30 Years of the Marrakesh Agreement
World Trade Organization (WTO) is celebrating 30 years of the Marrakesh Agreement.
- Marrakesh Agreement was signed in Marrakesh, Morocco, by 123 countries in 1994 after the conclusion of the Uruguay Round.
- It led to the establishment of the WTO in 1995, replacing General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) as an international organization.
About Marrakesh Agreement
- It serves as basic framework for trade relations among all WTO members.
- It expanded the scope beyond trade in goods to trade in services, intellectual property, and other topics.
- It established modern multilateral trading system, facilitating negotiations, dispute settlement, and economic cooperation among members.
- It created WTO’s governance, establishing the Ministerial Conference (highest decision making body), General Council, and specialized councils.
Achievements of WTO
- Lowering trade barriers: Since 1995, real volume of world trade has expanded by 2.7 times and average tariffs have almost halved, from 10.5% to 6.4%.
- Rise of Global Value Chains: Trade within these value chains today accounts for almost 70% of total merchandise trade.
- Growth in developing countries: Fastest poverty reduction since 1995 and increased purchasing power in all countries.
- International Trade Agreements and Rules: TRIPS Agreement, Nairobi Package, Trade Facilitation Agreement, Doha Development Agenda etc.
- Tags :
- World Trade Organization
- 30 years of Marrakesh Agreement
UNCTAD rebranded as UN Trade and Development

United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) rebranded as UN Trade and Development.
- The rebranding marks the start of the 60th anniversary of the organization.
- This strategic move underscores the organization's commitment to increasing its global voice on the behalf of developing countries.
Key Achievements:
- Implementation of Financing for Development, as mandated by the global community in the Addis Ababa Agenda (2015), together with four other major institutional stakeholders.
- The institution includes the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, the World Trade Organization, and the United Nations Development Programme.
- Assisted countries under the Debt Management and Financial Analysis System (DMFAS) Programme.
- Tags :
- UNCTAD
- Addis Ababa Agenda
Living Wage and Minimum Wage
- The government sought technical assistance from ILO to create a framework for living wage
- Presently, India follows the minimum wage, which has remained stagnant since 2017.
- The Code on Wages passed (2019), proposed a universal wage floor which shall apply to all states once implemented.
- Issues with the present system
- The Minimum Wages Act, 1948 provides guidelines but does not specify the minimum wage.
- Fixing minimum wages in some jobs falls under both the Minimum Wages Act, 1948, and the Contract Labour (Regulation and Abolition) Act, 1970, leading to potential confusion.
- Wage payment discrepancies due to the lack of enforceability of the national wage floor across states.
- Gender disparity as scheduled employment with more women workers has lower minimum wages than those with more men.
- Advantages of Living Wage
- Accelerate Poverty alleviation efforts, aligning with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Addresses wage insufficiency, especially considering inflation, and fosters a more equitable and sustainable economy.
- Challenges of Living Wage
- Implementing a national living wage framework across states due to the diversity of living costs in different regions of India.
- Financial strain especially for small businesses and MSMEs, due to increased labour costs.
