Factors like health, education, technology, and institutions are key determinants of social mobility. Equality of opportunities ensures greater social mobility through an equal and merit-driven framework. Low social mobility entrenches historical inequalities, and higher income inequalities fuel lower social mobility.
Chapter Precap
Poverty
Social Sector Expenditure
| Rural Economy
|
Social Justice
| |
Lifting Millions Up: Progress on Poverty and Inequality
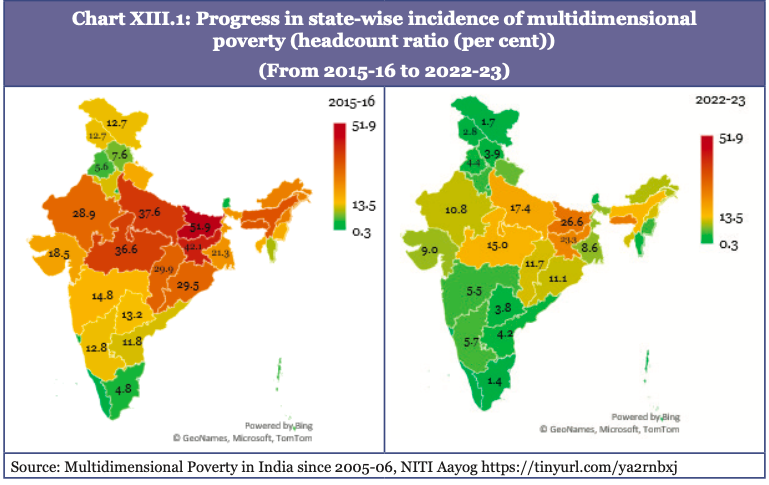
- Poverty rates for India in 2022-23 (as per revised IPL): 5.3% for extreme poverty and 23.9% for lower-middle-income poverty.
- In June 2025, World Bank's (WB) International Poverty Line (IPL) was raised from USD 2.15 to USD 3.00 a day, adjusted for the purchasing power of money to 2021 prices.
- The WB Multidimensional Poverty Measure for India stood at 15.5% in 2022-23.
- NITI Ayog's Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI): It declined from 55.3% in 2005-06 to 14.96% by 2019-21, estimated to have decreased further to 11.28% in 2022-23.
- Poverty estimates on Tendulkar committee poverty line also indicate a sharp and broad-based decline in poverty.
- Between 2011-12 and 2023-24, poverty rate estimated to have reduced from 21.9% in 2011-12 to 4.7% in 2022-23 and further to 2.3% in 2023-24.
- Key Reforms: State's initiatives like Bihar's 'Satat Jeevikoparjan Yojana (SJY)', using 'Graduation approach'; Kerala's Poverty Eradication Model; Union Government's 'Samaveshi Aajeevika Yojana' programme under umbrella of Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY- NRLM), built on 'Graduation approach.
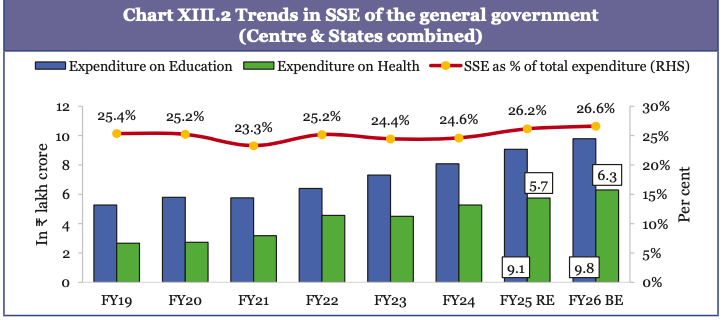
Social Sector Expenditure Trends
- Population covered by social protection systems: It increased from 22% in 2016 to 64.3% in 2025. (as per Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation's latest Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) National Indicator Framework (NIF) Progress Report, 2025)
- Population using improved drinking water sources in rural areas increased from 94.6% in 2015-16 to 99.6% in 2024-25.
- 100% districts declared open defecation free (ODF) in 2019- 20, and over 96% of Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) villages achieved ODF plus status (31 December 2025).
