Why in the News?
Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) has started first crude oil production from its Cluster-2 deep-sea project in the Krishna-Godavari (KG) basin in the Bay of Bengal.
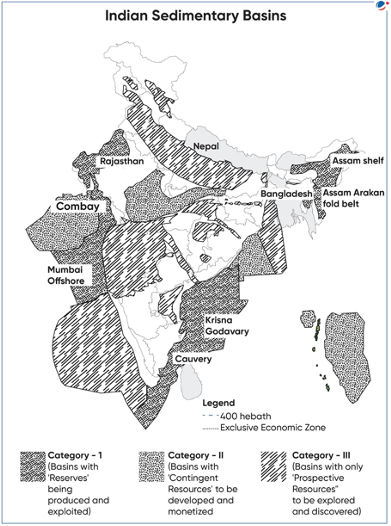
Petroleum basin in India
- A petroleum basin includes a diverse collection of rocks and sediments, but most importantly it contains source rocks.
- Source rocks are specific shale formations in a basin where oil and gas are born.
- There are 26 sedimentary basins in India, covering a total area of 3.4 million square kilometer.
- Of the total sedimentary area,
- 49% of total area is located on land,
- 12% in shallow water (up to 400 meter water depth) and
- 39% in the deepwater area (farther up to Exclusive Economic Zone or EEZ).
- The jurisdiction of the EEZ extends 200 nautical miles from the coastline, thereby conferring on the coastal state the right to manage, explore, exploit, and conserve all resources within its purview, be they living or non-living.
- These basins are also divided into three categories based on maturity of hydrocarbon resources as under:
- Category-I: Commercially established & producing basins. Total 7 basins (refer to the map)
- Category-II: Prospectivity identified. Total 5 basins (Kutch, Mahanadi- North East Coast (NEC) region & Andaman-Nicobar, Vindhyan, Saurashtra)
- Category-III: Prospective. Total 14 basins (Himalayan Foreland, Ganga, Kerala-Konkan-Lakshadweep, Bengal, Karewa, Spiti-Zanskar, Satpura-South RewaDamodar, Narmada, DecanSyneclise, Bhima-Kaladgi,Cuddapah, Pranhita-Godavari, Bastar, Chhattisgarh)
- Methods of Extracting Crude Oil:
- Offshore drilling: In marine environments, offshore basins like Arabian Sea or Bay of Bengal.
- Onshore drilling: On land, covering various sedimentary basins across the country.
- ONGC is India’s largest oil and gas producer contributing 72% of the country’s hydrocarbon production.

Steps taken for enhancing Petroleum E&P
- Directorate General of Hydrocarbons (DGH) was formed to promote sound management of the oil and natural gas resources.
- Approval processes have been streamlined by digitization and standardization of contractual submissions on the e-platform.
- National Data Repository (NDR), launched for public in 2017, serves as a government data bank promoting E&P activities.
- Upgrade of the NDR to a cloud-based, state-of-the-art facility with virtual data rooms is in progress for investors for 24x7 access to E&P data.
- As per India Hydrocarbon Vision 2025, lays the broad contours/targets for the development of Hydrocarbons.
- 100% FDI through automatic route for exploration activities of oil and natural gas fields, infrastructure related to marketing of petroleum products and natural gas, etc.
- National Seismic Programme (NSP) aims to undertake a fresh appraisal in all sedimentary basins across India.
Challenges in Petroleum E&P
- Capital: Oil production units are capital intensive in nature. It requires expensive equipment and highly skilled labours.
- Technological: Extracting petroleum from challenging geological formations requires advanced drilling technologies.
- Accidents: E&P activities involve the risk of spills, leaks, and other accidents. For e.g., recent event of Ennore oil spill in Tamil Nadu.
- Environmental: Loss of habitats and wildlife due to drilling, pipelines, and other infrastructure.
- Community displacement: Displacement of local communities, leading to social and cultural challenges.

Way forward
- Investment: Explore opportunities for joint E&P of oil and gas assets with Global companies.
- Also, stable tax regime and tax break would help attracting more private investment.
- Industry-academia collaboration: It provides access to the latest research and technologies, bridges the divide between theory and practice.
- For e.g., MoU signed between DGH and Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology for application of AI/ML in Amguri and adjoining areas of Upper Assam.
- Sustainable E&P: For example, Oil India Limited has taken steps for sustainable oil production by partnering with the Assam State Biodiversity Board and the IUCN.
- They signed an agreement to study the impact of oil production on Dibru Saikhowa National Park (of Assam) and develop an oil production plan in response to the findings.
- Control Oil spills: by using latest technologies like oil-zappers. Provide comprehensive training for industry personnel on spill prevention and response protocols.
- Mitigating impact on community: Project planning should involves carrying out an impact assessment to understand the potential effects on local communities, including people’s health, livelihood etc.
About HELP
|
Unconventional Petroleum Resources
|








