Introduction
Public health and education are mutually reinforcing pillars of human capital development. However, variations in quality, regional differences, digital divides, and infrastructural gaps continue to influence the equitable distribution of these essential services.
Chapter Precap
Education
| Health
|
Education: Enhancing Quality and Access
Progress in school education
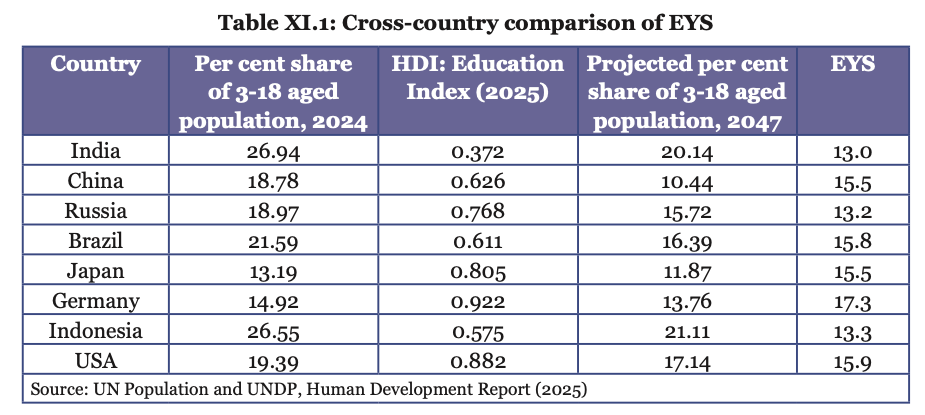
- In 2024, nearly 27% of India's population was in the school-going age group (3–18 years).
- However, India's Education Index, under UN's Human Development Index (HDI), remains modest, due to relatively low expected years of schooling (EYS) trailing behind global peers.
- India needs to raise its EYS to 15-year set by National Education Policy, 2020 (NEP)'s 5+3+3+4 schooling structure for ages 3-18 requiring holistic, lifestyle approach encompassing early childhood education, foundational literacy and numeracy (FLN), etc.
- NEP emphasises on Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE) for school education.
- Government launched school-level schemes like Sarv Shiksha Abhiyan, ULLAS, PM-SHRI(PM-Schools for Rising India), PM POSHAN (PM Poshan Shakti Nirman) and initiatives like PARAKH, Vidya Pravesh, DIKSHA (Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing), NIPUN Bharat Mission and Atal Tinkering Labs to achieve the NEP goals.
School infrastructure
- India operates one of the world's largest school systems, serving around 25 crore students across 14.71 lakh schools (UDISE+ 2024-25).
- Government schools constitute 69%, enrolling nearly half of all students, while private schools account for 26% of schools and 41% of total enrolment.
- APAAR (Automated Permanent Academic Account Registry) IDs using Aadhaar-based authentication to digitally store academic records and track student enrolment monitors progress towards NEP goal of 100% GER by 2030.
Achievements/Objectives of Key School Education Programmes | |
| PM SHRI Scheme | Establish over 14,500 PM SHRI Schools nationwide. Total of 13,076 PM SHRI schools established in 33 states/UTs. |
| Co-location of Anganwadi Centres (AWCs) with schools | In total, 4,81,004 of the government and government-aided schools with Grade I have some form of pre-school facility (Balvatika, co-located AWC, or both). |
| Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN) |
|
Multilingual textbooks
|
|
| Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalayas (KGBVs) | Residential schools for girls belonging to Socio-Economically Disadvantaged Groups in Educationally Backwards Blocks. |
| Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan | Construction of residential hostels to improve educational access for tribal students. |
| ULLAS: Adult education scheme | Ladakh, Mizoram, Goa, Tripura and Himachal Pradesh, have achieved full literacy under it. |
Community Participation in Education
|
Innovative pedagogy and community participation
- While India improved enrolment at early levels, secondary age-specific net enrolment (NER) remains low at 52.2% due to uneven distribution of schools
- Urban areas have a higher share of secondary schools compared to rural ones.
- Further action along with Schemes like Poshan Shakti Nirman and Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan in the form of strengthening open schooling, developing teacher skills through strengthened DIETs (District Institute of Education & Training), and SCERTs (State Council of Educational Research and Training), is needed.
