Swasth Nari Sashakt Parivar Abhiyan
Recently, Prime Minister launched ‘Swasth Nari Sashakt Parivar’ Abhiyan.
About Swasth Nari Sashakt Parivar Abhiyan
- The Abhiyan will organize over one lakh health camps to screen women for anaemia, hypertension, diabetes, and cancer, while supporting immunization and nutrition to reduce maternal and child mortality.
- Ministries: Joint effort of Ministry of Health & Family Welfare and Ministry of Women & Child Development.
- Technology: SASHAKT portal willtrack progress and ensures accountability in real time.
- Community Role: Anganwadis, Nikshay Mitras, private hospitals, etc. will also participate.
- Tags :
- Swasth Nari Sashakt Parivar
- SASHAKT Portal
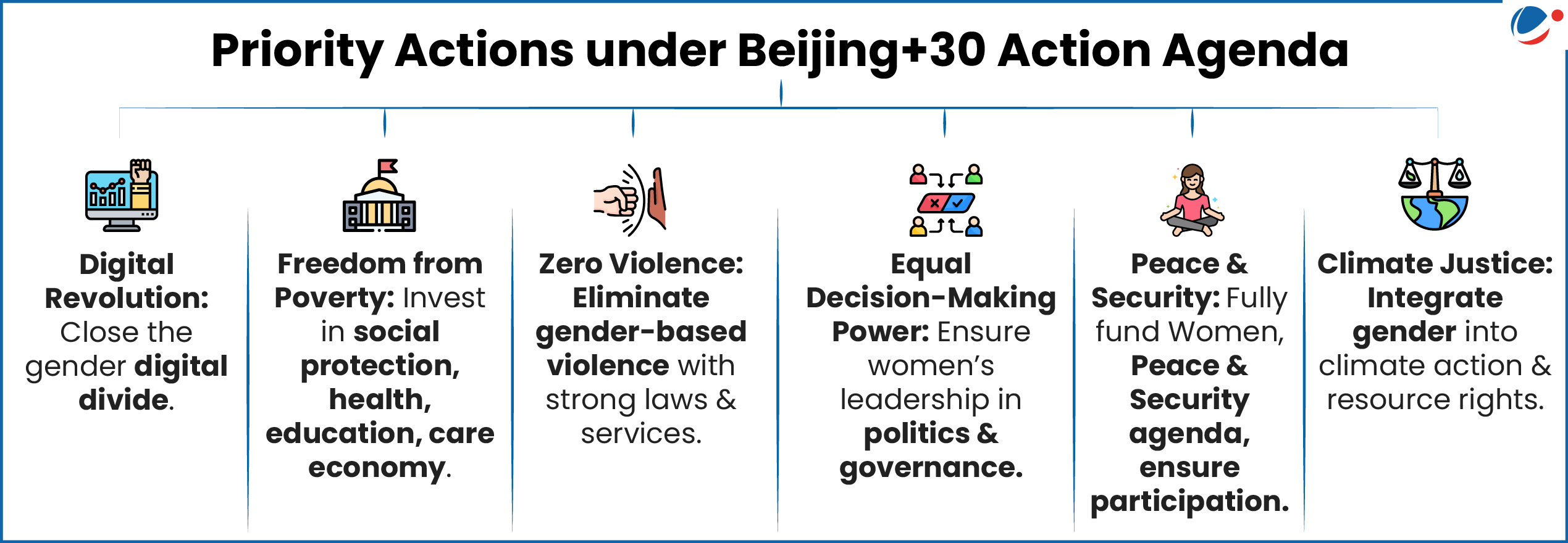
Progress On The Sustainable Development Goals: The Gender Snapshot 2025
The document jointly released by the UN Women and UN DESA (Department of Economic and Social Affairs) offers a comprehensive overview of the global state of gender equality across all 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Key Highlights of the Gender Snapshot 2025
- Poverty & Food Security: 376M women in extreme poverty (9.2%); anaemia projected to rise to 33% by 2030.
