Why in the News?
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the Employment Linked Incentive (ELI) Scheme which is expected to enhance youth employability, nurture skills and facilitate job retention in private sector.
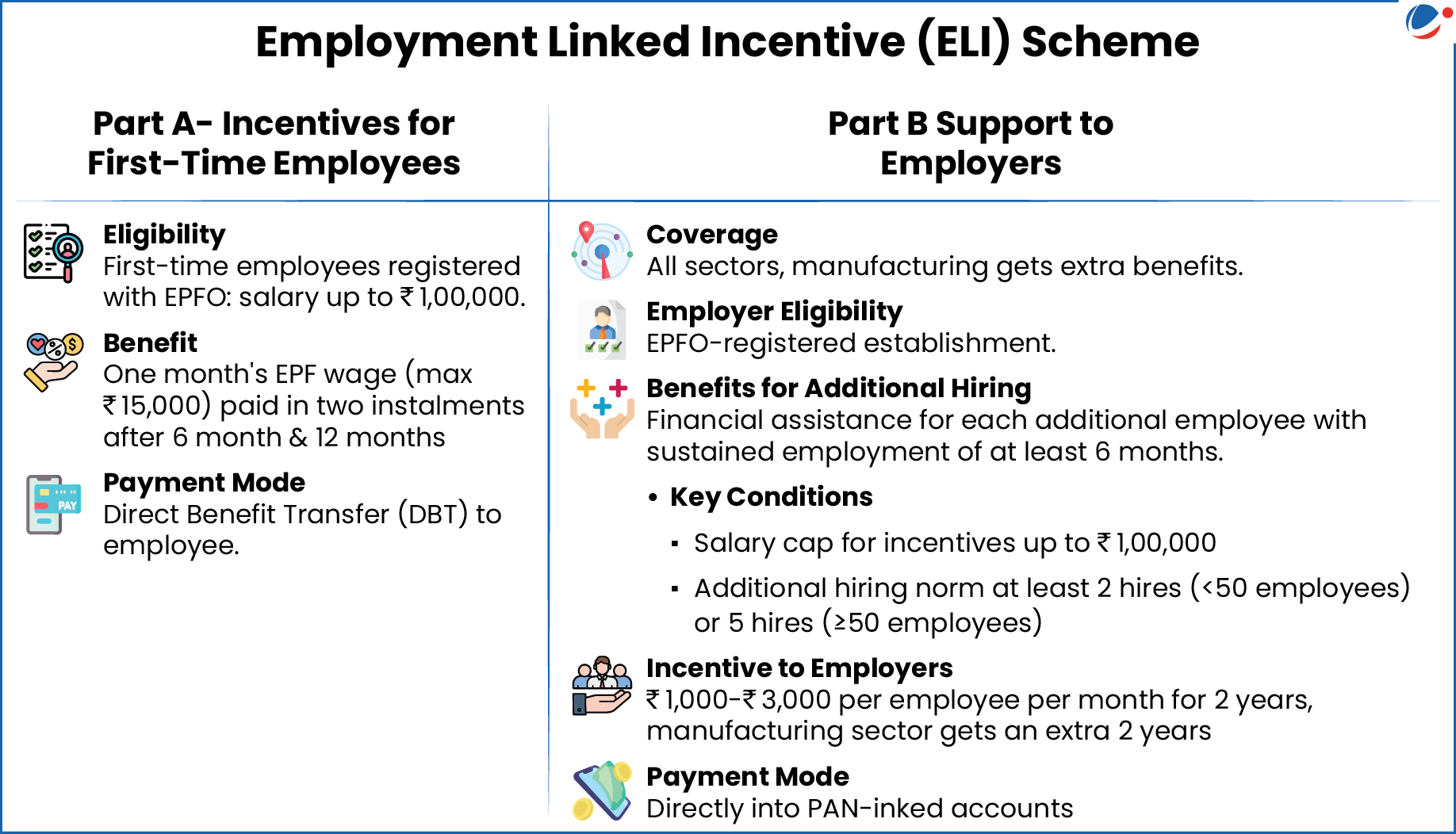
About Employment Linked Incentive (ELI) Scheme
- Background: Announced in the Union Budget 2024-25 as part of PM's package of five schemes to facilitate employment, and skilling opportunities for youth.
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Labour & Employment
- Purpose: Promote job creation, enhance employability, and expand social security across sectors, specifically manufacturing
- Target: 3.5 crore jobs (including first-time employees)
About Employability and Skilling In India
According to the India Skills Report 2025:
- Employability: Over 50% of graduates (53.47% for Male and 46.53% for Female) are employable in 2024, up from 33% a decade ago (17% rise).
- Drivers: Growth driven by focus on emerging technologies like AI, cloud computing, and automation.
Challenges Existing In India's Employability and Skilling Landscape
India is expected to add 10 million workers annually over the next decade. However, in FY 2023-24 only, 4.67 crore jobs were created. To fully reap the benefits of the demographic dividend, the key challenges are as follows
- Mismatch Between Education and Industry Needs: Universities focus more on theory than practical skills. Graduates often lack hands-on experience and technical competencies leading to lower employability in technical fields.
- Threat from Automation: Graduates are significantly less prepared for technical roles, even in high-demand fields like AI and data science. 69% of jobs in India face automation risk (World Bank)
- Limited Emphasis on Soft Skills Development: The growing importance of soft skills such as communication, teamwork, and critical thinking remains undervalued in many university programs.
- This oversight contributes to graduates who are not only technically unprepared but also lack the interpersonal skills necessary for success in the workplace.
Key Initiatives Taken for Employability And Skilling
|
Conclusion
Harnessing the demographic dividend needs strong skills. Immediate investment in education, training, healthcare, and social protection is key. Strengthening human capital, fixing labour market gaps, and matching technology with workforce needs will drive inclusive and sustainable growth.







