- Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is an intergovernmental Organization.
- Established at the Baghdad Conference in 1960, by Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela.
- Its other members are Algeria, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Libya, Nigeria, the Republic of the Congo, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Key Objective: Co-ordinate and unify petroleum policies among Member Countries, to secure fair and stable prices for petroleum producers.
- And, ensure efficient, economic, and regular supply of petroleum to consuming nations.
- HQ: Vienna, Austria.
- Established at the Baghdad Conference in 1960, by Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela.
- Significance of OPEC: It possess more than 80% of the world’s total crude oil (mixture of hydrocarbons that exists in liquid phase) reserves.
- Also, OPEC+ represents around 40% of world oil production.
- OPEC+ is a coalition of OPEC and 10 other major oil-exporting nations, including Russia.
- Also, OPEC+ represents around 40% of world oil production.
- How does OPEC regulate the Crude oil Prices?
- Oil prices are mainly determined by demand and supply.
- It mainly uses a spot or future sale mechanism.
- Oil spot prices represent the cost of buying or selling oil immediately.
- Oil futures are contracts in which one agrees to exchange an amount of oil at a set price on a set date.
- OPEC uses Brent Crude as a benchmark for quality.
- WTI (West Texas Intermediate) is another major benchmark.
- India started a four-year term as a member of the UNSC.
- UNSC, established in 1946 is the highest body of global statistical system.
- Members: Consists of 24 member countries of UN elected by ECOSOC.

- Allahabad High Court mandates that India, a member of the Apostille Convention, must accept foreign apostille-authenticated documents.
- Hague Apostille Convention, 1961
- It simplified the global circulation of public documents.
- These public documents include certificates of birth, marriage, and death, and educational documents among others.
- Contracting parties issue an Apostille certificate to authenticate a document's origin, allowing it to be presented abroad to another Contracting Party.
- Non-member countries require extra certification from the State of origin for document acceptance.
- It simplified the global circulation of public documents.
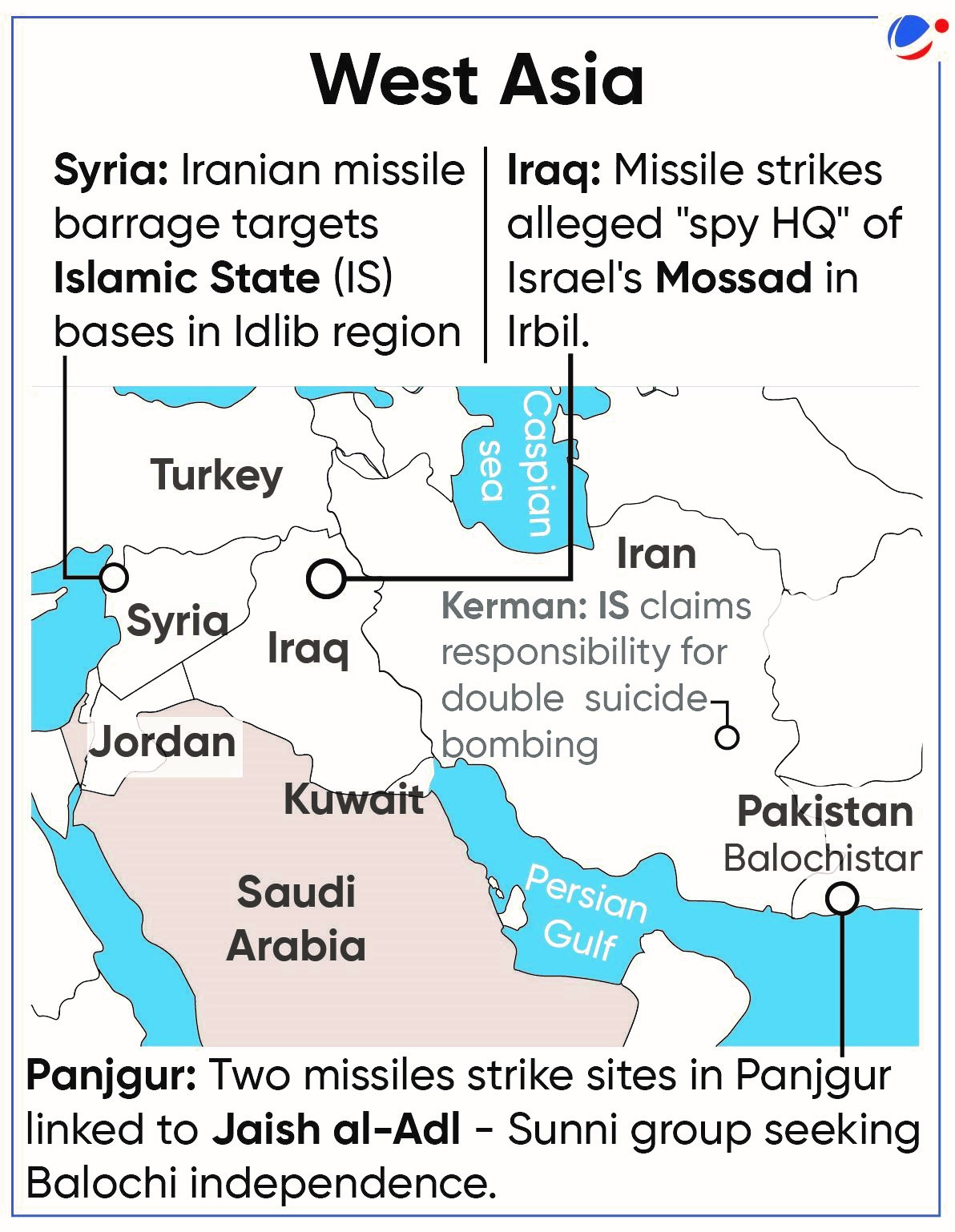
- Iran's retaliatory strikes in Syria, Iraq, and Pakistan were prompted by a terrorist attack in its Kerman province (refer to the map).
- India's Interests in West Asia