- Health: Maternal mortality decreased by 39% (2000–23), but women spend 3 more years in poor health than men.
- Education: Girls surpass boys in enrolment, yet lag in secondary completion in Africa & Asia; women rarely head schools.
- Leadership & Work: Women hold 27% of parliamentary seats, 30% of management roles.
- Violence: 12.5% women face intimate partner violence; 19% of young women married before 18.
- Digital Divide: 65% women online vs 70% men; women’s jobs more exposed to AI automation.
- Climate & Resources: Climate change could push 158M more women into poverty; 896M lack clean cooking fuels.
- Peace & Security: 676M women lived near deadly conflict in 2024.
- Intersectionality: Women with disabilities face limited reproductive rights, Internet access, and political participation.
- Tags :
- Gender Snapshot 2025
- Beijing+30 Action Agenda
UDISE+ 2024-25 Report
- Unified District Information System for Education Plus (UDISE+) 2024-25 Report was recently released by Ministry of Education.
- It aligns its findings as per NEP 2020 recommendations and has shifted to individual student-wise data collection mechanism.
Major Findings for the year 2024-25
- The total number of teachers has crossed the 1 crore mark in 2024–25 (rise of 6% from 2022-23) for the first time since the beginning of UDISE+.
- Pupil-Teacher Ratios (PTRs) have surpassed NEP's recommended 1:30 ratio.
- Present PTR: Foundational (10), Preparatory (13), Middle (17), and Secondary levels (21).
- Drop-out rates: It has decreased to 2.3% (Preparatory), Middle (3.5) and Secondary (8.2).
- Gross Enrolment Ratio: It has improved to 90.3% (Middle) and 68.5% (Secondary) levels
- Zero enrolment (decreased by 6%) and single-teacher schools (38% decrease) has shown progressive changes.
Data and Trends in Indian School Education in percentage terms (2022-23 to 2024-25)
Category | Indicator | 2023-24 | 2024-25 |
Infrastructure Facilities | Computer access | 57.2 | 64.7 |
Internet | 53.9 | 63.5 | |
Girls Toilet | 97.2 | 97.3 | |
Female Representation | Girls Enrollment | 48.1 | 48.3 |
Female Teachers | 53.3 | 54.2 |
- Tags :
- UDISE+ 2024-25 Report
- Trends in School Education
Articles Sources
Comprehensive Modular Survey (CMS) on Education
The Comprehensive Modular Survey (CMS) on Education, which forms part of the 80th round of the National Sample Survey (NSS) was recently released.
- It is released by the National Statistics Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI)
- It used Computer-Assisted Personal Interviews (CAPI) for data collection
- This survey differs from previous surveys (the most recent CMS undertaken by NSS was the 75th Round (July 2017–June 2018))
- Coverage: Unlike the previous survey, which included all levels of education, this one focuses only on school education.
- Anganwadi Centres: Classified under pre-primary education in this survey, unlike the 75th Round, where they were counted as 'other non-formal' education.
- Private Coaching: Unlike the 75th Round, the CMS separately collected and presented spending on school education and private coaching.
Key Highlights of the Survey
- Role of Government Education: Government schools account for 55.9 % of total enrolments.
- It is higher in rural areas (66%), in comparison to urban areas (30.1%).
- Private School Enrolment: Private unaided (recognised) schools account for 31.9 % of total enrolment across the country.
- Prevalence of private coaching: 27% of students were taking/had taken private coaching,
- It is more prevalent in urban areas (30.7 %) than in rural areas (25.5 %).
- Family Funding as main source of education: Approximately 95.0 % of students rely on other household members as their primary source of funding for education expenditure.
- Tags :
- Education
- NSS
Articles Sources
National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) 2025
Recently, NIRF rankings 2025 were released by the Union Government.
Key highlights
- IIT Madras topped the overall category
- Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru topped the Universities Category.
About NIRF
- Origin: Launched in 2015 by the Ministry of Education to rank Indian institutions.
- Provides a transparent, reliable system for students, parents, and policymakers to evaluate colleges and universities.
