Why in the news?
Recently, India and Russia signed three documents including a Protocol on consultations during the External Affairs Minister’s official visit to Russia in December 2023.
More about the news
- The protocol will foster progress in military and economic cooperation, energy trade, military-technical cooperation, connectivity and people-to-people exchanges.
- The duration of the protocol is four years (2024-2028).
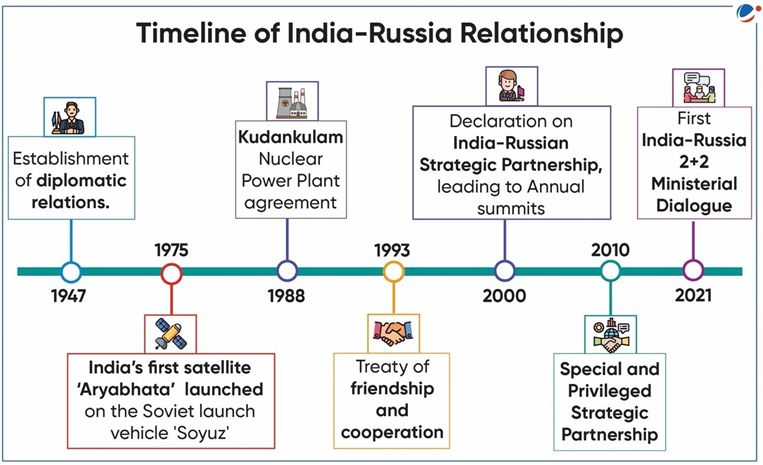
- Two other documents relating to the Kudan Kulam Nuclear Power Plants and an MoU on cooperation in pharmaceuticals and healthcare were also signed during the visit.
The longstanding and time-tested partnership between India and Russia is driven by shared interests of multilateralism, and global peace and prosperity.
Major Areas of India-Russia Cooperation and Its Significance
Defence and Security Cooperation |
|
International /Multilateral Cooperation |
|
Trade and Economic Cooperation |
|
Other Areas of Cooperation |
|
Challenges to India-Russia Relationship
- Defence Challenges: India needs to reduce its defence supplies from Russia as part of defence modernization, and diversification and to avoid USA sanctions under CAATSA.
About CAATSA
|
- Changing World Order: The USA-China rivalry is shifting the world order towards a bipolar world. It is against India-Russia’s vision for a multipolar world.
- Expanding Geo-strategic Interests: As India grows beyond a regional power; its geo-strategic interests are expanding beyond the Indian Ocean and South Asia. E.g.
- The Indo-Pacific Region and the Eurasian Region where India is partnering with countries having stressed relations with Russia.
- Natural inclination towards the West: Many experts believe that being the biggest democracy in the world, India shares a natural affinity towards the West (USA and major European nations) due to their democratic set-up.
- Economic Challenges: High trade deficit between two nations. The regulatory impediments and the use of phytosanitary standards and non-tariff barriers by Russia add to it. E.g.
- Russia classifies tea as fruit and vegetable, leading to more phytosanitary restrictions.
- The increased oil purchases in 2022 and the strengthening of the Russian Ruble against the Indian Rupee will increase the deficit further.
Way Forward
- Modernization of Defence Supplies from Russia through joint development and co-production of advanced weapons, promoting self-sufficiency and reduced dependence of India on others for modernization and diversity under Make in India.
- Joint manufacturing of Spare parts and Reciprocal Logistics Support for increased defence cooperation can also add to it.
- Protect Multilateralism/Multipolarity at UN and other forums such as BRICS, SCO etc. for more rules-based international order.
- Diversification of Trade to overcome the issues of limited economic relationship with high trade deficit.
- Positive outcome on the recent list of over 500 products from Russia to India for exports can be a good starting point.
- Increasing private sector participation in the economic relationship with removal of barriers to trade and investment.
- Operationalising Eastern Maritime Corridor: The proposed sea route that connects Chennai and Vladivostok (Russia’s Far East) will improve logistical connectivity.
- Broaden collaboration on bilateral and regional issues covering new theatres of cooperation as part of shared common responsibilities on global peace and stability.




