Why in the news?
ISRO successfully launched the X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) by Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) -C58.
More on news
- PSLV-C58 was the 60th flight of ISRO’s Polar Satellite launch Vehicle.
- PSLV is a 4-stage launch vehicle propelled by Solid fuel at first and third stages and Liquid fuel at second and fourth stages.
- It has multiple satellite launch capability and multiple orbit capability.
- After Placing XPoSAT at orbit of 650 km altitude, Fourth stage of PSLV was brought to a lower altitude (about 350 km) for conducting the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-3 (POEM-3) experiment.
- POEM-3 experiment will be executed to meet the objective of 10 identified payloads, supplied by ISRO and IN-SPACe.
What is Polarization and X-ray polarimetry?
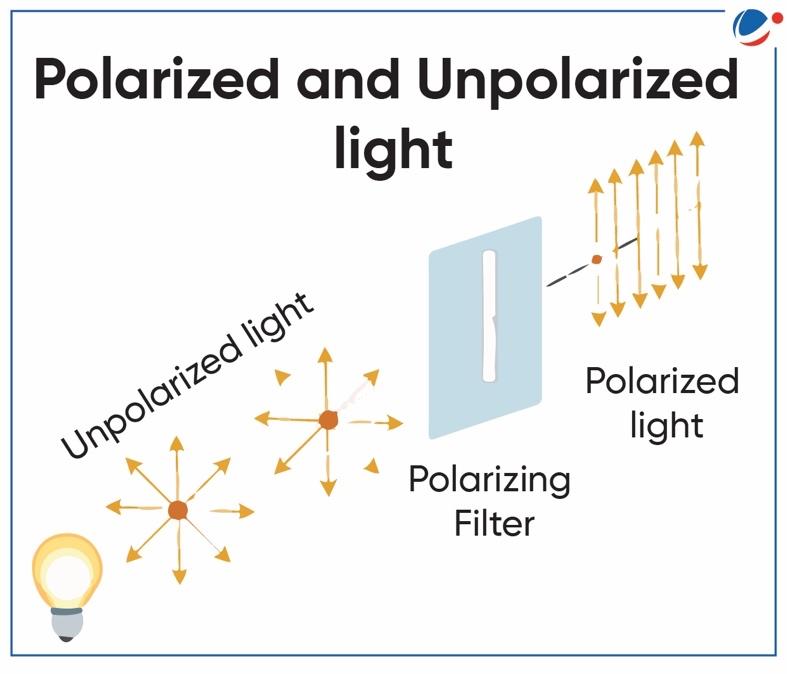
- Normal light (unpolarized light) consists of electric field and magnetic field vectors which vibrate perpendicularly to each other. (refer to figure)
- Light waves that travel in a single plane are known as polarized light waves.
- The process of transforming unpolarized light into polarized light is known as polarization and can be achieved through Scattering, reflection, refraction or use of Polaroid/ polarizing filter.
- Studying/measuring the polarization of X-rays is X-Ray polarimetry.
- X-rays are high-energy electromagnetic waves.
- It involves studying:
- Angle of the polarization i.e. the direction of electric field vector with respect to a reference direction.
- Degree of polarization i.e. Portion of an electromagnetic wave from a light source, which is polarized.
About XPoSat (X-ray Polarimeter Satellite)
- XPoSat is the first dedicated satellite from ISRO to carry out research and measure X-ray emission from celestial sources like black holes and neutron stars.
- It is the second satellite in the world to study X-ray polarization, first being NASA’s Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE), launched in 2021.
- XPoSat payloads:
- POLIX (Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays): To measure polarization of X-rays in the energy band 8-30keV.
- It is expected to observe about 40 bright astronomical sources during the mission’s lifetime of about 5 years.
- XSPECT (X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing): To provide fast timing and good spectroscopic resolution in soft X-rays.
- It will carry out long-term spectral and temporal studies of cosmic X-ray sources, e.g. pulsars, black hole binaries, magnetars, etc.
- POLIX (Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays): To measure polarization of X-rays in the energy band 8-30keV.
Significance of the Mission
- Understanding the nature of radiations: Polarization measurements lead to better understanding of the emission processes from astronomical sources.
- Advanced data collection: Polarization study of celestial sources was done either in the optical or radio bands before. X-ray polarimetry in medium energy band is being done for the first time.
- Chemical Composition of celestial bodies: X ray polarimetry reveals the physics and elemental composition of celestial bodies like Pulsars, Magnetars etc. and can provide insights into interaction of matter with magnetic fields.
- Better understanding of Universe: X-ray polarization measurements, especially on celestial objects like black holes, neutron stars, and active galactic nuclei, hold the potential to significantly improve the understanding of their physics.
Conclusion:
XPoSAT is a crucial step forward in quest to understand the intricate workings of complex universe; mission has implications for various scientific disciplines and technological developments.
About PSLV Orbital Experimental Module (POEM)
|
Related News
|