Improvement in learning outcomes
- Key Issues
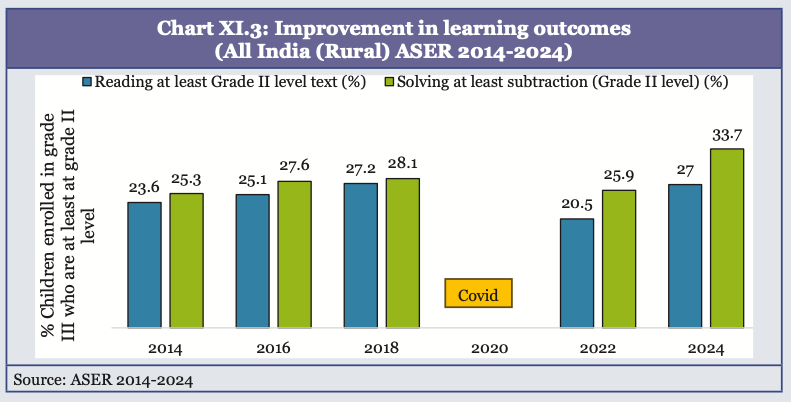
- Institutionalised systemic assessments: Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) 2024 and NAS findings suggest school-based assessments are unable to generate diagnostic evidence to identify learning gaps and inform corrective action.
- Best Practices: National Assessment of Educational Progress in USA; National Assessment Programme - Literacy and Numeracy in Australia for course-correction could be considered.
- Lack of Independent evaluation and System-wide Benchmarking: Relying solely on internal compliance and self-reporting of schools could be inadequate.
- Best Practices: Knowledge and Human Development Authority in Dubai and India's National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) ranking for higher education institutions enables comparison among institutions.
- Institutionalised systemic assessments: Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) 2024 and NAS findings suggest school-based assessments are unable to generate diagnostic evidence to identify learning gaps and inform corrective action.
Structural factors Shaping Learning Gains (ASER 2024)
|
- Key Initiatives: The PARAKH ((Performance Assessment, Review, and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development) Rashtriya Sarvekshan 2024 (formerly National Achievement Survey) by NCERT under Ministry of Education; Vidya Samiksha Kendras across all states/UTs.
School-to-Skill Pathways
- Nearly 2 crore adolescents aged 14–18 years are out-of-school. (PLFS 2023–24)
- Need to supplement household income, is the single largest reason for adolescent drop out accounting for 44% of drop-outs, particularly among boys (67.3%).
- Domestic and care responsibilities remain a major constraint for girls affecting over 55%.
- Only 0.97% of 14-18-year-olds have received institutional skilling, ~7% acquired skills informally while nearly 92 % have no skilling exposure (PLFS 2023-24).
Proposed Viksit Bharat Shiksha Adhishthan (VBSA)
|
Progress in Higher Education
- Number of Higher Education Institutions (HEIs): Increased from 51,534 in 2014-15 to 70,018 (June 2025), marked by substantial growth in universities and colleges.
- GER for Higher Education at the national level: 29.5 in 2022-23 up from 28.4 in 2021-22. (NEP target is 50% GER by 2035).
- Initiatives: National Credit Framework (NCrF) under NEP aims to blend academic and skills-based learning; Flexible entry-exit pathways and biannual admissions; Anusandhan National Research Foundation; Multidisciplinary Education and Research Improvement in Technical Education (MERITE) Scheme.
- Regulation: 'Light but Tight' regulatory framework like Viksit Bharat Shiksha Adhishthan (VBSA) Bill, 2025.
Developing state capacity to strengthen higher education
- 495 State Public Universities (SPUs) in India (highest in Karnataka) account for nearly 81% of the total student enrolment in HEIs, with a decadal improvement (from 2011-12 to 2021-22) of 38%.
- Noteworthy States noteworthy initiatives: Gujarat's Public Universities Act 2023 provided greater autonomy, simpler procedures, and more professional leadership structures; Capacity-building initiatives such as Maharashtra's State Faculty Development Academy; Alumni engagement in Odisha's Mo College initiative; Research Parks at IIT Madras and IISc (Indian Institute of Science) Bengaluru etc.
Industry-academia integration in STEM education
- TeamLease Edtech report shows that 75% of HEIs lack industry-readiness reflecting negatively in placement outcomes.
- Government initiatives like AICTE-Industry Fellowship Programme, Indian Science Technology and Engineering facilities Map (I-STEM), 'Professor of Practice' (PoP) category at HEIs by the UGC and the AICTE deepens industry engagement in higher education.
- PoP concept allows industry professionals to bring real- world practices and experiences into the classroom and also augment faculty resources.
Internationalisation of Higher Education
- Number of Indians studying overseas: It rose from 6.85 lakh in 2016 to over 18 lakh by 2025.
- In 2024, for every one international student coming to India, 28 Indian students went abroad, with significant associated foreign exchange costs.