- Tags :
- Living Wages
- Minimum wage
- LIVING WAGE AND MINIMUM WAGE
- Standard of living
Credit Deposit Ratio (CDR)
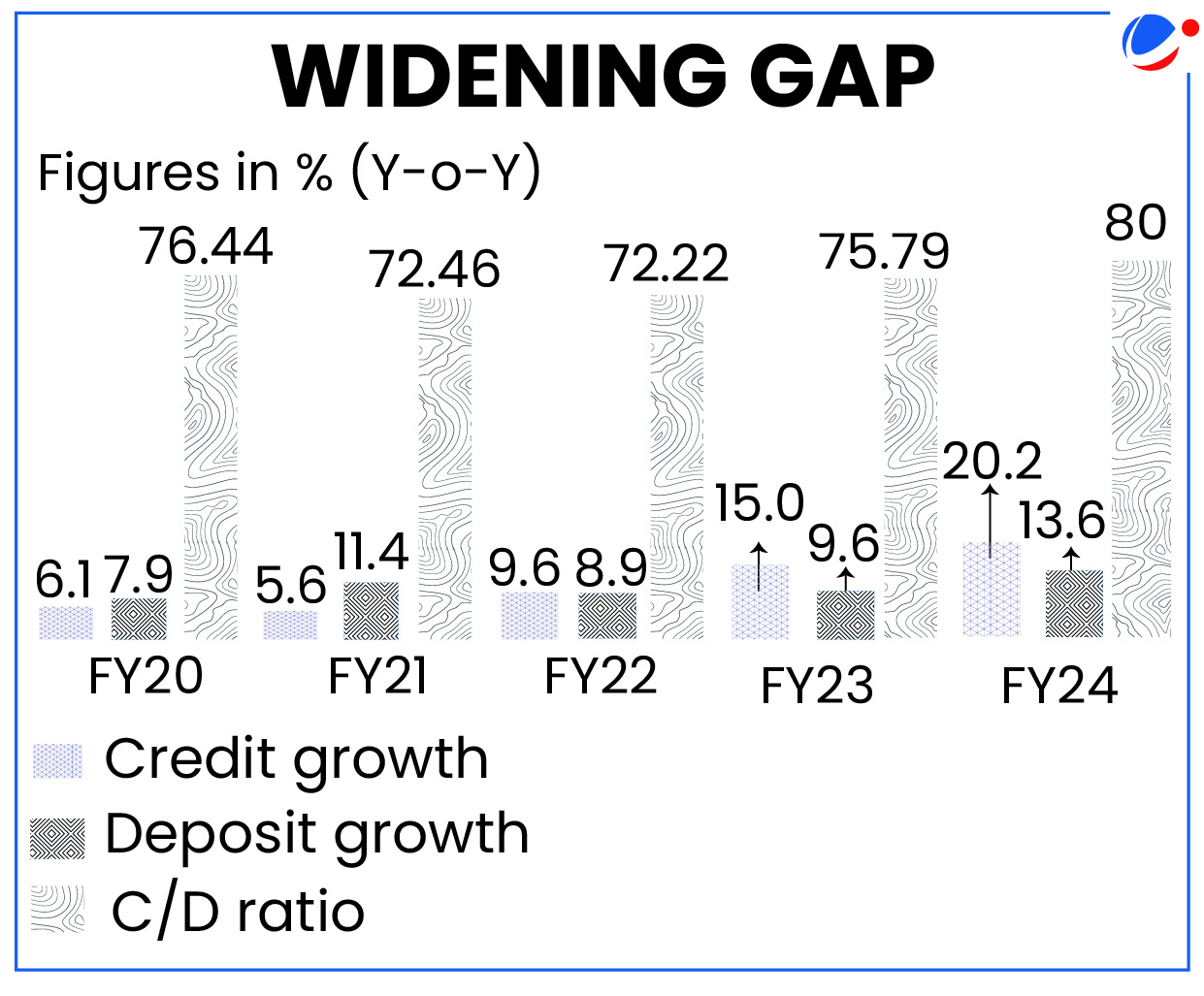
- Indian banks are battling the worst deposit crunch in 20 years and at 80%, the credit-deposit ratio is at its highest since 2005.
- About CDR:
- It is the ratio of how much a bank lends out of the deposits it has mobilised.
- A higher CDR suggests that a significant portion of the bank's resources are allocated to loans.
- It could potentially stimulate economic growth but also implies higher risk.
- Regulators often monitor CDR to ensure banks maintain a prudent balance between lending and risk management.
- Tags :
- CDR
- CREDIT DEPOSIT RATIO
SEBI Complaint Redress System (SCORES 2.0)
- Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) launched SCORES 2.0 version which strengthens investor complaint redress mechanism in securities market by making process more efficient.
- SCORES is an online system where investors in securities market can lodge their complaints through web URL and an App.
- Salient features of SCORES 2.0
- Reduced timelines for redressal of investor complaints across Securities Market i.e. 21 Calendar days from date of receipt of complaint.
- Introduction of auto-routing of complaints to concerned regulated entity to eliminate time lapses.
- Integration with KYC Registration Agency database for easy registration.
- Tags :
- SEBI
- SCORES 2.0
Cluster Development Programme (CDP) – SURAKSHA
- Several states are using SURAKSHA platform for disbursing subsidies to horticulture farmers under the CDP.
- CDP is a component of the central sector scheme of National Horticulture Board (NHB).
