Innovations in Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA) project, National Livestock Mission, Gobar-Dhan Scheme, New National Biogas and Organic Manure Programme etc.
The World Energy Employment 2024 report has been released by the International Energy Agency.
Key findings
- Global energy employment outperformed broader labor market trends in 2023.
- Clean energy remains the primary engine of job growth.
India-Specific Findings
- India’s energy jobs account for over 8.5 million i.e., 1.5 % of total employment (566 million) in 2023.
- India’s energy sector, like many others, relies heavily on informal labor.
- The energy workforce, particularly in clean energy, is poised to see further growth with government initiatives fueling job creation.
Article Sources
1 sourceWorld’s First CO₂ to Methanol Plant launched by NTPC at Vindhyachal
- NTPC announced successful synthesis of CO2 captured from flue gas with hydrogen produced from a Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) electrolyzer, which was then converted into methanol.
- NTPC has also developed its first indigenous methanol synthesis catalyst.
- It is considered to be a historic step in carbon management and sustainable fuel production.
About Methanol (CH3OH)
- Also known as methyl/wood alcohol, it is the simplest alcohol and mixes completely with water.
- It’s a clear, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odour similar to ethanol (drinking alcohol).
Article Sources
1 sourceRecently, the Union Minister of Power, Housing & Urban Affairs unveiled ‘EV as a Service’ Programme of Convergence Energy Services Limited (CESL), a subsidiary of Energy Efficiency Services Limited.
- It follows the launch of the PM E-DRIVE Scheme to fast-tracking India’s shift to electric mobility.
- EV-as-a-Service model offers subscription-based access to electric vehicles, eliminating the high upfront costs of purchasing an EV.
About EV-as-a-Service Programme
- Aims to deploy 5,000 E-Cars in government departments over the next two years.
- Aligns with India’s ambitious goal of achieving net zero emissions by 2070.
Article Sources
1 sourceGuru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve (TR) notified as 56th TR of India.
- On the advice of National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA), Chhattisgarh government notified the areas comprising the Guru Ghasidas National Park and Tamor Pingla Wildlife Sanctuary as the 56th TR of India.
Key details
- After Guru Ghasidas – Tamor Pingla TR being notified Chhattisgarh now has 4 TRs: Indravati TR, Udanti-Sitanadi TR & Achanakmar.
- TR is notified by State Governments under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 on advice of NTCA.
- It’s the 3rd largest TR after Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam TR (A.P) and Manas TR (Assam).
- A TR comprises:
- Core/critical area: Required to be kept as inviolate, without affecting the rights of the Scheduled Tribes or such other forest dwellers as per the Forest Rights Act, 2006.
- Buffer/peripheral area: It promotes human-wildlife coexistence, with lesser protection. It recognizes local rights, determined through Gram Sabha.
Location & Landscape of Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla TR:
- Geography: Chota Nagpur plateau and partly in Baghelkhand plateau.
- Fauna: leopards, hyenas, jackals, wolves, sloth bears, etc.
- Rivers: Hasdeo Gopad, Baranga etc.
- Adopts Landscape approach to conservation: As envisaged in the National Wildlife Action Plan (2017-31), the TR is contiguous with the Sanjay Dubri TR (MP), and connected with Bandhavgarh TR (MP) and Palamau TR (Jharkhand)
About Landscape approach to tiger conservation:
|
Article Sources
1 sourceThe report ‘Coral Triangle at Risk: Fossil Fuel Threats and Impact’ released at the 16th Conference of Parties (COP16) to the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD).
About the Report
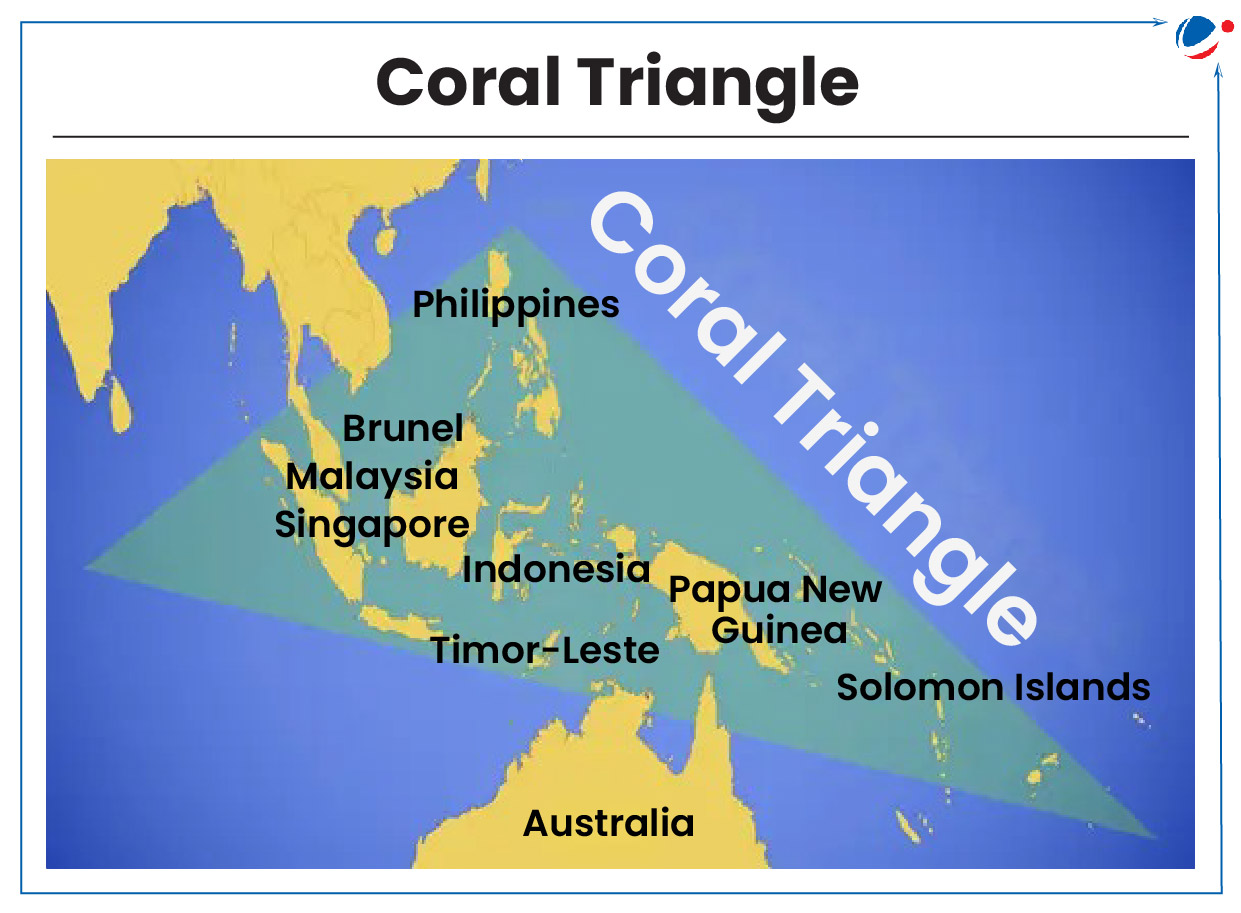
- The report released by Earth Insight and SkyTruth highlights the potential threats posed by fossil fuels to the Coral Triangle.