- Neighbourhood first policy: West Asia is a part of India’s extended neighbourhood and Look West Policy, and maintaining peace and stability in the region aligns with India's strategic interests.
- Diaspora: Indians constitute more than 30% of total expatriate workers in the in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC).
- Remittance: 18% of India's total remittances come only from the UAE, 5.1% from Saudi Arabia, while Kuwait, Oman and Qatar also have significant contributions.
- Connectivity and Infrastructure:
- INSTC is a land- and sea-based multi-modal transport network that will connect the Indian Ocean and the Persian Gulf with the Caspian Sea.
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor spans India to Europe via West Asia.
- Chabahar port is vital for India for transporting cargo to Europe.
- Energy security:
- More than 80% of India's oil and over 50% of gas are imported.
- Iraq and Saudi Arabia serve as major oil suppliers, while Qatar is a significant supplier of LNG.
- UAE-India Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) Council (UICC) was launched at India- United Arab Emirates (UAE) Business Summit.
- UICC will encourage close partnerships and tangible cooperation across all levels of UAE and Indian business communities.
- UICC emphasises on start-ups, women entrepreneurs, Micro, Small, and Medium-Sized Enterprises (MSMEs), and services sectors.
- India- UAE CEPA came into force in 2022. It is the first full free trade Agreement to be signed by India with any country in past decade.
- It covers Trade in Goods and services, Rules of Origin, customs cooperation, Dispute Settlement etc.
- Bilateral trade has increased by approximately 15% since CEPA came into force.
- Significance of CEPA
- Enhanced access for cross-border trade in services and provide thrust to pharmaceutical sector.
- Raise bilateral merchandise trade to $100 billion in five years from about $43 billion in FY21.
- Special safeguard measures provide protection against imports surge from UAE due to tariff concessions.
- UAE can act as gateway to West Asian countries and Africa for Indian exporters.
India- UAE Relations
|
- HPI was released by Henley & Partners, a global leader in residence and citizenship planning.
- HPI ranks different passports according to number of destinations their holders can visit without a prior visa.
- It covers 227 destinations and 199 passports.
- Rankings are based on data provided by International Air Transport Association.
- Key findings
- India stands at 80th rank in list of most powerful passports. Its passport has visa-free access to 62 nations.
- France, Germany, Italy and Spain, Japan and Singapore are sharing number one spot.