- Annual outward remittance under the 'studies abroad' component: It has increased to USD 3.4 billion in FY24.
- Indian students abroad are concentrated in countries, including Canada, USA, UK, and Australia.
- India remains the principal host within South Asia, attracting over four-fifths of all inbound students to sub-region in 2023, largely from Nepal, Afghanistan, Bangladesh, and Bhutan.
- State-wise, earlier hubs like Karnataka and Tamil Nadu have seen declines in international student enrolment, while Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, and Andhra Pradesh emerged as hosts.
- Limited international visibility and regulatory frictions have limited India's ability to convert its cost and scale advantages into an equivalent pull factor.
- Key Initiatives serving as Pull Factors:
- Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation Programme, Ministry of External Affairs.
- UGC's Regulations on Academic Collaboration between Indian and Foreign Higher Educational Institutions, 2022,
- 100% foreign direct investment (FDI) in higher education.
- UGC (Setting Up and Operation of Campuses of Foreign Higher Educational Institutions in India) Regulations, 2023 in which 15 foreign HEIs are to set up campuses in India.
- Caution must be heeded to the working of market forces leading to increase in the cost of education, excessive commercialisation, exclusion of marginalised, overemphasis on borrowed knowledge systems undermining indigenous/ local traditions.
Health: Strengthening Public and Preventive Healthcare
- Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR): It has been reduced by 86%, exceeding the global average of 48% since 1990.
- Under-five mortality rate (U5MR): India witnessed 78% decline during 1990-2023
- Neonatal mortality rate (NMR): 70% decline during 1990-2023.
- Infant mortality rate (IMR) : It dropped more than 37% declining from 40 deaths per thousand live births in 2013 to 25 in 2023.
- Key Interventions: Strengthened neonatal care protocols, expanded immunisation programmes; ICT interventions under the PM Jan Arogya Yojana, Centres of Excellence for AI-driven reform at AIIMS Delhi, PGIMER Chandigarh, and AIIMS Rishikesh; Clinical Decision Support System integrated with e-Sanjeevani, etc.
Achievements/Objectives of Health Sector Schemes | |
Ayushman Bharat
| Holistically address health (covering prevention, promotion and ambulatory care), at primary, secondary and tertiary levels. |
| Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY) | Covered 49% of female beneficiaries; and 6 crore senior citizens. |
| National Programme for Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (NP-NCD) | Systematically identify high-risk individuals and link them to appropriate care.
|
| Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission | Strengthening health systems to ensure a continuum of care across all levels - primary, secondary, and tertiary. |
| National Tuberculosis Elimination Programme | Incidence rate declined by 21%, from 237/lakh (2015) to 187/lakh (2024); double the global decline (12%). |
| Universal Immunisation Programme | U-WIN portal |
| Pradhan Mantri National Dialysis Programme | Financial risk protection for patients by preventing them from incurring the out-of-pocket expenditure of ₹9741.25 crores. |
| Swasth Nari Sashakt Parivar Abhiyaan | Nationwide campaign for inclusive healthcare and empowering women. |
India's Epidemiological Transition
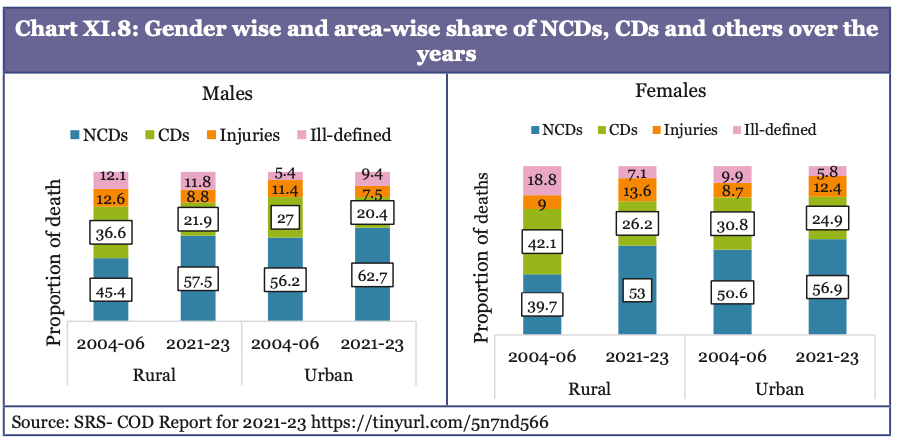
- India is a witnessing a linear shift from infectious to non- communicable diseases (NCDs).
- Over the past few decades, India experienced a decline in mortality from infectious diseases and an increase in life expectancy at birth from 49.7 years in 1973 to 70.3 years in 2023.
