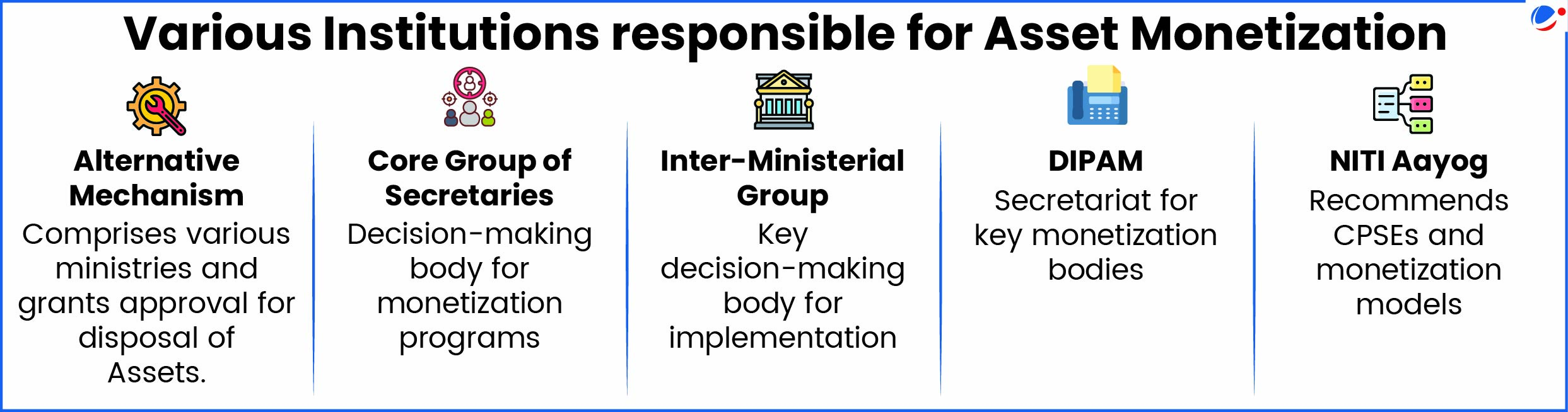
Why in the News?
National Highway Authority of India has outlined its strategy to monetize assets to unlock value and increase public-private participation for developing road infrastructure in India.
More on the News
- The strategy presents a structured framework to mobilise capital through mechanisms such as Toll-Operate-Transfer (ToT), Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs), and securitisation models.
- These instruments have helped NHAI raise over ₹1.4 lakh crore across more than 6,100 km of National Highways under National Monetisation Pipeline.
What is meant by Asset Monetization?
- It is the process of creating new/alternative sources of revenue by unlocking the economic value of underutilised public assets. It is also known as asset or capital recycling. It does not necessarily mean disinvestment of the asset.
Need for Asset Monetization
- Bridging Investment Gaps: Development of infrastructure requires massive investments. With limited fiscal space, monetization helps in mobilization of non-tax revenue.
- Overcoming Public Sector Inefficiencies: It helps in enhancing managerial and operational efficiency through participation of private sector.
- Unlocking Value from Brownfield Assets: It focuses on brownfield de-risked assets with stable revenue streams and makes them attractive to investors.
- Enhancing Global Competitiveness: High-quality infrastructure attracts foreign investments in the form of better FDI inflow, logistics and increased market access. It also leads to improving India's integration with the global value chain.
Models of Asset Monetization in India
- Toll, Operate & Transfer (TOT): It aims to attract private capital for management of completed assets in exchange for toll collection rights. The concessionaire pays a lump sum amount in the beginning and undertakes Operations and Maintenance obligations.
- Design-Build-Finance-Operate- Transfer (DBFOT): Concessionaire has responsibility of designing, building, financing and operating the facility before transferring the project to government after expiry of specified period.
- Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs): It is a pooled investment vehicle that raises funds from investors by issuing units. It offers stable and predictable cash flows, and diversification and tax benefits. It is regulated by SEBI.
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): They are pooled investment vehicles like mutual funds. However, they invest in real estate.
- Project-based Financing: It allows sectors to raise long-term finance from banks by securitizing user fee receipts. E.g. Toll Plazas
- Long Term Lease: Lessor confers to the lessee the right to use an asset for an agreed period in return for a payment or series of payments.
- Asset Concession: It consists of mining assets, real estate transactions and other monetisation projects such as station redevelopment and airport concessions.
Initiatives for Asset Monetization in India
- National Monetization Pipeline: It aims to generate (~Rs. 6 lakh crore) by leasing out public infrastructure assets over the course of four years, from 2022 to 2025.
- National Land Monetization Corporation (NLMC): It is a 100% government owned company under administrative control of the Department of Public Enterprises to carry out monetization of non-core assets of CPSEs.
- Asset Monetisation dashboard: It tracks progress and provides visibility to investors.
Asset Monetization in India: Impediments versus Strategic Interventions
Domain | Impediments in Asset Monetization | Strategic Interventions Required |
Transparency & Governance |
|
|
Sectoral Issues |
|
|
Valuation Discovery & Competitive Bidding |
|
|
State-Level Readiness |
|
|
Consumer & Public Interest |
|
|
Institutional Fragmentation |
|
|
Regulatory Uncertainty |
|
|
Fiscal Utilization & Public Trust |
|
|
Monitoring & Performance Tracking |
|
|
Conclusion
Asset Monetization Strategy is not just a financial tool but a transformative approach that aligns with the broader goals of economic growth and sustainable development. By unlocking the value of existing assets and reinvesting in new projects, asset monetization can pave the way for a robust and resilient infrastructure network that will support India's growth for years to come.