- Assessment Parameters: 5 broad categories with different weightage are used
- Teaching, Learning & Resources (0.30)
- Research and Professional Practice (0.30)
- Graduation Outcome (0.20)
- Outreach and Inclusivity (0.10)
- Perception (0.10)
- Tags :
- NIRF
- NIRF Rankings
Articles Sources
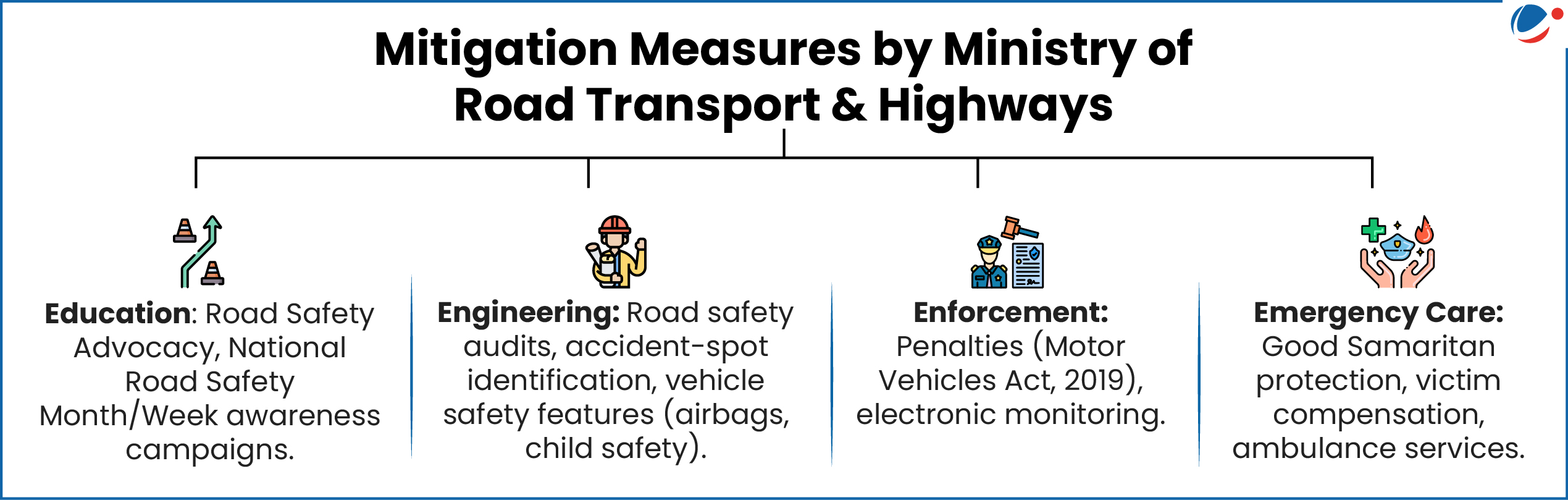
Road Accidents In India 2023 Report
Road Accidents in India 2023 Report was recently released by Ministry Of Road Transport And Highways.
Key Statistics
- Total Accidents and Fatalities: In 2023, 480,583 road accidents occurred (increased by 4.2% compared to 2022).
- Young adults in the age group of 18 - 45 years accounted for 66.4% of victims during 2023.
- Highest Share: Tamil Nadu recorded the highest number of road accidents in 2023 followed by Madhya Pradesh.
- Uttar Pradesh had the most fatalities followed by Tamil Nadu.
- Accident prone Highways: Highways with ~5% of the total road network accounted for > 53% of total accidents and 59% of fatalities.
- Road user categories: Two-wheeler riders constituted the highest percentage of accident deaths (45%) followed by pedestrians.
Major causes of Road Accidents:
- Human Error: It includes traffic rule violations, driving without a valid driver license and non-use of safety devices.
- Road Environment: It includes accidents happening in a particular geographical area (residential etc.), those related to road features, weather conditions etc.
- Vehicular conditions: E.g., Age of vehicle and Overloading.
- Tags :
- Road Accident