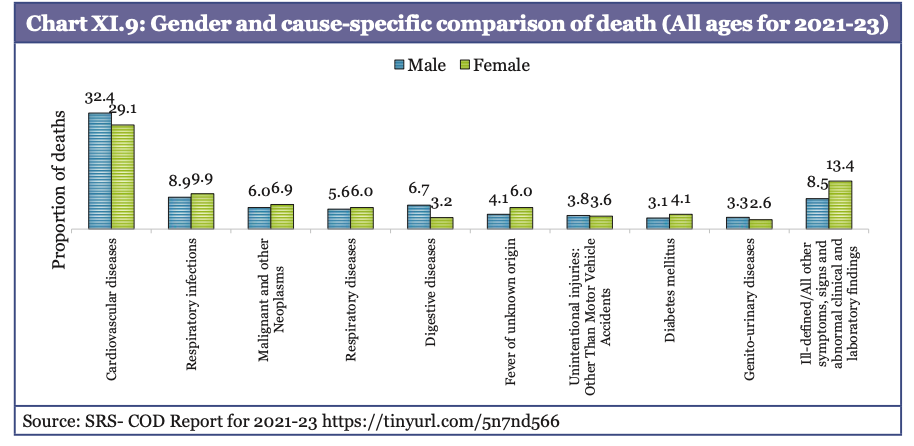
- However, it faces a double burden of persistent communicable diseases (CDs) (e.g., tuberculosis, vector-borne infections) coexisting with rapidly rising NCDs like cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancers.
- NCDs account for more than 57% of all deaths in the country.
Tackling the Obesity Challenge
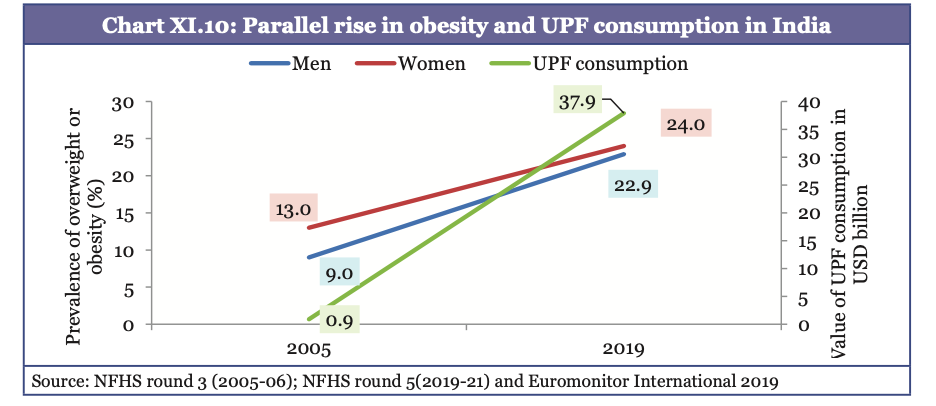
- 24% Indian women and 23% men are overweight/obese (2019-21 National Family Health Survey).
- Excess weight among children under five: It has risen from 2.1% in 2015-16 to 3.4% in 2019-21.
- Over 3.3 crore children in India were obese in 2020, projected to reach 8.3 crore children by 2035.
- Link with Ultra Processed Foods (UPF): India is one of fastest-growing markets for UPF sales growing by more than 150% from 2009 to 2023 with obesity doubled in both men and women during the same period.
- Government Initiatives: POSHAN Abhiyaan & Poshan 2.0, Fit India Movement, Khelo India, Eat Right India, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare (MoHFW) instructions to all states/UTs for a 10% reduction in oil consumption; National Programme for Prevention and Control of NCDs (NP- NCD) platforms; FSSAI's 'Stop Obesity & Fight Obesity- Awareness Initiative to Stop Obesity' campaign, etc.
Addressing Ultra Processed Foods Challenges
|
Nutritional Intake Trends
- Daily per capita intake of calories and protein: It increased in both rural and urban areas between 2009-10 and 2023-24
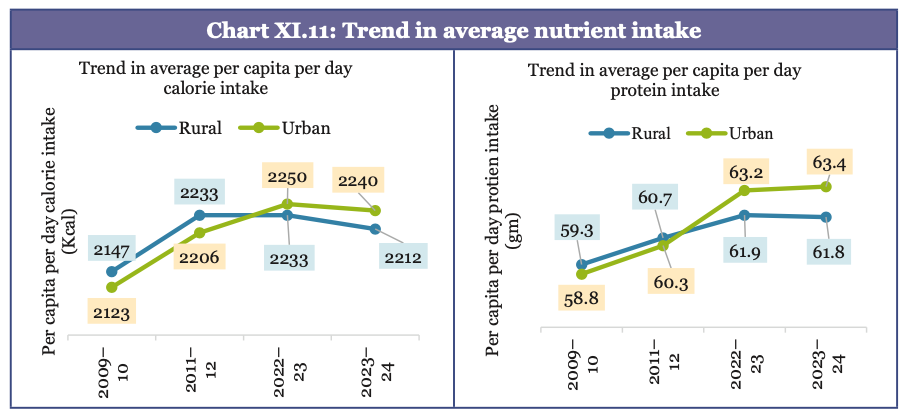
- Calorie intakes for rural and urban populations are similar at nearly every income level.