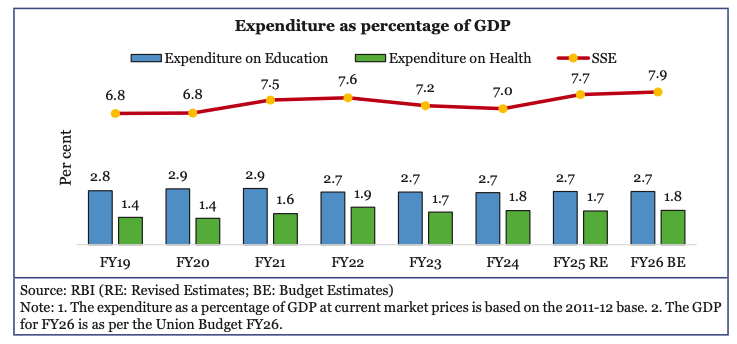
- From FY22 to FY26 (BE), Social Service Expenditure (SSE) grew at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12%.
- Expenditure on education grew at a CAGR of 11% while on health grew at 8%.
Transforming the Rural Economy
- Rural Landscape forms the backbone of the nation with 6.65 lakh villages and 2.68 lakh Gram Panchayats (GPs) and Rural Local Bodies.
- NABARD's latest Rural Economic Conditions and Sentiments Survey (RECSS) (November 2025) shows broad-based strengthening of rural economic fundamentals.
- Decline in dependence on the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) is evident with decline in work demanded.
- Person days generated declined from 389.09 crore person days in FY21 to 183.77 crore in FY26 (up to 31 December 2025), by over 53%.
- Decline coincides with a decrease in rural unemployment, from 3.3% in 2020-21 to 2.5% in 2023-24.
- Women's participation rose from 48% to 58.1% between FY14 and FY25.
Reimagining rural employment in a changing rural economy
- Viksit Bharat- Guarantee for Rozgar and Ajeevika Mission (Gramin) Act, 2025 or VB - G RAM G Act, 2025: Deeper structural issues in MGNREGA caused accumulation of misappropriation over time leading to the enactment of VB - G RAM G Act, 2025, representing a decisive shift in India's rural employment policy.
- Act offers timely payment mechanism where wages are disbursed on a weekly basis, or within a fortnight of work completion.
- It increases administrative expenditure ceiling from 6 to 9% of total expenditure.
VB G-RAM G Bill 2025 - Reforming MGNREGA for Viksit Bharat
| Feature | MGNREGS | VB G RAM G |
| Days of employment | 100 days of wage employment per rural household | Legal guarantee of 125 days of unskilled wage employment per rural household per financial year. |
Focus of works
| Multiple and scattered categories with limited strategic focus. | Four clearly defined priority areas: water security, rural infrastructure, livelihoods and works towards disaster preparedness. |
Unemployment Allowance
| If employment not provided within stipulated time; Disentitlement clause existed. | If employment not provided within stipulated time; the disentitlement clauses removed. |
Pause window
| No explicit statutory 'pause window'. | States can notify periods aggregating 60 days when works shall not be undertaken. |
Funding approach
| Demand-based funding with unpredictable allocations.
| Demand-driven, State-wise normative allocation ensuring equity, fairness, and balanced regional development. |
Local planning
| Gram Panchayat (GP) planning is central. | Decentralised, participatory, bottom-up through Gram Sabha led Viksit GP plans. |
Technology-driven Participation
- As of December 2025, drone survey under SVAMITVA has been completed in 3.28 lakh villages, against a target of nearly 3.44 lakh villages notified.
- Lead Fertiliser Companies distributed 1,094 drones to SHG Drone Didis in 2023-24 with 500 of these drones provided under Namo Drone Didi Scheme.
- Registration of land and property computerised under Digital India Land Records Modernisation Programme (DILRMP) to extent of 95.73% of Sub Registration Offices.
- Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (ULPIN)/Bhu-Aadhaar assigned to 36.67 crore land parcels to date.
- Digitisation of Record of Rights in rural area is done for 99.8% of available land records.
- Rural Technology Action Group (RuTAGe) Smart Village Centre (RSVC), inaugurated in Mandaura village, Sonipat, as a permanent hub at Panchayat level to support 15-20 villages with 12 technology tracks.
Village Commons in India: Need for a fresh approach
- 2011 Census estimated India's common land to be around 6.6 crore hectares with such ecosystems generating an economic dividend of USD 9.05 crore per year.
- As per Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas, degraded land expanded from 94.53 million hectares (28.8% of geographical area) during 2003-05 to 97.85 million hectares (29.8%) by 2018-19, adding 2.2 lakh hectares annually.
