Why in the news?
Nepal and India have inked an agreement setting the target to reach 10,000 megawatts of electricity export to India in the coming decade.
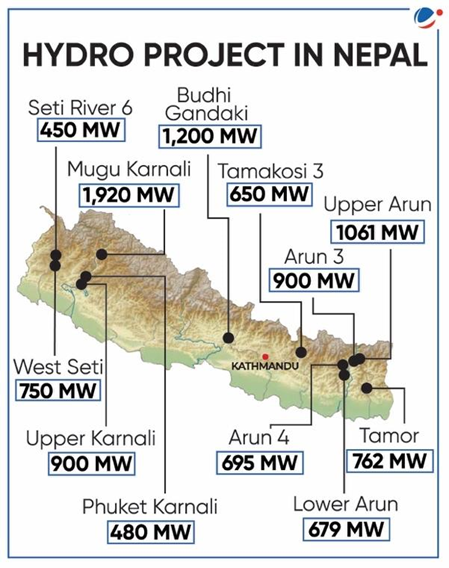
Indian Hydropower projects in Nepal
- West Seti and Seti River (SR6) projects (1,200 MW).
- Sapta Kosi high dam project on Kosi river.
- Mahakali Treaty (6,480 MW), the Upper Karnali Project (900 MW) and the Arun - III projects (900 MW).
- Phukot Karnali Hydroelectric Project
- Through agreements between NHPC and VUCL (Vidyut Utpadan Company Ltd), Nepal.
- Lower Arun Hydroelectric Project
- Through an agreement between SJVN (India) and the Investment Board of Nepal.
Significance of cooperation for India | Significance of cooperation for Nepal |
|
|
Major areas of concern in the development of hydropower
- Natural constraints: Fragile geological features and inadequate hydrological data, High sediment load in rivers in Nepal, and the presence of glacial silt.
- Lack of Infrastructure: Lack of adequate access to transport facilities, and transmission grid for power evacuation decreases the viability of the projects.
- Chinese concern: India is reluctant to purchase energy produced by hydropower projects which are run by Chinese companies in Nepal.
- Lack of policy, and regulatory mechanism for the third party access to the grid.
- Water sharing issues: The issue of downstream water use and flood control etc. also emanates with bigger multipurpose projects.
Road Ahead
- Resilient and effective infrastructure: Aiding Nepal in developing its transmission network within the country and also the interconnections with India.
- Hydropower as a multiplier: Both sides should view hydropower projects in Nepal as an enabler of long-term cooperation and regional stability.
- More Coverage: The projects can also be extended to other regional partners under the Bangladesh-Bhutan-India-Nepal (BBIN) framework for cross-border energy cooperation.