- Positive correlation between consumption expenditure and calorie intake in both rural and urban India.
- Dietary diversity of micronutrient intake improved significantly over last decade (2011-12 to 2022- 23) across all consumption classes, largest gains among bottom 20% households.
- Steps Needed: Whole-of-life approach; Traditional foods, like millets and lesser- known pulses for public distribution system; regulation of nutraceuticals, etc.
- Food to Nutritional Security: National Food Security Act of 2013; Saksham Anganwadi and POSHAN 2.0, Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY) and Poshan Shakti Nirman; 2024 ICMR–NIN Dietary Guidelines to tackle the dual burden of malnutrition-undernutrition.
Social & Behaviour Change Communication (SBCC): Lessons from the Rajasthan Cash Plus Model
|
Digital addiction: Cognitive and Psychological Impacts
- Digital economy contributed 11.74% to the national income in FY23, with projections of 13.42% in FY25.
- Internet connections grew from 25.15 crore (2014) to 96.96 crore (2024), supported by nationwide 5G deployment and Bharat Net fibre connectivity to 2.18 lakh Gram Panchayats.
- Analysis shows that Suicide Death Rate (SDR) shows reverse correlation with District Social Connectedness Index (SCI) i.e. states having districts with higher connectedness, and better in- person social networks, generally seen as having lower SDRs.
Tackling Digital Addiction | |
Global Responses
| India's Response
|
Way Forward
| |
Outlook
- Open acknowledgement and constructive public discussion.
- Technology-driven surveys using platforms like the UDISE+, AISHE, ABDM and integration of AI tools can identify 'health hotspots' like prevalence of obesity in urban slums, etc.
- Public-private partnership, employing technology like mobile apps, AI chatbots (ASHABot166), and digital dashboards (e.g., ASHA Kirana's M-CAT167 and ASHA Digital Health168), etc.
What does the Budget say?
- Biopharma SHAKTI (Strategy for Healthcare Advancement through Knowledge, Technology & Innovation) to be launched with an outlay of ₹ 10,000 crores over next 5 years
- Institutions to be upgraded to add 100,000 Allied Health Professionals over next 5 years in 10 disciplines, including optometry, radiology, and anaesthesia.
- A scheme to support states in setting up five Regional Medical Hubs to be launched to position India as global hub for Medical value tourism.
- 3 new All India Institutes of Ayurveda to be set up, alongside upgrades to WHO Global Traditional Medicine Centre in Jamnagar.
- Government to support states in creating 5 University Townships near industrial and logistic corridors.
- A girls' hostel will be established in every district.
- Four Telescope Infrastructure facilities to be set up/upgraded: National Large Solar Telescope, National Large Optical-infrared Telescope, Himalayan Chandra Telescope and COSMOS-2 Planetarium.
Glossary
Term | Meaning |
| Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) | Total enrolment in a particular level of school education, regardless of age, expressed as a percentage of the population of official age-group which corresponds to given level of school education in a given school year. |
| Demographic Transition | Shift from high to low birth and death rates as societies modernise. |
| epidemiological transition | Change in leading causes of death from infectious diseases to chronic, non-communicable conditions. |
| Maternal Mortality Ratio (MMR) | Number of maternal deaths during a given time period per 100,000 live births during the same time period. |
| Neonatal Mortality Rate (NMR) | Number of deaths of infants under 28 days of age per 1,000 live births. |
| Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) | Number of deaths of infants under one year of age per 1,000 live births. |
| Under-5 Mortality Rate (U5MR) | Number of deaths of children under five years of age per 1,000 live births. |
| Nutraceuticals | 'Specially designed preparations', formulated for fulfilling specific dietary requirements and/or offer preventive health care. |
| Digital Addiction | Behavioural pattern of excessive/compulsive engagement with digital devices or online activities that leads to distress and functional impairment. |