- Key Restoration Initiatives: Mission Amrit Sarovar, SVAMITVA Yojana; PM Krishi Sinchai Yojana - Har Khet Ko Pani; Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch The Rain, etc.
- Protecting village commons in India aligns with Elinor Ostrom's principles for sustainable management of common-pool resources.
- Done with categorisation of village commons as a distinct land use category; community participation, well-structured capacity building through institutions such as National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj (NIRD&PR), etc.
Harnessing Social Capital for Livelihood
- India has around 26% population in 10-24 age where search for job drives rural to urban migration with nearly one in four rural Indians (26.8%) being a migrant in 2020-21.
- However, cities are reaching capacity limits, with approximately 65% of the population still residing in rural areas.
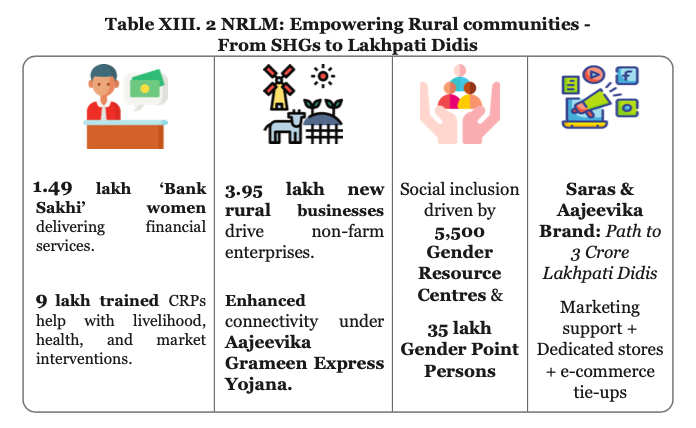
- Key Initiative: DAY-NRLM invests in four core components, viz., social mobilisation and financially sustainable community institutions for rural poor women; financial inclusion; sustainable livelihoods; and social inclusion.
- For implementation, SHG members acts as Community Resource Persons (CRPs). With over 9 lakh CRPs, the mission's federations give women a collective voice and agency.
Skilling initiatives
- Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY) is a state-led scheme being implemented in public-private partnership (PPP) mode, based on demand-driven target sanction process.
- It mandates independent third- party certification, through Sector Skill Councils (SSC) of National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC).
- Rural Self-Employment Training Institutes (RSETIs) Programme: Unique PPP initiative implemented through sponsor banks in collaboration with state governments.
- Currently, 629 RSETIs are operational supported by 25 financial institutions.
Capacity Building for better governance
Panchayat Advancement Index (PAI)
|
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme, Rashtriya Gram Swaraj Abhiyan (RGSA): revamped in 2022, trained more than 35 lakh participants in FY25.
- Digital Governance: e-Panchayat Mission Mode Project is digitising planning, budgeting, and service delivery through platforms like e-Gram Swaraj
- e-Gram SWARAJ portal: Launched in 2020, provides single window with complete GP profile.
- 48 So far, 2.54 lakh GPs have prepared and uploaded their GPDP for FY25 on e-Gram SWARAJ.
- Participatory Democracy: AI tools like Sabha Saar (As of November 2025, about one lakh GPs conducted 1.38 lakh Gram Sabhas and generated automatic minutes of meetings through Sabha Saar).
Rural Infrastructure
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) (PMGSY-I), 2000: Provides all-weather road connectivity to eligible unconnected habitations in rural India (500 persons and above in plains & 250 persons and above in hilly and NE areas as per 2001 census).
- As of 15 January 2026, 99.6% of eligible households provided with connectivity.
- PMGSY-II, 2013: To consolidate the existing Rural Road Network.
- So far, 6,612 roads (49,087 km) & 749 bridges have been completed.
- PMGSY-III,2019: Consolidation of 1,25,000 km of routes and major rural links connecting habitations, Gramin Agricultural Markets, higher secondary schools, and hospitals.
- 12,699 roads (1,02,926 km) & 1,734 bridges completed as of 15 January 2026.
- SBM-Grameen II: Chhattisgarh constructed its first plastic waste-mixed bituminous road in Bastar district, embodying 'Waste to Wealth' vision of SBM-Grameen Phase II.
- Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN): Targets 75 Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in 18 states and one UT.
- Under it, 263 roads (1,314 km) have been completed as of 15 January 2026.
- Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Vikas Mission (PMJVM): Under PMJVM, 4105 Van Dhan Vikas Kendras established, benefiting approximately 12 lakh people.
- Forest Rights Act 2006: Enabled distribution of 23.92 lakh individual and 1.22 lakh community titles, covering 233.48 lakh acres.
- Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana -Gramin: Aims to provide 4.95 crore pucca houses with basic amenities to all eligible houseless households living in kutcha and dilapidated houses in rural areas by 2029. So far, 2.93 crore have been completed so far.
- Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM): By 2025, over 12.50 crore more households were covered, increasing total coverage to about 15.74 crore (81.31%).
- It has caused significant gains, as per WHO estimates, there is a daily time savings of over 5.5 crore hours, prevention of 4 lakh diarrhoeal deaths, and savings of 14 million Disability Adjusted Life Years.
Tribal Population and Key Initiatives for their Empowerment
|
Rural Wellbeing
- Telemedicine has potential to improve health outcomes in underserved areas.
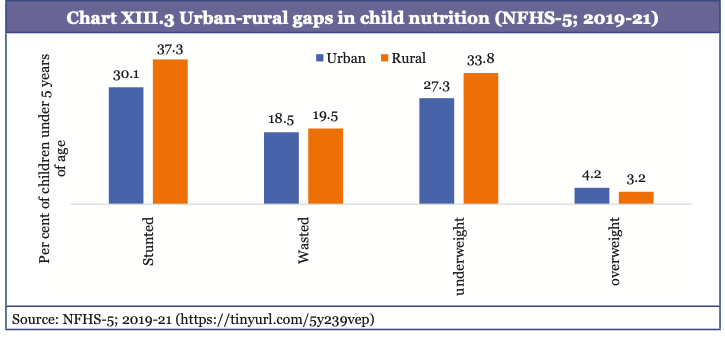
- Strengthening front-line workers led outreach by supporting ASHA, ANM, and AWW with technology integration like mobile apps, AI chatbots, and dashboards (e.g. ASHABot, ASHA Kirana's M-CAT and ASHA Digital Health).
Participatory Budgeting and Planning
- Greater Financial Independence: Own Sources of Revenue (OSR) enables PRIs to make more informed decisions on expenditure.
- Incentives: Matching Grants in Andaman & Nicobar and financial rewards in Goa, along with shared mining royalties, the District Mineral Fund (DMF), Goods and Services Tax (GST) further support PRI revenues.
- Key Initiatives: Samarth application for generating and collecting tax demands and collaboration with institutions like IIM-A on capacity-building modules.
- Creating Awareness: Meri Panchayat App, developed by MoPR; e-Gram Swaraj-BHASHINI integration allows e-Gram Swaraj to provide services in 22 scheduled languages through Bhashini's AI-powered translation.
- State Specific Operational Strategies: DAY- NRLM implements Food, Nutrition, Health and WASH (FNHW) interventions focussing on creation of awareness for improving nutritional intake.
- Around 6,406 blocks of 683 districts have initiated FNHW interventions.
Social Justice as an Enabler of Inclusion
- Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment: Adopts comprehensive approach to empower vulnerable populations across four key focus areas: social, economic, educational, and rehabilitative empowerment.
- Key Initiatives:
- E.g., Venture capital fund for Scheduled Caste (SC) and Backward Classes startups supported over 160 enterprises from these communities.
- The VISVAS Yojana (Vanchit Ikai Samooh Aur Vargon Ko Aarthik Sahayata), an initiative for financial inclusion, offering credit support, interest subvention, working in convergence with other programmes like MUDRA, NRLM, PRAYAAS, etc.
- National Social Assistance Programme (NSAP) implemented as a social security programme catering to 3.09 crore BPL beneficiaries.
- Aadhaar-based Mobile Application for Digital Life Certification (DLC) of NSAP pension beneficiaries launched in July, 2025.
- Total of 47.76 lakh beneficiaries have been authenticated through DLC. (January 2026)
- Schemes by Ministry of Minority Affairs:
- Educational scholarships (Pre-Matric, Post-Matric, Merit-cum-Means),
- employment support via Pradhan Mantri Virasat ka Samvardhan and National Minorities Development and Finance Corporation (NMDFC) loans,
- special initiatives like Jiyo Parsi; Pradhan Mantri Jan Vikas Karyakram scheme.