- About CDP-SURAKSHA
- SURAKSHA stands for ‘System for Unified Resource Allocation, Knowledge, and Secure Horticulture Assistance’.
- It allows an instant disbursal of subsidies to farmers in their bank account by utilising the e-RUPI voucher from the NPCI.
- Its key features are database integration with PM-KISAN, UIDAI validation, geotagging, geo-fencing etc.
- CDP-SURAKSHA allows access to farmers, vendors, Implementing Agencies, Cluster Development Agencies etc.
- Tags :
- Horticulture
- SURAKSHA platform
Expert Committee Report on Gift City
- Expert Committee on developing GIFT IFSC as ‘Global Finance and Accounting Hub’ submitted report to IFSCA.
- Committee was formed following a Ministry of Finance notification.
- The notification classified book-keeping, accounting, taxation, and financial crime compliance as ‘financial services’ under International Financial Services Centre (IFSC) Act, 2019.
- Gujarat International Finance Tech- City (GIFT City)-IFSC was established as Special Economic Zone (SEZ) in 2015, in Gujarat.
- An IFSC caters to customers outside the jurisdiction of the domestic economy. Such centres deal with flows of finance, financial products and services across borders.
- Opportunities for GIFT IFSC to become Global Finance and Accounting Hub
- Strong technology-driven outsourcing capabilities.
- Large talent pool of skilled manpower in the fields of accounting, etc.
- “Accounting and finance services” recognised as one of the 12 Champion sectors in services for exports.
- Recommendations
- Proposes a new regulation, providing for comprehensive and inclusive definition for Bookkeeping, Accounting, Taxation, and Financial Crime Compliance Services.
- Only firms that are registered as a company or a Limited liability partnership should be allowed to offer these services.
- Long-term strategies for education and skill acquisition through developing specialized degree or diploma programs, etc.
- Proposes a new regulation, providing for comprehensive and inclusive definition for Bookkeeping, Accounting, Taxation, and Financial Crime Compliance Services.
IFSC Authority
- IFSC Authority is a statutory body established under IFSC Act,2019.
- A unified regulator for development and regulation of financial products, financial services and financial institutions in IFSCs in India.
- Tags :
- GIFT CITY
- IFSCs
- Global Finance and Accounting Hub
Payment Aggregator (PA)
- PayU has received an in-principle approval from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to operate as a PA.
- About PAs
- It is a financial technology company that simplifies the process of accepting electronic payments for businesses. E.g., GooglePay, PhonePe, Cashfree etc.
- It acts as an intermediary between the business and the financial institutions.
- It is incorporated as a company under the Companies Act, 1956 / 2013.
- Non-bank PAs require authorisation from RBI under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007.
- Tags :
- FinTech
- PAYMENT AGGREGATOR
India Gaming Report 2024 Released
- Interactive Entertainment and Innovation Council (IEIC) and WinZO released India Gaming Report 2024 .
- Key findings:
- With 568 million users, India is officially the largest gaming market and accounts for every one in five online gamers globally.
- Indian gaming market is expected to reach $6 Billion by 2028.
- Number of Indian gaming companies surged from 25 in 2015 to over 1400 in 2023.
- Factors responsible for boost in gaming industry:
- Rise of affordable high-speed internet ($0.17/GB) and increase in smartphone penetration (820 million users).
- Burgeoning share of young population (~600 million) and rising disposable income.
- Supply side factors include global investments in game development, rewarding gaming career, vernacular language content and gamification of Indian culture etc.
- Gaming’s contribution to society: Reduction in social isolation, community building, especially for women gamers, and its role in enhancing research, education and skilling.
- It also improves penetration of emerging technologies like Virtual Reality, Artificial Intelligence among others.
- Challenges to gaming sector:
- Sustainability issues from 'internet pollution' (3.7% of Greenhouse Gas emissions).
- Financial literacy gaps, regulatory complexities, and data security challenges.
- Gaming can have a detrimental impact on physical and mental health in certain cases. E.g., issues like ‘Blue Whale Challenge’.
- Recommendations:
- Utilise green innovations and virtual environments for sustainable gaming.
- Establish a global gaming cluster with policy support, supporting startups and talent development.
- Prioritise R&D for online safety and digital literacy.

- Tags :
- Online Gaming
- INDIA GAMING REPORT
- Gaming sector



