Child Adoption
CARA issues directions to states for strengthening counseling support at all stages of Child adoption.
- These directions are given to State Adoption Resource Agencies (SARAs) under Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015 (amended 2021) and in line with Adoption Regulations, 2022.
Key Directions given to SARAs:
- Reinforce psychosocial support framework for all key stakeholders prospective adoptive parents (PAPs), adopted children, and biological parents.
- SARAs instructed to designate/ empanel qualified counsellors at District and State Levels.
- Provisions for psychosocial intervention in any other circumstances as assessed by the Specialised Adoption Agencies (SAAs) or District Child Protection Units (DCPUs).
Child adoption In India
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- Primary legislation: Adoption in India is governed by the Hindu Adoption and Maintenance Act, 1956 and the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015.
- Nodal Central Agency: Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA), established under the JJ Act, regulates domestic and intercountry adoptions.
- Hague Convention on Protection of Children and Cooperation in Respect of Intercountry Adoption (1993) ensures ethical, legal, and transparent international adoptions while preventing child trafficking.
- Responsibility of States/UTs: states and UTs implement the JJ Act through institutions like
- State Adoption Resource Agencies (SARA)
- local Child Welfare Committees
- District Child Protection Units (DCPUs)

- Tags :
- Adoption Regulations, 2022
- Central Adoption Resource Authority
Articles Sources
Kashi Declaration adopted in Youth Spiritual Summit for Drug-free India
As part of broader Mera Yuva (MY) Bharat framework, the Youth Spiritual Summit laid the foundation for a national youth-led anti-drug campaign.
- MY Bharat is an autonomous body set up by the Government of India to provide an institutional mechanism powered by technology for youth development and youth-led development.
About Kashi Declaration
- Sets a 5 year roadmap for De-Addiction Movement.
- Affirms a national consensus to treat substance abuse as a multi-faceted public health and societal challenge.
- Approach to be followed:
- Proposes institutional mechanisms for multi-ministerial coordination, including the formation of a Joint National Committee, annual progress reporting, and a national platform for linking affected individuals to support services.
- Integration of spiritual, cultural, educational, and technological efforts to prevent addiction.
Other Initiatives taken to reduce Drug Abuse
- The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1985.
- The Prevention of Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act, 1988.
- National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction (NAPDDR), 2018-25.
- Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyaan (NMBA), 2020.
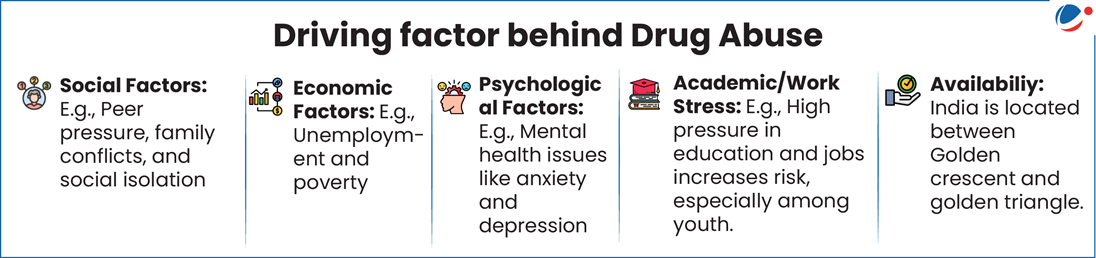
Status of Drug-abuse in India (as per National Survey on Substance Use, 2019)
 |
- Tags :
- MYBharat Framework
- Youth-led Development
Articles Sources
TALASH Initiative
The National Education Society for Tribal Students (NESTS), under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, in partnership with UNICEF India launched TALASH (Tribal Aptitude, Life Skills and Self-Esteem Hub) Initiative.
About TALASH
- It is a national- program to support the all-round development (both educational and personal growth) of students in Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRSs).
- EMRS is a central sector scheme under Ministry of Tribal Affairs to provide residential schooling to tribal children in blocks having more than 50% of Scheduled Tribes (ST) population
- It is an innovative digital platform which offers-
- Psychometric Assessments: Inspired by NCERT’s ‘Tamanna’ initiative,
- Career Counselling,
- Life Skills & Self-Esteem Modules,
- E-Learning for Teachers,
- Tags :
- UNICEF
- Eklavya Model Residential Schools
State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World (SOFI) 2025 Report Released
SOFI is a flagship publication as part of The State of the World series of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Key findings of the report

- Global hunger decreased to an estimated 8.2% in 2024 from 2022 levels.
- However, hunger continues to climb in most subregions of Africa and Western Asia.
- Moderate or severe food insecurity has declined gradually since 2021.
- Food prices rose throughout 2023 and 2024, pushing up the average cost of a healthy diet globally.
- The pandemic and the war in Ukraine have intensified food price inflation worldwide
- Despite the increase, people unable to afford a healthy diet in the world fell from 2.76 billion in 2019 to 2.60 billion in 2024.
- Anaemia in women (aged 15–49 years) and adult obesity (12.1% in 2012 to15.8% in 2022) on the rise globally.
India related findings
- Excluding India, there is an increasing trend in lower-middle-income countries in the number of people unable to afford a healthy diet.
- Mobile phone adoption by fishermen and wholesalers in Kerala reduced price dispersion and waste.
Key recommendation
- Time-bound and targeted fiscal measures, such as temporary tax relief on essential goods and social protection Programmes.
- Align fiscal and monetary policies to stabilize markets.
- Robust agricultural market information systems are key to managing price volatility and preventing speculation.
- Tags :
- Food and Agriculture Organization
- Adult Obesity



