Why in the News?
The Centenary celebrations of iconic 'Bose-Einstein' (B-E) Statistics was recently inaugurated by Ministry of Science and Technology.
More about News
- S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences (under Department of Science and Technology) is celebrating the centenary of Bose's colossal work in theoretical physics to honour the great scientist.
- In 1924, Satyendra Nath Bose proposed a new approach to understand the behaviour of particles or photons, based on quantum theory.
- His collaboration with the Albert Einstein eventually led to postulation of B-E statistics.
About Satyendra Nath Bose (1894-1974)
- Satyendra Nath Bose was an Indian physicist renowned for developing the theory of Bose–Einstein Statistics and the concept of the Bose–Einstein Condensate.
- He hailed from the Nadia district in West Bengal.
- Bose pursued his education at Presidency College, Kolkata, where he studied under prominent teachers like Prafulla Chandra Ray and Jagadish Chandra Bose.
- He served in the Physics Departments of both the University of Calcutta and Dacca University.
Scientific Contributions of S. N. Bose

- Bose-Einstein Statistics: It describe how a collection of non-interacting and indistinguishable particles distribute themselves among a set of available discrete energy states at thermodynamic equilibrium.
- Basically, it provides a framework for understanding how these particles distribute themselves among available quantum states at different energy levels, particularly at low temperatures.
- The statistics was extended to gas molecules by Einstein and Particles which obey B–E statistics principle are referred as "Bosons", named after S. N Bose.
- Bosons are fundamental articles that have integer values of spin(0, 1, 2, etc.). E.g. Photon, Gluon, etc.
- Bose-Einstein statistics predict phenomena such as:
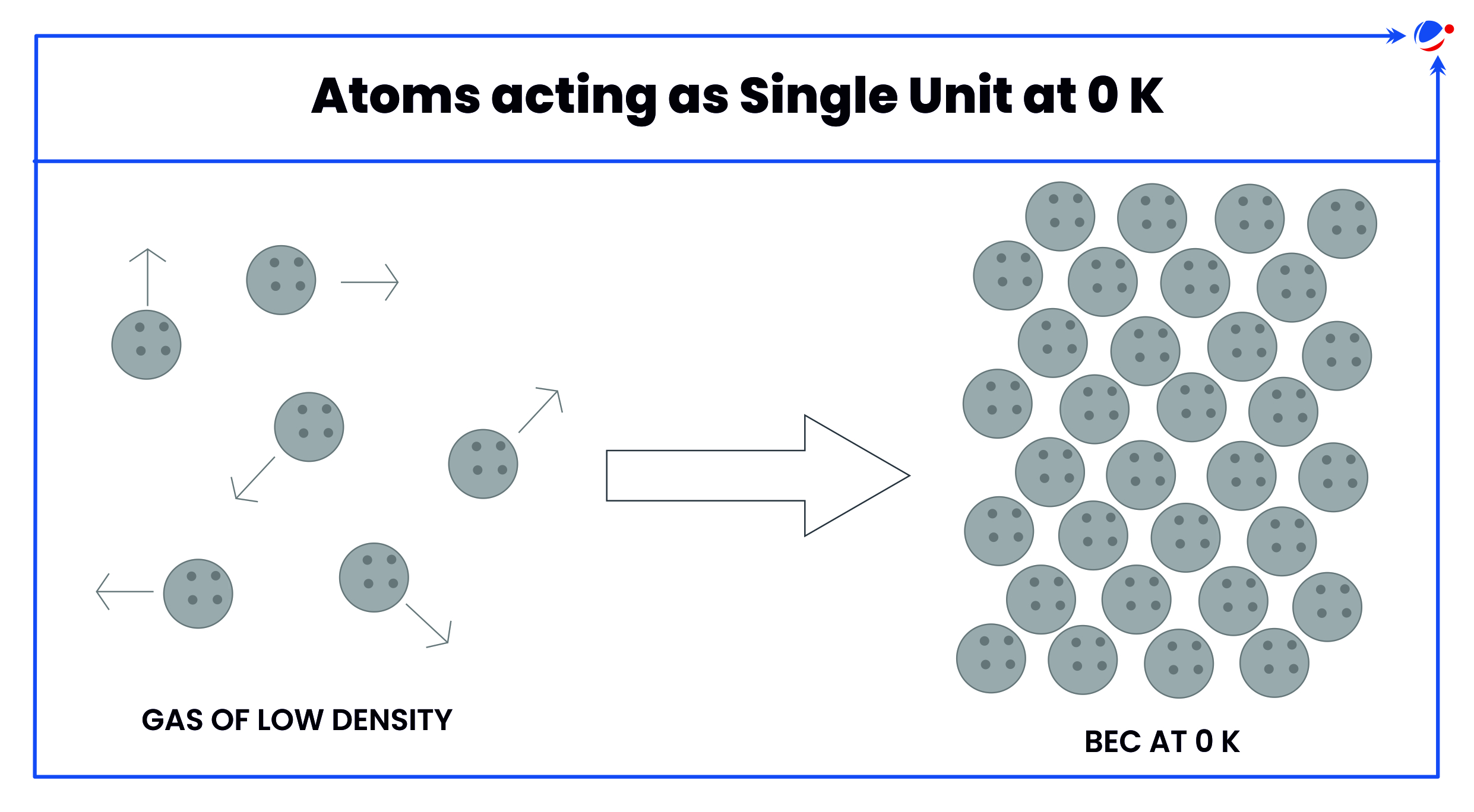
- Bose-Einstein Condensates (BEC): At extremely low temperatures, a large fraction of bosons can occupy the same lowest-energy quantum state, forming a unique state of matter (e.g., superfluid helium or ultracold atomic gases).
- Enabled first Quantum revolution in 20th century which helped in development of technologies such as lasers, the transistor, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, and semiconductors.
- Second revolution is defined by developments in technologies like quantum computing and quantum sensing, etc.
- Photon Behavior: The statistical rules explain blackbody radiation and the Planck distribution of energy, leading to the development of quantum mechanics.
- Bose-Einstein Condensates (BEC): It is a quantum phenomenon predicted by Bose and Einstein (1925).
- It is a state of matter created when particles are cooled to near absolute zero (-273.15 degrees Celsius/0 Kelvin).
- All the atoms become a single entity at this point, and possess quantum properties, wherein each particle together functions as a wave of matter.
- Referred to as the 'fifth state of matter'
- Properties of BEC include:
- Super fluidity: BEC has zero viscosity and can flow without resistance.
- Super conductivity: The zero resistance leads to optimal conductivity.
- Coherence: All particles in the BEC are in the same quantum state behaving as a single entity.
- Macroscopic Occupation: In a BEC, a number of particles occupy a same quantum state, leading to a macroscopic wave function.
- Super solid: Scientists have observed that BECs form high density 'droplets' that repel each other. When placed under certain conditions, including a trap, these droplets arrange themselves in an ordered lattice.
- A Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) exists at higher temperatures also in materials hosting bosonic quasiparticles such as magnons, excitons and polaritons.
- Organic chemistry: X-ray diffraction methods and the differential thermal analysis were employed in order to understand the atomic structure of common clay minerals.
- Thermoluminescence: He designed a rapid scanning spectrophotometer of comparatively high sensitivity to meet the requirements of the experimental workers in this field.
- Discovery of GOD Particle: The Higgs Boson, also known as the God Particle, was discovered using scientific principles rooted in Bose-Einstein statistics and the concept of BEC.
- The God Particle originates from an invisible field (Higgs Field) that permeates all space, imparting mass to particles. Even when the universe appears empty, this field exists.