- Capacity-Building Initiatives: Like Adi Karmyogi Abhiyaan; DA-JGUA; Eklavya Model Residential Schools to provide quality education to ST children in remote areas; credit support through National Scheduled Tribes Finance and Development Corporation.
Key schemes to improve social justice
Schemes | Current FY26 (December, 2025) |
Pre-matric scholarship schemes for SCs & others - Centrally sponsored scheme | 17.14 lakh beneficiaries.
|
Post-matric scholarship schemes for the SCs. | 34.42 lakh beneficiaries. |
SMILE - Rehabilitation for the welfare of transgender persons | 23 Garima Grehs, shelter homes in 17 states/UTs. |
SMILE - Comprehensive rehabilitation of persons engaged in the act of begging | Covers 181 cities; 26,781 individuals identified. |
Scheme for implementation of Protection of Civil Rights Act, 1955 and Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989 - Centrally sponsored scheme | Around 87,426 victims of atrocity are proposed to be provided relief.
|
National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction - Centrally sponsored scheme | 349 Integrated Rehabilitation Centres for addicts. |
Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan | 25.53 crore people sensitised since launch. |
Atal Vayo Abhyuday Yojana
| ₹287.81 crore utilised under four Programmes: Integrated Programme for Senior Citizens, State Action Plan for Senior Citizens, Rashtriya Vayoshri Yojana, Elder line: National Helpline for Senior Citizens. |
Pradhan Mantri Anusuchit Jaati Abhyuday Yojana | 2611 Adarsh gram declared |
Scholarships for higher education for young achievers' scheme (SHREYAS) for SCs | Supported 3974 beneficiaries for higher studies in India. |
Uplifting sanitation workers and waste pickers
- Supreme Court Directions: Recently directed banning manual scavenging in six major metropolitan cities, and enhanced compensation for deaths of sanitation workers to ₹30 lakh.
- National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) Scheme, 2023: 89,104 sewer and septic tank workers (SSW) validated and profiled across country.
- Involvement of Civil Society; Urban Local Bodies in identifying SSWs; distribution of safety kits like Personal Protective Equipment, Safety Device Kits for Emergency Response Units, etc.
- Global Practices: Local governments in Japan utilise robotic cleaners, and suction systems; EU's automated systems like PipeGuard and PIPEON, integrates robotics, predictive maintenance, and real-time monitoring.
- Other Efforts in India: Indigenously developed vehicle-integrated machines and robotic cleaners; over 70,000 SSWs covered under Ayushman Bharat – PM Jan Arogya Yojana; National Safai Karamcharis Finance and Development Corporation, etc.
Outlook
- Idea of equality, crucial for inclusive development, rests on the belief that everyone have the same opportunities while essentially not the same outcome.
- Government policies have had a significant influence on income distribution, primarily through subsidies, pensions, direct transfers, and public expenditures on social services.
- Recent Household Consumption Expenditure Survey 2023-24, reports decline in consumption inequality showing that the largest growth in average monthly per capita expenditure (MPCE) between 2022-23 and 2023-24 occurred among the bottom 5-10% in both rural and urban areas.
What does the Budget say?
- Integrated development of 500 reservoirs and Amrit Sarovars towards strengthening fisheries value chains.
- Support entrepreneurship through credit-linked subsidies, modernization of livestock enterprises, and creation of Livestock Farmer Producers Organisations.
- Government to support crops like coconut, sandalwood, cocoa, and cashew in coastal areas, as well as agar trees in the North East.
- A Coconut Promotion Scheme to replace old trees to boost productivity.
- Dedicated program to make India self-reliant in raw cashew and cocoa, transforming them into global brands by 2030 to be launched.
- A multilingual AI tool called Bharat-VISTAAR (Virtually Integrated System to Access Agricultural Resources) will be launched to integrate agricultural portals with AI systems
- SHE-Marts (Self-Help Entrepreneur Marts) will be established as community-owned retail outlets to help women transition from credit-led livelihoods to business ownership.
Glossary
| Graduation approach | Evidence-informed anti-poverty programme combining asset transfers, training, financial support, coaching, and health services to address multiple constraints simultaneously. |
| Social Mobility | Inter-generational and intra-generational mobility, i.e. changes in a person's social or economic status during their own lifetime. |
| International Poverty Line | Minimum amount of money a person needs per day to afford basic necessities such as food, clothing, and shelter. |
| Village Commons or Common Property Resources |
|



