Why in the News?
The Union Cabinet recently approved RDI Scheme with a corpus of ₹1 lakh Crore.
About RDI Scheme
- Nodal Department: Department of Science and Technology.
- Key objective of the scheme
- Encourage the private sector to scale up research, development, and innovation (RDI) in sunrise domains and in other sectors relevant for economic security, strategic purpose, and self-reliance;
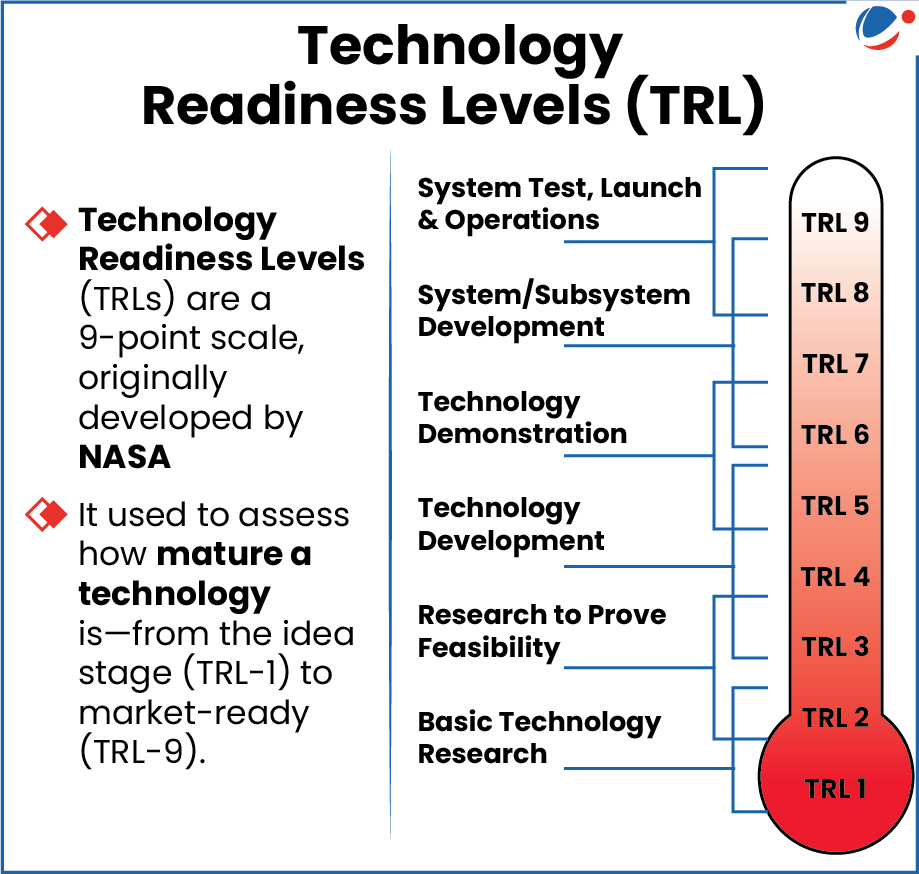
- Finance transformative projects at higher levels of Technology Readiness Levels (TRL)
- Support acquisition of technologies which are critical or of high strategic importance;
- Facilitate setting up of a Deep-Tech Fund of Funds.
- Funding and Financial Support
- Total Budget: ₹1 lakh crore
- Modes of Financing:
- Long-term loan at low or nil interest rates.
- Equity infusion, especially in case of startups.
- Contributions to Deep-Tech Fund of Funds
- Exclusions: Grants and short-term loans are not supported
- Coverage
- Financing can cover up to 50% of assessed project cost for transformative RDI projects at TRLs 4 and above;
- Exceptions may be approved by the Empowered Group of Secretaries (EGoS)
- Implementation Structure
- Special Purpose Fund: Being set up under the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) to serve as the first-level custodian.
- The governing board of ANRF also provides strategic direction to RDI Scheme.
- Second-Level Fund Managers: May include Alternate Investment Funds (AIFs), Development Finance Institutions (DFIs), Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs), or Focused Research Organizations (FROs) such as Technology Development Board (TDB), IIT Research Parks, or similar entities
- Special Purpose Fund: Being set up under the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) to serve as the first-level custodian.
Significance of the Scheme
- Recognize Private sector role in R&D: It directly addresses and overcomes critical funding constraints and challenges faced by the private sector, by providing growth & risk capital.
- Catalyst for Private Sector Investment: The RDI scheme, in partnership with ANRF, aims to boost private sector investment in R&D.
- Public R&D expenditure can have a "leverage" effect on catalyzing private R&D activity.
- Driving Commercialization: Unlike public R&D, industrial R&D primarily focuses on marketable, profitable products, essential for real-world economic impact.
- Fostering Self-Reliance: It supports technologies where indigenisation is essential for strategic or economic reasons, aligning with the vision of Atmanirbharta.

- Creates and maintains jobs: Incentivizing R&D will create more opportunities, especially for graduates.
Challenges in Research and Development in India
- Low R&D Investment and Diversification: India's R&D expenditure stands at only 0.6–0.7% of GDP over the past two decades, significantly lower than global leaders like South Korea (4.8%) and Israel (5.6%).
- Moreover, in FY 2021–22, the private sector contributed just 36.4% of GERD (Gross Expenditure on Research and Development), compared to over 70% in countries like the US and China.
- Limited State-level R&D funding: During 2020–21, States accounted for only 6.7% of national R&D spending.
- Limited Collaboration between Industry and Academia: The "Triple Helix" model (seen in the US) remains underdeveloped, hindering commercialization and innovation.
- Underutilization of Funds: Departments such as DBT and DST utilized only 72% and 61% of their budgets in 2022–23, reflecting systemic inefficiencies.
- Insufficient Recognition of Scientific Talent: Although India produces over 40,000 PhDs annually, systemic issues like bureaucracy and lack of incentives deter innovation despite available human capital.
Way forward
- Increase and Diversify R&D Funding: Raise Gross Expenditure on R&D (GERD) to at least 2% of GDP by 2030 in line with National STI Policy targets.
- Incentivise private sector investment through tax rebates, innovation-linked funding, and credit guarantees.
- State-Specific S&T Need Mapping: Establish State Science, Technology & Innovation Councils to design localized R&D roadmaps.
- Promote regional innovation hubs like Kerala's Startup Mission or Bengaluru's biotech cluster.
- Strengthen Institutional Structures: Implement research cluster models like CSIR innovation hubs to pool expertise and avoid duplication.
- Foster Industry–Academia Collaboration: Set up joint R&D centres funded by industry and government (e.g., Semiconductor Mission partnerships).
- Use models like ISRO–industry partnerships in satellite manufacturing for other sectors.
- Efficient Resource Utilisation: Adopt output-based funding, linking budget allocations to research publications, patents, and societal impact.
- Recognise and Retain Scientific Talent: Expand fellowships like Prime Minister's Research Fellowship (PMRF) and introduce global talent repatriation schemes.
- Provide fast-track funding for young innovators and women scientists through schemes like CURIE and KIRAN.
Government initiatives to boost R&D in India :
|