- According to the report coral triangle spans seven countries in Southeast Asia and Melanesia: Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Singapore, Timor-Leste and Solomon Islands.
- It is one of the world’s most bio-diverse marine regions.
Significance of Coral Triangle:
- It hosts 76% of world’s coral species, over 2,000 coral fish species, and six of seven marine turtle species.
- It supports 120 million people who rely on it for food, and income, with its habitats critical for marine diversity, earning it nickname “the Amazon of the seas.”
Threats being faced by Coral Triangle:
- Oil and Gas Exploration: Over 100 offshore oil and gas blocks are currently operating in Triangle.
- It threatens Triangle’s delicate ecosystems, including coral reefs, mangroves, and seagrasses
- Noise pollution: From shipping and exploration activities harms marine life. Eg: Man-made noises can alter animal behaviors by damaging hearing or masking animal sounds.
Recommendations by report:
- Enact a moratorium on oil and gas development in Coral Triangle, while phasing out existing fossil fuel operations.
- Experts recommend Coral Triangle be classified as a Particularly Sensitive Sea Area to provide it with special protection from harmful maritime activities.
Villages in Odisha conceptual by Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO (UNESCO-IOC) as ‘Tsunami Ready’.
- The 24 coastal villages in Odisha were recognized as Tsunami Ready during the 2nd Global Tsunami Symposium in Indonesia, based on verification by the National Tsunami Ready Recognition Board (NTRB).
- NTRB, comprising scientists from Indian National Centre for Ocean Information Services (INCOIS) and officers of National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), implements Tsunami Ready Recognition Programme.
UNESCO-IOC Tsunami Ready Recognition Programme (TRRP)
- TRRP is a voluntary, international community-based effort to bolster risk prevention and mitigation across global coastal zones.
- Aim: To build tsunami resilience through awareness and preparedness strategies that will protect life, livelihoods and property from tsunamis.
- Methodology: It has 12 preparedness indicators for a consistent evaluation, and recognition is renewable every four years.
About Tsunami
- Definition: Tsunamis are a series of enormous waves created by underwater disturbances, often associated with earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, landslides, or coastal rock falls.
- Origin: The word “tsunami” comprises the Japanese words “tsu” (meaning harbour) and “nami” (meaning wave).
- Characteristics:
- Speed: Over 500 miles per hour (mph) and as a tsunami enters shallow water, it slows off to 20 to 30 mph. The wavelength decreases, the height increases.
- Tsunami wave speed depends on ocean depth, not distance from the wave’s source.
Steps taken by India
|
Recent catastrophic flash floods in Spain are attributed to DANA.
About DANA:
- DANA is a phenomenon in which a mass of very cold polar air becomes isolated from polar jet stream and begins to circulate at very high altitudes (5-9 km).
- It forms independently of polar or subtropical jet streams unlike common storms.
- When it collides with warmer, more humid air in Mediterranean Sea, it generates strong storms, especially at end of northern summer and beginning of autumn.
- Unlike a common storm, which moves eastwards, a DANA can remain stranded in same place or even move westwards.
Article Sources
1 sourceRecently, a bomb cyclone struck North-western US and western Canada.
About Bomb Cyclone
- Also referred to as bombogenesis, it describes a mid-latitude cyclone (low pressure region) that rapidly intensifies over a 24-hour period.
- Witness a drop in their central air pressure to at least 24 millibars in 24 hours.
- Majority of these occur over the ocean and can be tropical or non-tropical in nature.
- Usually coupled with weather events, ranging from blizzards to severe thunderstorms to heavy precipitation.
Article Sources
1 sourceA drought has drained Lake Kariba close to record lows, causing power shortage in the region.
About Lake Kariba
- It is the world’s largest artificial lake and reservoir by volume.
- Kariba lake is located in Central Africa in the Zambezi River basin between Zambia and Zimbabwe.
- Its construction was started during 1950s when British ruled Northern and Southern Rhodesia (now Zambia and Zimbabwe).
- Kariba Dam provides electric power to both Zambia and Zimbabwe and supports a thriving commercial fishing industry in Africa.








